159 posts
Latest Posts by xnzda - Page 2

This is one of the largest and most prolific star-forming regions near our Milky Way. Located about 160,000 light years away in the neighboring Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy, the Tarantula nebula is sculpted by searing radiation and strong winds that comes from the massive stars at its center. If fact, it is estimated that at least 40 of these huge stars have gone supernova within the last 10,000 years including the most recent one, SN 1987a. (Composite Image from Multiple Data Sources. Hubble Space Telescope, ESO, Amateur Data. Image Assembly and Processing : Robert Gendler and Roberto Colombari)
What Happened to Mars?
Billions of years ago, Mars was a very different world. Liquid water flowed in long rivers that emptied into lakes and shallow seas. A thick atmosphere blanketed the planet and kept it warm.

Today, Mars is bitter cold. The Red Planet’s thin and wispy atmosphere provides scant cover for the surface below.

Our MAVEN Mission
The Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) mission is part of our Mars Scout program. This spacecraft launched in November 2013, and is exploring the Red Planet’s upper atmosphere, ionosphere and interactions with the sun and solar wind.

The purpose of the MAVEN mission is to determine the state of the upper atmosphere of Mars, the processes that control it and the overall atmospheric loss that is currently occurring. Specifically, MAVEN is exploring the processes through which the top of the Martian atmosphere can be lost to space. Scientists think that this loss could be important in explaining the changes in the climate of Mars that have occurred over the last four billion years.
New Findings
Today, Nov. 5, we will share new details of key science findings from our ongoing exploration of Mars during a news briefing at 2 p.m. EDT. This event will be broadcast live on NASA Television. Have questions? Use #askNASA during the briefing.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

DAT MILKY WAY

M94: Bursting With Stars
Located about 16 million light-years away, this new Hubble image shows the sparkling galaxy Messier 94. You’ll notice the bright ring (or starburst ring) around Messier 94 where new stars are forming at a high rate. The cause of this star-forming region is thought to be a pressure wave going outwards from the galactic center, compressing the gas and dust in the outer region. The compression of material means the gas starts to collapse into denser clouds. Inside these dense clouds, gravity pulls the gas and dust together until temperature and pressure are high enough for stars to be born. (Image credit: NASA / ESA / Hubble)
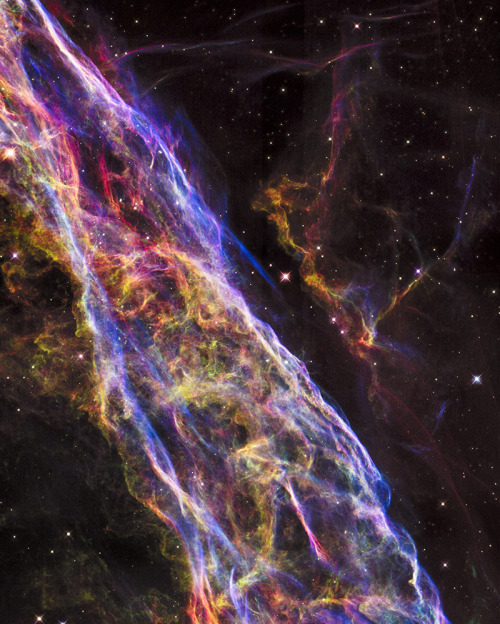

Veil Nebula Supernova Remnant
via NASA Hubble Space Telescope has unveiled in stunning detail a small section of the expanding remains of a massive star that exploded about 8,000 years ago.
Called the Veil Nebula, the debris is one of the best-known supernova remnants, deriving its name from its delicate, draped filamentary structures. The entire nebula is 110 light-years across, covering six full moons on the sky as seen from Earth, and resides about 2,100 light-years away in the constellation Cygnus, the Swan.
This view is a mosaic of six Hubble pictures of a small area roughly two light-years across, covering only a tiny fraction of the nebula’s vast structure.
This close-up look unveils wisps of gas, which are all that remain of what was once a star 20 times more massive than our sun. The fast-moving blast wave from the ancient explosion is plowing into a wall of cool, denser interstellar gas, emitting light. The nebula lies along the edge of a large bubble of low-density gas that was blown into space by the dying star prior to its self-detonation.
Image Credit: NASA/ESA/Hubble Heritage Team

Photographer Luc Jamet recently won astronomy photographer of the year for this gorgeous and eerie image of the total solar eclipse seen from the Norwegian territory of Svalbard on March 20, 2015.

Located about 27 million light years away lies Messier 63, better known as the Sunflower Galaxy due to its glowing yellow center. For galaxies like Messier 63 the winding arms shine bright because of the presence of recently formed, blue–white giant stars, readily seen in this Hubble image. (Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA)

Today’s APOD is particularly stunning.
Have you watched the Perseid meteor shower? Though the annual shower’s predicted peak was last night, meteor activity should continue tonight (August 13/14), best enjoyed by just looking up in clear, dark skies after midnight. Of course, this year’s Perseid shower has the advantage of being active near the August 14 New Moon. Since the nearly New Moon doesn’t rise before the morning twilight many fainter meteors are easier to spot until then, with no interference from bright moonlight. The Perseid meteor shower last occurred near a New Moon in 2013. That’s when the exposures used to construct this image were made, under dark, moonless skies from Hvar Island off the coast of Croatia. The widefield composite includes 67 meteors streaming from the heroic constellation Perseus, the shower’s radiant, captured during 2013 August 8-14 against a background of faint zodiacal light and the Milky Way. The next moonless Perseid meteor shower will be in August 2018.
Image Credit & Copyright: Petr Horálek

NASA’s planet-hunting Kepler Telescope has spotted the first roughly Earth-sized world orbiting in the “Goldilocks zone” of another star – offering perhaps the best bet so far for life elsewhere in the universe.
A year on Kepler 452b, which is about 1,400 light years from us in the constellation Cygnus, is 385 days, meaning its orbit is just a bit farther away from its star than the Earth is from the sun. That places it squarely within what planetary scientists call the habitable zone, or “Goldilocks” zone — not too cold and not too hot.
“In my mind, this is the closest planet indeed to Earth,” Jon Jenkins, Kepler data analysis lead at NASA’s Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, Calif, said at a media briefing. “The star is a little bit older and a little bit bigger and brighter, so it’s good that it’s a bit farther from its star.”
Kepler Telescope Introduces Earth To A Very Distant Cousin
Image: Artist’s concept compares Earth (left) to the new planet, called Kepler-452b, which is about 60 percent larger in diameter. Courtesy of NASA/JPL-Caltech/T. Pyle
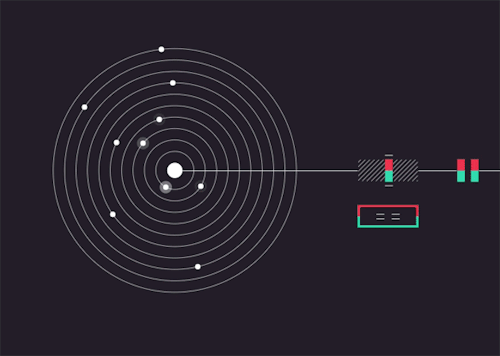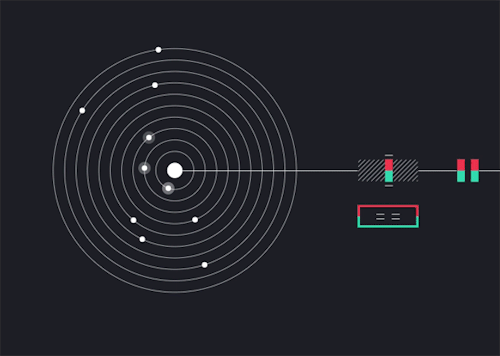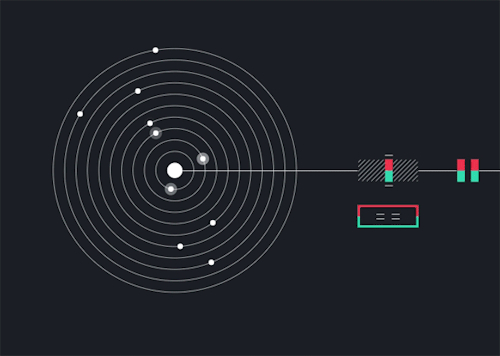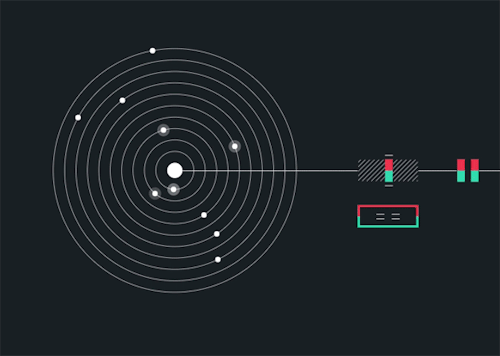
Solarbeat
This is magical. whitevinyldesign.com/solarbeat
via wired
Because every planet has its own orbital period, “it ends up generating this unending, interesting pattern,” Twyman says. For example, Mercury, which has an orbit of 88 Earth days, is the backbeat to the sound, while Pluto, which takes approximately 248 years to orbit the sun, rarely makes an appearance in the music. “It really lends itself to generating ambient music,” he says. You can tweak the speed of orbit, slowing it down to make a soothing tinkle of a child’s mobile or speeding it up to orchestrate a chaotic planetary choir. New features allow you to add sound effects like echo, flutter and bass, and you can choose from eight different chords to personalize the sound. READ MORE
So it turns out, Pluto is red.

What color is Pluto? If you search for the dwarf planet on Google, images suggest that it’s a sort of steely blue or gray color. But now, NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft is closing in on it, and has learned Mars isn’t the only red planet in our solar system. But the reason it’s red couldn’t be more different from Mars.

Cosmic Fireworks
Like an incredible celestial firework display, dust, ionized material and molecular gas from a dying star form the Helix Nebula. The star is evolving to become a white dwarf star and appears as the tiny blue dot seen at the center. This picture, taken in infrared light by the ESO’s VISTA telescope at the Paranal Observatory, reveals strands of cold nebular gas that is invisible in images taken in visible light. The main ring of the Helix is about two light-years across, roughly half the distance between the Sun and the nearest star. Material from the nebula spreads out from the star to at least four light-years. The Helix Nebula lies in the constellation of Aquarius about 700 light years from Earth. (Credit: ESO)

“For small creatures such as we the vastness is bearable only through love.” – Carl Sagan

Astronomy Photo of the Day: 5/30/15 — Vividly Blue NGC 7822
This beautifully blue image comes from Manuel Fernández Suarez—an award winning astrophotographer. It provides a window into the heart of a stellar nursery, found approximately 3,000 light-years from Earth in the Cepheus constellation.
Called NGC 7822, it lurks on the outskirts of a behemoth molecular cloud (one of the largest in our galaxy), and contains numerous features, like the star cluster known as Berkeley 59, along with one of the hottest stars in our local part of the galaxy—called BD+66 1673 (there, temperatures can exceed 45,000 K).
As we noted before, “The region, formally known as NGC 7822, contains hundreds of newborn stars that are leaving their own mark on the interstellar material surrounding them, seeding it with heavy elements that will ultimately collapse to give life to a new generation of stars. These same stars are also slowly chipping away at some of the material, they in turn, give it its distinct shape and its designation as an emission nebula.”
Sources & Other Resources: http://bit.ly/1LPOf5M
Image Credit: Manuel Fernández Suarez

A stellar fingerprint - an emission-line star known as IRAS 12196-6300
js

#BlackHistoryMonth #tbt: Being the first African American woman to travel to space is one of Mae Jemison’s many accomplishments. A dancer, Peace Corps doctor, public speaker and astronaut, Mae went to college at age 16, holds 9 honorary doctorates and has founded many STEM-related programs for students.
Holiday Lights from the Universe
Although there are no seasons in space, some cosmic vistas invoke thoughts of a frosty winter landscape. Here are a few stellar images of holiday wonderlands from across the galaxy…

Located in our galaxy about 5,500 light years from Earth, this region is actually a “cluster of clusters,” containing at least three clusters of young stars, including many hot, massive, luminous stars.

The outstretched “wings” of this nebula looks like a soaring, celestial snow angel. Twin lobes of super-hot gas, glowing blue in this image, stretch outward from the central star. This hot gas creates the “wings” of our angel. A ring of dust and gas orbiting the star acts like a belt, clinching the expanding nebula into an “hourglass” shape.

At this time of year, holiday parties often include festive lights. When galaxies get together, they also may be surrounded by a spectacular light show. This pair of spiral galaxies has been caught in a grazing encounter. This region has hosted three supernova explosions in the past 15 years and has produced one of the most bountiful collections of super-bright X-ray lights known.

What do the following things have in common: a cone, the fur of a fox and a Christmas tree? Answer: they all occur in the constellation of the unicorn (Monoceros). Pictured as a star forming region, the complex jumble of cosmic gas and dust is about 2,700 light-years away.

Resembling festive lights on a holiday wreath, this Hubble Space Telescope image of a nearby spiral galaxy is an iconic reminder of the impending season. Bright knots of glowing gas light up the spiral arms, indicating a rich environment of star formation.

The Hubble Space Telescope captured two festive-looking nebulas, situated so as to appear as one. Intense radiation from the brilliant central stars is heating hydrogen in each of the nebulas, causing them to glow red…like a holiday light.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com


Spirit sends one of those pictures that looks like it could come from the red rock deserts of the American West, but actually shows part of the landscape in Gusev crater, a mere 60 million miles away. Credit: NASA
The dune field at the center of Victoria Crater, seen in a new false-color shot. Credit: NASA
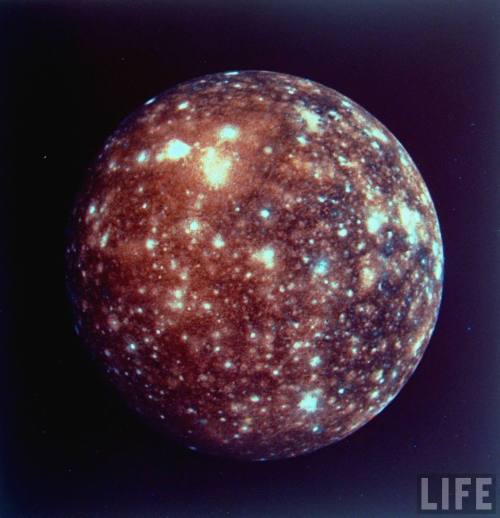
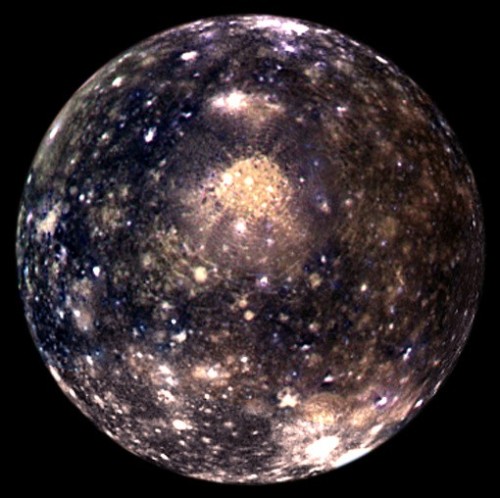
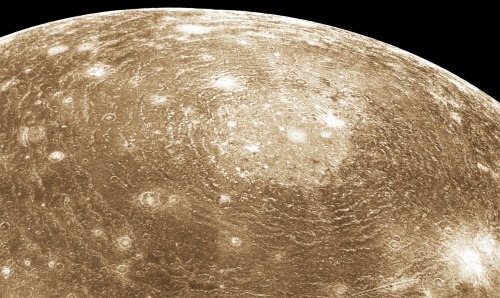
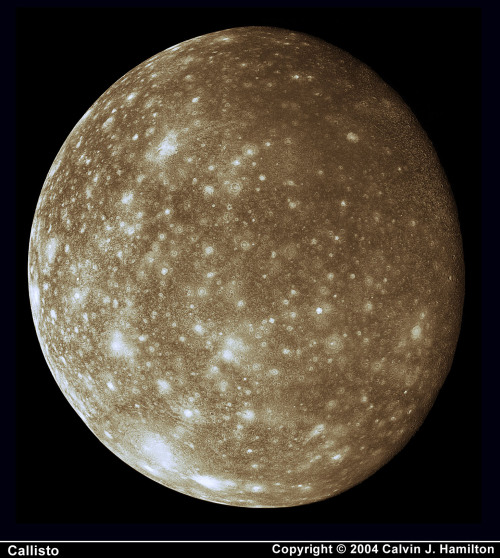
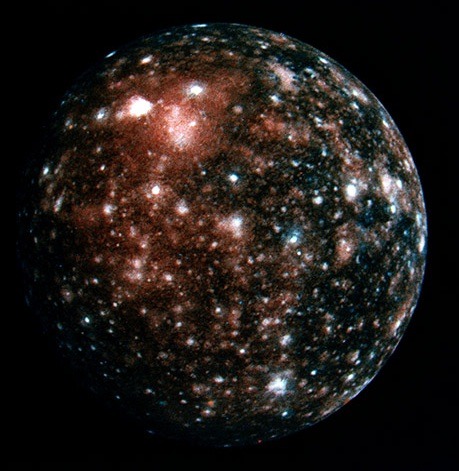




Jupiter’s moon, Callisto.
Remember kids: Pluto is not a planet, WAS never a planet, and any acknowledgement of Pluto as a planet was an error of assumption

December 2006: Constructing the Space Station : NASA astronaut Robert Curbeam works on the International Space Station’s S1 truss during the space shuttle Discovery’s STS-116 mission in Dec. 2006. (via NASA)

Hubble captures stunning image of Messier 94 Galaxy showing a starburst ring.
js

Cygnus entering the atmosphere, photographed by Alexander Gerst on the ISS.








All here… Sorry, Pluto, you don’t belong here
PS: I do follow back

At the Heart of Orion.
I realized why the idea of constellations has always swayed me. constellations are so very human.
our wonder of the stars is bone-sunk; we’ve been thinking and dreaming and watching and watching and watching since the beginning of time, and we looked for so long that we started making connections.
we played a celestial game of connect-the-dots; trying to find order in something so vast and trying to show that the stars are in everything and everything is in the stars.
we plucked pictures out of the infinite; there’s a dog, there’s a bear, there’s a lion, see? look, right there; the stars hold and mirror back everything we see.
but then it went a step further. instead of everyday things, we stopped picking out the cups and the bears, and instead we saw stories.
look, Andromeda, chained to a rock and waiting to be devoured by Cetus. there’s Orion, and Hercules, and do you see Orpheus’ lyre? Zeus sent an eagle to retrieve it after Orpheus’ death and he placed it in the sky.
we did the most human thing imaginable: we wrote our stories into the stars. we filled the night sky; previously so vast, so unknowable; with our history. we forged connections to the stars and made it so our children will always know where they come from.





Flying Across The Universe (From Top to Bottom: Horsehead Nebula, Orion Nebula, Eagle Nebula, Tarantula Nebula, and NGC 3603)

Spectacular!
Credit: Fragile Oasis

A Gallery of ‘Tadpole Galaxies’
These postage-stamp-size images reveal 36 young galaxies caught in the act of merging with other galaxies. These galaxies appear as they existed many billions of years ago. Astronomers have dubbed them “tadpole galaxies” because of their distinct knot-and-tail shapes, which suggest that they are engaging in galactic mergers.
Credit: NASA, A. Straughn, S. Cohen, and R. Windhorst (Arizona State University), and the HUDF team (Space Telescope Science Institute) Source: http://www.spacetelescope.org/images/opo0604a/


Michael Benson
1. Mimas Above Saturn’s Rings and Shadows, Cassini, November, 7, 2004
2. Mimas Transits Saturn’s Ring Shadows, Cassini, January 18, 2005