xnzda
159 posts
Latest Posts by xnzda

stars, mercury, and solar corona, photographed by stereo a, january 2009.
27 frames, photographed over 36 hours, 2nd-3rd january. the sun is out of frame right.
image credit: nasa/stereo. animation: ageofdestruction.

Pew! Pew! Pew!
Imagine slow-motion fireworks that started exploding 170 years ago and are still continuing. This type of firework is not launched into Earth’s atmosphere, but rather into space by a doomed super-massive star, called Eta Carinae.
Enjoy the the latest view from our Hubble Space Telescope.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.










- Carl Sagan, Cosmos: A Spacetime Odyssey
Cosmic rays
Cosmic rays provide one of our few direct samples of matter from outside the solar system. They are high energy particles that move through space at nearly the speed of light. Most cosmic rays are atomic nuclei stripped of their atoms with protons (hydrogen nuclei) being the most abundant type but nuclei of elements as heavy as lead have been measured. Within cosmic-rays however we also find other sub-atomic particles like neutrons electrons and neutrinos.

Since cosmic rays are charged – positively charged protons or nuclei, or negatively charged electrons – their paths through space can be deflected by magnetic fields (except for the highest energy cosmic rays). On their journey to Earth, the magnetic fields of the galaxy, the solar system, and the Earth scramble their flight paths so much that we can no longer know exactly where they came from. That means we have to determine where cosmic rays come from by indirect means.

Because cosmic rays carry electric charge, their direction changes as they travel through magnetic fields. By the time the particles reach us, their paths are completely scrambled, as shown by the blue path. We can’t trace them back to their sources. Light travels to us straight from their sources, as shown by the purple path.

One way we learn about cosmic rays is by studying their composition. What are they made of? What fraction are electrons? protons (often referred to as hydrogen nuclei)? helium nuclei? other nuclei from elements on the periodic table? Measuring the quantity of each different element is relatively easy, since the different charges of each nucleus give very different signatures. Harder to measure, but a better fingerprint, is the isotopic composition (nuclei of the same element but with different numbers of neutrons). To tell the isotopes apart involves, in effect, weighing each atomic nucleus that enters the cosmic ray detector.

All of the natural elements in the periodic table are present in cosmic rays. This includes elements lighter than iron, which are produced in stars, and heavier elements that are produced in violent conditions, such as a supernova at the end of a massive star’s life.

Detailed differences in their abundances can tell us about cosmic ray sources and their trip through the galaxy. About 90% of the cosmic ray nuclei are hydrogen (protons), about 9% are helium (alpha particles), and all of the rest of the elements make up only 1%. Even in this one percent there are very rare elements and isotopes. Elements heavier than iron are significantly more rare in the cosmic-ray flux but measuring them yields critical information to understand the source material and acceleration of cosmic rays.

Even if we can’t trace cosmic rays directly to a source, they can still tell us about cosmic objects. Most galactic cosmic rays are probably accelerated in the blast waves of supernova remnants. The remnants of the explosions – expanding clouds of gas and magnetic field – can last for thousands of years, and this is where cosmic rays are accelerated. Bouncing back and forth in the magnetic field of the remnant randomly lets some of the particles gain energy, and become cosmic rays. Eventually they build up enough speed that the remnant can no longer contain them, and they escape into the galaxy.

Cosmic rays accelerated in supernova remnants can only reach a certain maximum energy, which depends on the size of the acceleration region and the magnetic field strength. However, cosmic rays have been observed at much higher energies than supernova remnants can generate, and where these ultra-high-energies come from is an open big question in astronomy. Perhaps they come from outside the galaxy, from active galactic nuclei, quasars or gamma ray bursts.

Or perhaps they’re the signature of some exotic new physics: superstrings, exotic dark matter, strongly-interacting neutrinos, or topological defects in the very structure of the universe. Questions like these tie cosmic-ray astrophysics to basic particle physics and the fundamental nature of the universe. (source)
have y’all seen that nasa pic of the earth with the sun behind it on the night time side it really really fucked me up my own soul became solid and like………….. weeped!
Dust, stars, and cosmic rays swirling around Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko, captured by the Rosetta probe. (Source)


Astronauts talking about viewing the earth from the moon, from The Overview Effect: Awe and Self-Transcendent Experience in Space Flight

lesbians in space

The orbit of Jupiter protects the Earth from asteroids.
some of my favourite absolutely SICK facts about the trappist-1 exoplanets: - theyre all very close to one another and to their star, so the length of a year on them varies from 1 to 20 DAYS - since they’re so close, the star appears a lot bigger than our sun from earth, and from one planet you could easily see the rest, some would even appear bigger than the moon from earth. you could literally see the surface of another planet with the naked eye!!! - they’re probably tidally locked to their star like our moon is locked to earth, meaning only one side of a planet ever faces the star, and on the other side it’s always night. the sun never sets or rises on any of the planets - the star is red, so the sunlight is red/orange, meaning if, for example, plants were to grow there, they could be black and that’s just what we know now, imagine how much cool stuff we have yet to discover about the trappist-1 system
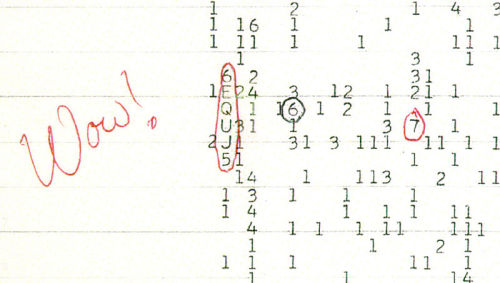
The Wow! signal.
A signal sequence that lasted for 72 seconds in 1977 but has never been seen again. The signal appeared to come from a globular cluster in the Sagittarius constellation, but to this day no definite answer for where the signal originated can be given.
is there a smell comparable to space ? i assume we dont know because we would die if we tried to smell it but thats so cool
yeah if humans tried to smell space just like that, we’d die, no doubt about it
but the smell of space lingers on spacewalk suits, and docking hatches when astronauts open them!
apparently, space itself smells like burning hot metal, or a hot barbeque grill with a slight hint of spent gasoline. The moon, apparently, smells like a gun after its been shot!
The coolest thing about it all is that the smell is actually what are left of dying stars- it’s literally the smell of stardust, and the particles smell like that because they’re so rich in hydrocarbons- something so very essential to life, and speculated by a lot of astronomers and astrobiologists and such to be the very thing life on earth started from!
another neat fact is that no two solar systems smell the same- ours smells like that because our solar system in particular is extremely rich in carbon, and other solar systems and places in the universe will have extremely different smells depending on what elements are most abundant in their system!
FUCKING NASA
I’m fucking pissing myself. You know how all of Jupiter’s moons are named after his lovers and affairs? Yeah. NASA is sending a craft to check up on Jupiter. You know what the craft is called?
JUNO.
Who’s Juno?
JUPITER’S WIFE.
NASA IS SENDING JUPITER’S WIFE TO CHECK ON JUPITER AND HIS AFFAIRS AND LOVERS.
FUCKING NASA
Five-dimensional black hole could 'break' general relativity
Cambridge UK (SPX) Feb 19, 2016 Researchers have shown how a bizarrely shaped black hole could cause Einstein’s general theory of relativity, a foundation of modern physics, to break down. However, such an object could only exist in a universe with five or more dimensions. The researchers, from the University of Cambridge and Queen Mary University of London, have successfully simulated a black hole shaped like a very thi Full article










Where Could Life Exist?
When NASA scientists announced earlier this year that they had found evidence of liquid water on Mars, imaginations ran wild with the possibility that life could exist somewhere other than here on Earth.
Scientists continue to explore the possibility that Mars once looked a lot like Earth — salty oceans, fresh water lakes, and a water cycle to go with it. That’s exciting stuff.
So where else are they looking? What exactly are they looking for?
There are nine places in our universe where scientists say life is a possibility. The locations range from a smoking hot planet like Venus to a moon that orbits Saturn called Enceladus, which looks a lot like a massive, tightly-packed ball of ice.
All of these places show signs that water is, or at least was, a possibility. They also appear to feature some kind of energy that could produce heat.
full resolution










If you couldn’t tell already, NASA is having a great year. From Pluto to food grown in space, even in the face of budget cuts, the nation’s space agency had some stellar highlights. Most mysteriously of all, a spacecraft found two eerily bright lights on a distant dwarf planet.
Charting the slow death of the Universe
Paris (SPX) Aug 12, 2015 The study, which is part of the Galaxy And Mass Assembly (GAMA) project, the largest multi-wavelength survey ever put together, involved many of the world’s most powerful telescopes [1]. “We used as many space and ground-based telescopes as we could get our hands on to measure the energy output of over 200 000 galaxies across as broad a wavelength range as possible,” says Simon Driver ICRA Full article
Charting the Milky Way From the Inside Out
NASA - Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) patch. June 4, 2015
Image above: This artist’s concept depicts the most up-to-date information about the shape of our own Milky Way galaxy. We live around a star, our sun, located about two-thirds of the way out from the center. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt (SSC/Caltech). Imagine trying to create a map of your house while confined to only the living room. You might peek through the doors into other rooms or look for light spilling in through the windows. But, in the end, the walls and lack of visibility would largely prevent you from seeing the big picture. The job of mapping our own Milky Way galaxy from planet Earth, situated about two-thirds of the way out from the galaxy’s center, is similarly difficult. Clouds of dust permeate the Milky Way, blocking our view of the galaxy’s stars. Today, researchers have a suitable map of our galaxy’s spiral structure, but, like early explorers charting new territory, they continue to patiently and meticulously fill in the blanks. Recently, researchers have turned to a new mapping method that takes advantage of data from NASA’s Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE. Using WISE, the research team has discovered more than 400 dust-shrouded nurseries of stars, which trace the shape of our galaxy’s spiral arms. Seven of these “embedded star clusters” are described in a new study published online May 20 in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Image above: (Annotated) This artist’s concept depicts the most up-to-date information about the shape of our own Milky Way galaxy. We live around a star, our sun, located about two-thirds of the way out from the center. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt (SSC/Caltech). “The sun’s location within the dust-obscured galactic disk is a complicating factor to observe the galactic structure,” said Denilso Camargo, lead author of the paper from the Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil. The results support the four-arm model of our galaxy’s spiral structure. For the last few years, various methods of charting the Milky Way have largely led to a picture of four spiral arms. The arms are where most stars in the galaxy are born. They are stuffed with gas and dust, the ingredients of stars. Two of the arms, called Perseus and Scutum-Centaurus, seem to be more prominent and jam-packed with stars, while the Sagittarius and Outer arms have as much gas as the other two arms but not as many stars. The new WISE study finds embedded star clusters in the Perseus, Sagittarius, and Outer arms. Data from the Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS), a ground-based predecessor of WISE from NASA, the National Science Foundation and the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, helped narrow down the distances to the clusters and pinpoint their location. Embedded star clusters are a powerful tool for visualizing the whereabouts of spiral arms because the clusters are young, and their stars haven’t yet drifted away and out of the arms. Stars begin their lives in the dense, gas-rich neighborhoods of spiral arms, but they migrate away over time. These embedded star clusters complement other techniques for mapping our galaxy, such as those used by radio telescopes, which detect the dense gas clouds in spiral arms.
Image above: Astronomers using data from NASA’s Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, are helping to trace the shape of our Milky Way galaxy’s spiral arms. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul. “Spiral arms are like traffic jams in that the gas and stars crowd together and move more slowly in the arms. As material passes through the dense spiral arms, it is compressed and this triggers more star formation,” said Camargo. WISE is ideal for finding the embedded star clusters because its infrared vision can cut through the dust that fills the galaxy and shrouds the clusters. What’s more, WISE scanned the whole sky, so it was able to perform a thorough survey of the shape of our Milky Way. NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope also uses infrared images to map the Milky Way’s territory. Spitzer looks along specific lines of sight and counts stars. The spiral arms will have the densest star populations.
NASA’s Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE. Image Credit: NASA
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California managed and operated WISE for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The spacecraft was put into hibernation mode in 2011, after it scanned the entire sky twice, thereby completing its main objectives. In September 2013, WISE was reactivated, renamed NEOWISE and assigned a new mission to assist NASA’s efforts to identify potentially hazardous near-Earth objects. Other authors of the study are: Charles Bonatto and Eduardo Bica, also with the Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul. For more information on WISE, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/wise Previous research from Camargo’s team found two embedded clusters far outside the plane of our Milky Way, 16,000 light-years away. A feature story about that work is online at: http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=4497 The new WISE study from the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society is online at: http://mnras.oxfordjournals.org/content/450/4/4150.full?keytype=ref&ijkey=tjeJAezGAmgdXzc Images (mentioned), Text, Credits: NASA/Felicia Chou/JPL/Whitney Clavin/Tony Greicius. Best regards, Orbiter.ch Full article
apparently nasa confirmed there’s an ocean on one of Jupiter’s moons say it with me kids: space mermaids
on the first day of class my astronomy professor asked us why the night sky was dark. if our universe is infinite, how can there be spaces between the stars? he didn’t answer the question until the last day– because our universe is relatively young, and is still growing. it is finite. not enough stars or galaxies have been formed to fill up the entire night sky.
but what that means to me is that somewhere, in an older universe, the night sky looks like a tapestry of diamonds. somewhere darkness is pale white and glittering. imagine being so surrounded. i haven’t gotten that image out of my head ever since– you could never navigate under such a sky but god it sounds lovely

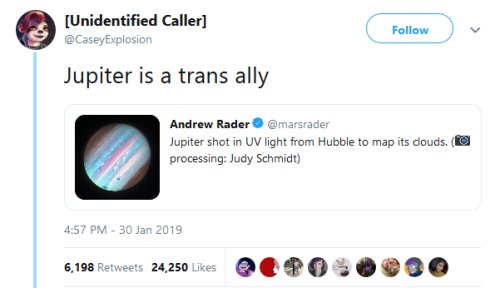
THE UNIVERSE SAID TRANS RIGHTS!! 🗣🗣

Atmospheric Jellyfish are described as jellyfish-like creature seen floating in the Earth’s atmosphere. Atmospheric Jellyfish are said to look like normal jellyfish except they are floating in the sky much like a cloud and are seen mostly around military bases. Skeptics believe that the Atmospheric Jellyfish could be misidentified clouds or weather balloons however believers hold true to the idea and remember the time that NASA sent 60,000 jellyfish into space during their From Undersea to Outer Space experiment.

The Carina Nebula - A Birthplace Of Stars
The Carina Nebula lies at an estimated distance of 6,500 to 10,000 light years away from Earth in the constellation Carina. This nebula is one of the most well studied in astrophysics and has a high rate of star formation. The star-burst in the Carina region started around three million years ago when the nebula’s first generation of newborn stars condensed and ignited in the middle of a huge cloud of cold molecular hydrogen. Radiation from these stars carved out an expanding bubble of hot gas. The island-like clumps of dark clouds scattered across the nebula are nodules of dust and gas that are resisting being eaten away by photons (particles of light) that are ionizing the surrounding gas (giving it an electrical charge).
Credit: NASA/Hubble









The best photographs that the Hubble space telescope has ever taken.
1. Sombrero galaxy
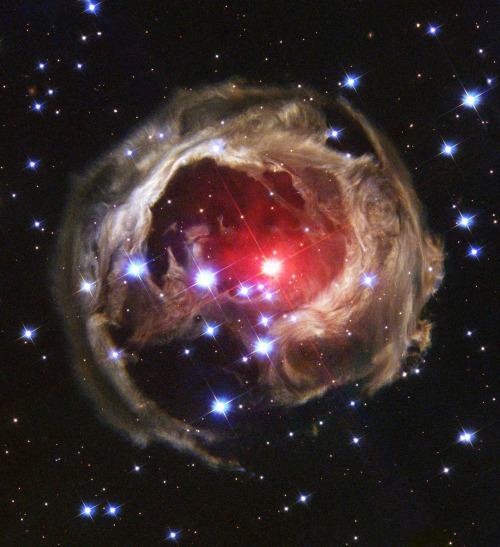
2. V838 Monocerotis
3. Jupiter’s great red spot
4. Carina nebula
5. Interacting galaxies
6. Pillars of creation
7. Cat’s eye nebula
8. Planetary Nebula NGC 5189
9. Abell 2744 Frontier Field
(Source)
Black holes

Perseus Black hole
Black holes are objects that have collapsed under their own weight to a point, creating an object that is very small but enormously dense. It is a region of space that has a gravitational pull so strong that no imminent particle or electromagnetic radiation can escape from it. This astonishing concept of black hole was first given by John Michell in 1783.He proposed that if you take the sun and compress it to a very small volume it would have a gravitational pull so strong that you have to travel at speeds greater than the speed of light to escape it.At first black holes are thought to be theoretical concepts which do not exist. But later they turned out to be very real. So how do these giant suckers form?
In order to understand the formation of a black hole we need to understand the formation and the life cycle of stars. A star is formed when large amounts of dust and gases, mainly hydrogen gas condense and collapse under its own gravitational force. As the gas collapses, the atoms of the gas collide with each other at higher and higher speeds resulting in the heating of the gas. Ultimately the gas becomes so hot that when the hydrogen atoms collide they don’t bounce off, but fuse together to form helium atoms, same as in the hydrogen bomb. As a result a large amount of heat is released which is the reason why stars shine. This heat increases the pressure of the gas until it balances out the gravitational pull and the gas stops contracting. Hence a star is formed.
The stars are usually stable as long as they have hydrogen in them. As the hydrogen runs out, the fusion reaction stops. To keep the fusion reaction going the star turns to its helium reserve. After it runs out of helium, it switches to carbon, and then oxygen. Stars with the mass of our Sun stop at this point as they don’t have enough energy to continue the fusion process and become white dwarfs. But stars with about 5 times the mass of our sun continue further to produce silicon, aluminum, potassium so on up to iron. No further energy can be produced by fusing iron atoms so the star starts to cool down. Once the external force of radiation stops acting the gravitational pull takes over and the star begins to contract. The entire mass of the star collapses into smaller and smaller volume of space. Eventually when the star has contracted to a certain critical radius, the gravitational field at the surface becomes so strong that even light cannot escape it. And this is how a black hole is formed.
Another way of formation of black hole is when two neutron stars collide with each other. When they collide their combined mass results in a very high gravitational force that leads to a collapse and a black hole is formed.

In this image, information from the Chandra X-ray Observatory is combined with images from the Hubble Space Telescope. NASA believes these two black holes are spiraling toward each other and have been doing so for 30 years.

Beware of the Big, Bad Wolf
Visible within the center of the Crescent nebula is what’s classified as a Wolf-Rayet star. This star is a staggering 250,000 times brighter than the Sun, 15 times more massive, and 3.3 times larger. Its surface temperature is nearly 70,000° C/ 125,000° F. At just 4.7 million years old, it is already toward the end of it’s life and is shedding its outer envelope, ejecting the equivalent of the Sun’s mass every 10,000 years. Within a few hundred thousand years, it is expected to explode as a supernova. (Image Credit: Michael Miller, Jimmy Walker)
What is it Like to Visit Jupiter?
Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system. For some perspective, if it were hollow, more than 1,300 Earths could fit inside of it! The giant planet contains two-thirds of all the planetary mass in the solar system and holds more than dozens of moons in its gravitational grip. But what about a visit to this giant planet?

Let’s be honest…Jupiter is not a nice place to visit. It’s a giant ball of gas and there’s nowhere to land. Any spacecraft – or person – passing through the colorful clouds gets crushed and melted. On Jupiter, the pressure is so strong it squishes gas into liquid. Its atmosphere can crush a metal spaceship like a paper cup.

Jupiter’s stripes and swirls are cold, windy clouds of ammonia and water. Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is a giant storm BIGGER THAN EARTH! This storm has lasted hundreds of years.

Since Jupiter’s atmosphere is made up of mostly hydrogen and helium, it’s poisonous. There’s also dangerous radiation, more than 1,000 times the lethal level for a human.
Scientists think that Jupiter’s core may be a thick, super hot soup…up to 50,000 degrees! Woah!
The Moons

Did you know that Jupiter has its own “mini solar system” of 50 moons? Scientists are most interested in the Galilean satellites – which are the four largest moons discovered by Galileo Galilei in 1610.
Today, Galileo would be astounded to know some of the facts about these moons. The moon Io has active volcanos. Ganymede has its own magnetic field while Europa has a frozen crust with liquid-water underneath making it a tempting place to explore for future missions.

When Juno arrives to Jupiter on July 4, it will bring with it a slew of instruments such as infrared imager/spectrometer and vector magnetometer among the half a dozen other scientific tools in its payload.
Juno will avoid Jupiter’s highest radiation regions by approaching over the north, dropping to an altitude below the planet’s radiation belts – which are analogous to Earth’s Van Allen belts, but far more deadly – and then exiting over the south. To protect sensitive spacecraft electronics, Juno will carry the first radiation shielded electronics vault, a critical feature for enabling sustained exploration in such a heavy radiation environment.
Follow our Juno mission on the web, Facebook, Twitter, YouTube and Tumblr.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

It’s easy to get lost in this Hubble image of NGC 339. Located in the Small Magellanic Cloud, it lies around 200,000 LY away. By measuring the brightnesses and colors of the stars of NGC 339, astronomers are able to estimate the age of the cluster at around 6.5 billion years old. In the background of this image, neighboring galaxies are revealed as fuzzy, extended blobs. Can you spot one? (Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt)

The only home we’ve ever known. Clouds and sunlight over the Indian Ocean, as seen from Discovery during the STS-96 mission in 1999.

Hubble’s Bubble
To celebrate 26 years in space, Hubble has captured this magnificent view of NGC 7635, better known as the Bubble Nebula. The “bubble” is created by the stellar wind from a hot, young central star that is 10-20 times the mass of our Sun.