The Moon Occluding The Sun During An Eclipse. The Fine Threads You Can See Are Part Of The Solar Corona,

The moon occluding the sun during an eclipse. The fine threads you can see are part of the solar corona, and actually titanic spools of ultra-hot plasma, curling and bending with the sun’s complex magnetic field.
More Posts from Xnzda and Others

The Icy Comet
This image of Comet C/2001 Q4 (NEAT) was taken at the WIYN 0.9-meter telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory near Tucson, Ariz
Image credit: NASA/ National Science Foundation
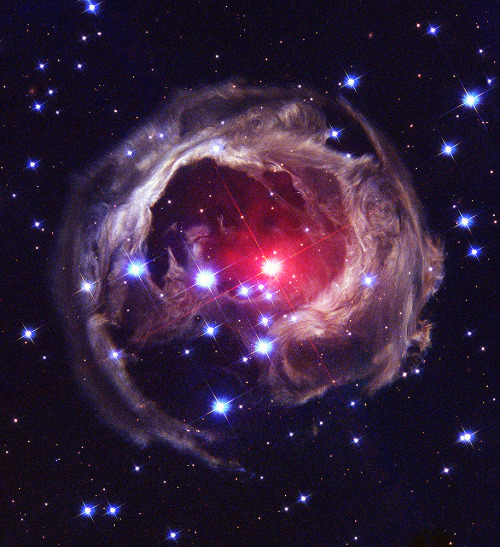

Light Echoes from V838 Mon
For reasons unknown, star V838 Mon’s outer surface suddenly greatly expanded with the result that it became the brightest star in the entire Milky Way Galaxy in January 2002. Then, just as suddenly, it faded. A stellar flash like this has never been seen before.
It’s true that supernovae and novae expel matter out into space. But while the V838 Mon flash appears to expel material into space, what is seen here is actually an outwardly moving light echo of the bright flash. In a light echo, light from the flash is reflected by successively more distant rings in the ambient interstellar dust that already surrounded the star.
V838 Mon lies about 20,000 light years away toward the constellation of Monoceros the unicorn. In this Hubble Space Telescope image from February 2004, the light echo is about six light years in diameter.
Image Credit: NASA, APOD, ESA, H. E. Bond (STScI)

“For small creatures such as we the vastness is bearable only through love.” – Carl Sagan

Beware of the Big, Bad Wolf
Visible within the center of the Crescent nebula is what’s classified as a Wolf-Rayet star. This star is a staggering 250,000 times brighter than the Sun, 15 times more massive, and 3.3 times larger. Its surface temperature is nearly 70,000° C/ 125,000° F. At just 4.7 million years old, it is already toward the end of it’s life and is shedding its outer envelope, ejecting the equivalent of the Sun’s mass every 10,000 years. Within a few hundred thousand years, it is expected to explode as a supernova. (Image Credit: Michael Miller, Jimmy Walker)
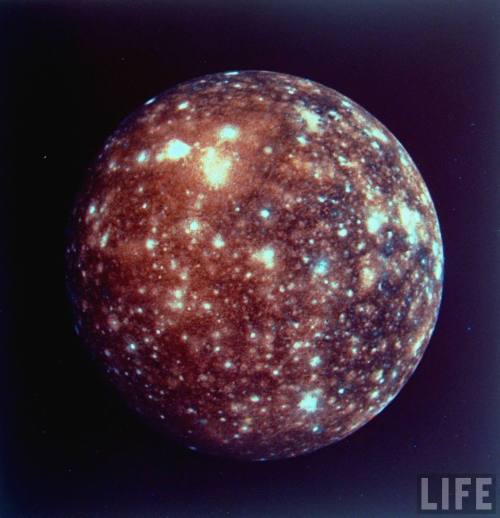
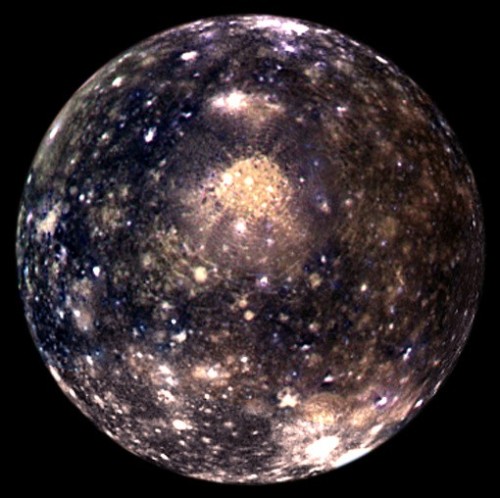
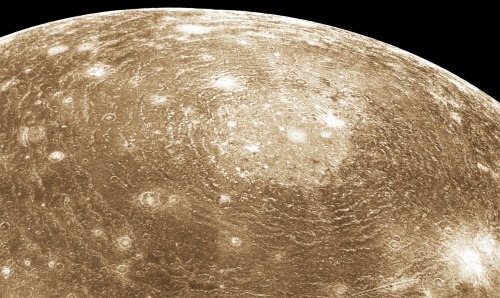
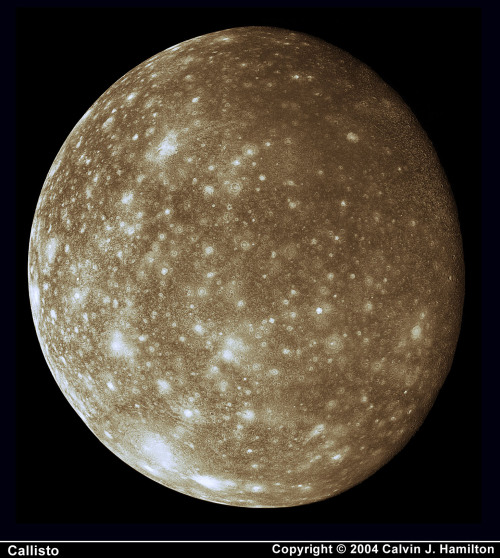
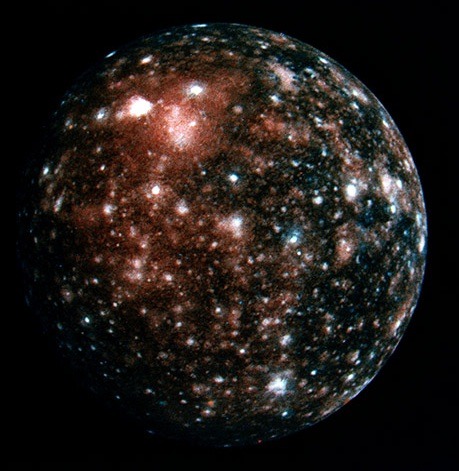




Jupiter’s moon, Callisto.

Close-up of M27, the Dumbbell Nebula
Credit: NASA/ESA, Hubble
-
 wildernestt reblogged this · 1 year ago
wildernestt reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 nidipoppy liked this · 2 years ago
nidipoppy liked this · 2 years ago -
 prala reblogged this · 2 years ago
prala reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 prala liked this · 2 years ago
prala liked this · 2 years ago -
 strawberry49sworld reblogged this · 3 years ago
strawberry49sworld reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 strawberry49sworld liked this · 3 years ago
strawberry49sworld liked this · 3 years ago -
 kookoeo reblogged this · 4 years ago
kookoeo reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 quartz-angel liked this · 4 years ago
quartz-angel liked this · 4 years ago -
 thenighteternal liked this · 4 years ago
thenighteternal liked this · 4 years ago -
 itsokaytobefreak liked this · 4 years ago
itsokaytobefreak liked this · 4 years ago -
 spectavistimemori reblogged this · 4 years ago
spectavistimemori reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 the123321a liked this · 5 years ago
the123321a liked this · 5 years ago -
 englishivyx reblogged this · 5 years ago
englishivyx reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 fullyydramaticc reblogged this · 5 years ago
fullyydramaticc reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 sii-coraggioso-blog reblogged this · 5 years ago
sii-coraggioso-blog reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 sii-coraggioso-blog liked this · 5 years ago
sii-coraggioso-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 phureist reblogged this · 6 years ago
phureist reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 leilafae reblogged this · 6 years ago
leilafae reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 niccup reblogged this · 6 years ago
niccup reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 rockragdoll reblogged this · 6 years ago
rockragdoll reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 mercurinium reblogged this · 6 years ago
mercurinium reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 ongreenergrasses reblogged this · 6 years ago
ongreenergrasses reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 cutlural reblogged this · 6 years ago
cutlural reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 vctrlf liked this · 6 years ago
vctrlf liked this · 6 years ago -
 turtonator reblogged this · 6 years ago
turtonator reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 shadows-of-the-mess-you-made reblogged this · 6 years ago
shadows-of-the-mess-you-made reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 myviolentdelight11 reblogged this · 6 years ago
myviolentdelight11 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 myviolentdelight11 liked this · 6 years ago
myviolentdelight11 liked this · 6 years ago -
 cutlural reblogged this · 6 years ago
cutlural reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 forgiving-and-forgetting-me reblogged this · 6 years ago
forgiving-and-forgetting-me reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 too-blue-to-be-cool liked this · 6 years ago
too-blue-to-be-cool liked this · 6 years ago -
 brander-666 liked this · 6 years ago
brander-666 liked this · 6 years ago -
 theonefrommercury reblogged this · 6 years ago
theonefrommercury reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 besoundstaysound reblogged this · 6 years ago
besoundstaysound reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 whenhopebeginstofade reblogged this · 6 years ago
whenhopebeginstofade reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 sugar-with-salt liked this · 6 years ago
sugar-with-salt liked this · 6 years ago -
 brjggs reblogged this · 6 years ago
brjggs reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 brjggs liked this · 6 years ago
brjggs liked this · 6 years ago -
 ambidexedition liked this · 6 years ago
ambidexedition liked this · 6 years ago -
 fresapendeja liked this · 6 years ago
fresapendeja liked this · 6 years ago -
 p3rsp3ctiv3 reblogged this · 6 years ago
p3rsp3ctiv3 reblogged this · 6 years ago
![M51, The Whirlpool Galaxy [3450 X 3697]](https://64.media.tumblr.com/e3d38132c6a1bab2d6a3d758e2137b6d/tumblr_plzsxlWKMO1ve10t6o1_500.jpg)


