NASA’s Juno Probe Returns Stunning New Image Of Jupiter

NASA’s Juno Probe Returns Stunning New Image of Jupiter
http://www.sci-news.com/space/juno-image-jupiter-05256.html
More Posts from Xyhor-astronomy and Others



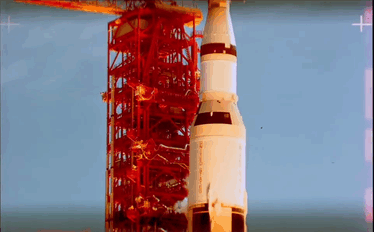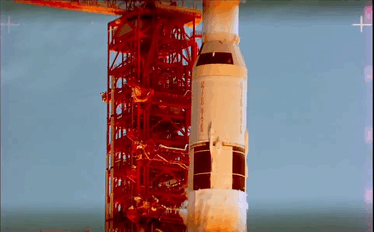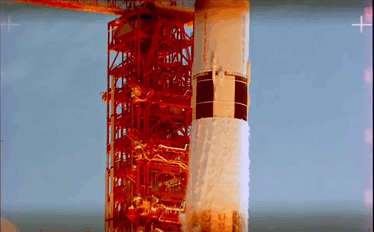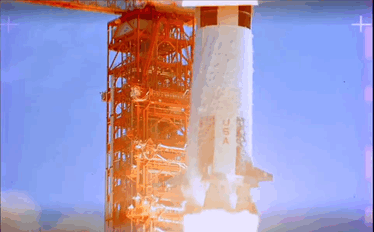

Apollo 11 Launch
ISS | Credit: NASA
Time-lapse imagery captured June 25, 2017 by Expedition 52.
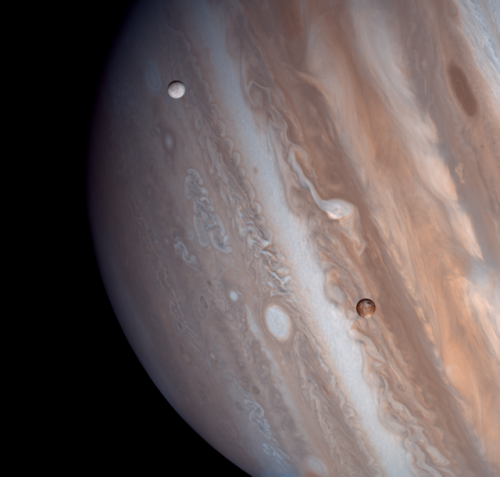

Io and Europa taken by the Voyager 1 spacecraft in 1979
Image credit: Justin Cowart
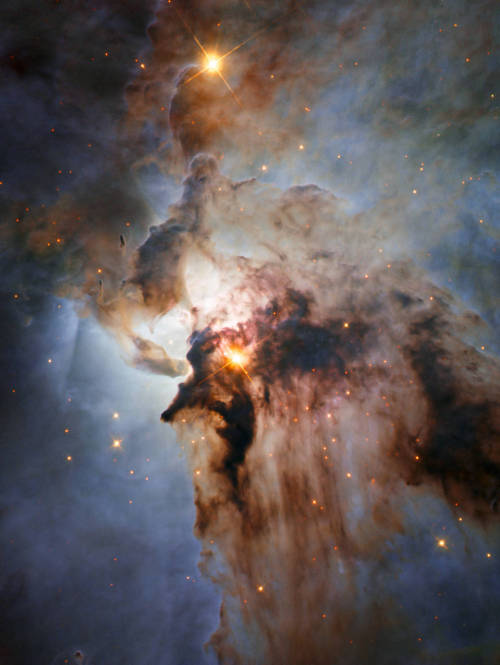

Stormy Seas in Sagittarius
This new NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows the center of the Lagoon Nebula, an object with a deceptively tranquil name, in the constellation of Sagittarius. The region is filled with intense winds from hot stars, churning funnels of gas, and energetic star formation, all embedded within an intricate haze of gas and pitch-dark dust.
Image Credit: NASA/JPL/ESA/J. Trauger
The dusty, star-forming galaxy took shape in the first billion years after the Big Bang and is likely to be one of the first galaxies to ever form, says Min Yun, astrophysicist of the University of Massachusetts Amherst.
The Daredevil Spacecraft That Will Touch the Sun
In the summer of 2018, we’re launching Parker Solar Probe, a spacecraft that will get closer to the Sun than any other in human history.

Parker Solar Probe will fly directly through the Sun’s atmosphere, called the corona. Getting better measurements of this region is key to understanding our Sun. For instance, the Sun releases a constant outflow of solar material, called the solar wind. We think the corona is where this solar wind is accelerated out into the solar system, and Parker Solar Probe’s measurements should help us pinpoint how that happens.

The solar wind, along with other changing conditions on the Sun and in space, can affect Earth and are collectively known as space weather. Space weather can trigger auroras, create problems with satellites, cause power outages (in extreme cases), and disrupt our communications signals. That’s because space weather interacts with Earth’s upper atmosphere, where signals like radio and GPS travel from place to place.

Parker Solar Probe is named after pioneering physicist Gene Parker. In the 1950s, Parker proposed a number of concepts about how stars — including our Sun — give off energy. He called this cascade of energy the solar wind. Parker also theorized an explanation for the superheated solar atmosphere, the corona, which is hotter than the surface of the Sun itself.

Getting the answers to our questions about the solar wind and the Sun’s energetic particles is only possible by sending a probe right into the furnace of the Sun’s corona, where the spacecraft can reach 2,500 degrees Fahrenheit. Parker Solar Probe and its four suites of instruments – studying magnetic and electric fields, energetic particles, and the solar wind – will be protected from the Sun’s enormous heat by a 4.5-inch-thick carbon-composite heat shield.
Over the course of its seven-year mission, Parker Solar Probe will make two dozen close approaches to the Sun, continuously breaking its own records and sending back unprecedented science data.

Getting close to the Sun is harder than you might think, since the inertia of a spacecraft launched from Earth will naturally carry it in repeated orbits on roughly the same path. To nudge the orbit closer to the Sun on successive trips, Parker Solar Probe will use Venus’ gravity.
This is a technique called a gravity assist, and it’s been used by Voyager, Cassini, and OSIRIS-REx, among other missions. Though most missions use gravity assists to speed up, Parker Solar Probe is using Venus’ gravity to slow down. This will let the spacecraft fall deeper into the Sun’s gravity and get closer to our star than any other spacecraft in human history.

You can get a behind-the-scenes at Parker Solar Probe under construction in a clean room at facebook.com/NASASunScience today (Sept. 25) at 1:45 PM EDT.

Keep up with all the latest on Parker Solar Probe at nasa.gov/solarprobe or on Twitter @NASASun.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.










The Largest Black Hole Merger Of All-Time Is Coming, And Soon
“Over in Andromeda, the nearest large galaxy to the Milky Way, a number of unusual systems have been found. One of them, J0045+41, was originally thought to be two stars orbiting one another with a period of just 80 days. When additional observations were taken in the X-ray, they revealed a surprise: J0045+41 weren’t stars at all.”
When you look at any narrow region of the sky, you don’t simply see what’s in front of you. Rather, you see everything along your line-of-sight, as far as your observing power can take you. In the case of the Panchromatic Hubble Andromeda Treasury, where hundreds of millions of stars were captured in impressive fashion, background objects thousands of times as distant can also be seen. One of them, J0045+41, was originally thought to be a binary star system that was quite tight: with just an 80 day orbital period. Follow-up observations in the X-ray, however, revealed that it wasn’t a binary star system after all, but an ultra-distant supermassive black hole pair, destined to merge in as little as 350 years. If we build the right observatory in space, we’ll be able to observe the entire inspiral-and-merger process for as long as we like!
Come get the full story, and some incredible pictures and visuals, on today’s Mostly Mute Monday!
A new detector can use neutrinos to help us take a peek inside Earth!

A slow-motion animation of the Crab Pulsar taken at 800 nm wavelength (near-infrared) using a Lucky Imaging camera from Cambridge University, showing the bright pulse and fainter interpulse.
Credit: Cambridge University Lucky Imaging Group









5 Questions You Were Too Embarrassed To Ask About The Expanding Universe
“5.) Are there galaxies moving away faster than the speed of light, and isn’t that forbidden? From our point of view, the space in between us and any distant point is expanding. The farther away something is, the faster it appears to recede from us. Even if the expansion rate were tiny, an object far enough away would eventually cross that threshold of any finite speed, since an expansion rate (a speed-per-distance) multiplied by a great enough distance will give you a speed as fast as you want. But this is okay in General Relativity! The law that nothing can travel faster than the speed of light only applies to an object’s motion through space, not to the expansion of space itself. In reality, the galaxies themselves only move around at speeds that are hundreds or thousands of km/s, much lower than the 300,000 km/s speed limit set by the speed of light. It’s the expansion of the Universe that causes this recession and the redshift, not a true galactic motion.”
The idea that the spatial fabric of the Universe itself is expanding, and that’s what’s behind the observed relationship between redshift and distance has long been controversial, and also long-misunderstood. After all, if more distant objects appear to recede more quickly, couldn’t there be a different explanation, like an explosion that flung many things outward? As it turns out, this isn’t a mere difference in interpretation, there are observations we can make that tell us the answer! The Universe is not expanding ‘into’ anything, despite what your intuition might tell you. The Hubble ‘constant’ isn’t actually a constant, but is rather decreasing as time goes on. The Universe looks like it’s going to expand forever, but even that scientific conclusion is subject to revision depending on what data shows in the future. And although 97% of the galaxies in the Universe are already unreachable, it isn’t a violation of relativity or a faster-than-light phenomenon that’s to blame.
Come learn the answers to five questions about the expanding Universe that many are too embarrassed to ask!
-
 prrrk03 reblogged this · 2 years ago
prrrk03 reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 redkingkel reblogged this · 5 years ago
redkingkel reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 di5app34r reblogged this · 5 years ago
di5app34r reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 di5app34r liked this · 5 years ago
di5app34r liked this · 5 years ago -
 wisent15 liked this · 5 years ago
wisent15 liked this · 5 years ago -
 wisent15 reblogged this · 5 years ago
wisent15 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 inquisitorstewie liked this · 5 years ago
inquisitorstewie liked this · 5 years ago -
 lizawolfwoman liked this · 5 years ago
lizawolfwoman liked this · 5 years ago -
 fernandopsy liked this · 5 years ago
fernandopsy liked this · 5 years ago -
 thunderapache-blog reblogged this · 5 years ago
thunderapache-blog reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 thunderapache-blog liked this · 5 years ago
thunderapache-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 sizzlingauthorfishbear liked this · 5 years ago
sizzlingauthorfishbear liked this · 5 years ago -
 the-fae-folk liked this · 5 years ago
the-fae-folk liked this · 5 years ago -
 straightoutta-kirkwall liked this · 5 years ago
straightoutta-kirkwall liked this · 5 years ago -
 thelitetravaler liked this · 5 years ago
thelitetravaler liked this · 5 years ago -
 mediocre-habits liked this · 5 years ago
mediocre-habits liked this · 5 years ago -
 marshmallowdoritos liked this · 5 years ago
marshmallowdoritos liked this · 5 years ago -
 mtlfootballfan reblogged this · 5 years ago
mtlfootballfan reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 the-seelie-one reblogged this · 5 years ago
the-seelie-one reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 the-seelie-one liked this · 5 years ago
the-seelie-one liked this · 5 years ago -
 thelitetravaler reblogged this · 5 years ago
thelitetravaler reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 ulk78 liked this · 5 years ago
ulk78 liked this · 5 years ago -
 marumanmoon liked this · 5 years ago
marumanmoon liked this · 5 years ago -
 jeebssred liked this · 5 years ago
jeebssred liked this · 5 years ago -
 da-mage liked this · 5 years ago
da-mage liked this · 5 years ago -
 knightpunk liked this · 5 years ago
knightpunk liked this · 5 years ago -
 aw-reginum liked this · 5 years ago
aw-reginum liked this · 5 years ago -
 justhereforstarwars liked this · 5 years ago
justhereforstarwars liked this · 5 years ago -
 fagdykefrank liked this · 5 years ago
fagdykefrank liked this · 5 years ago -
 srtrementine reblogged this · 5 years ago
srtrementine reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 king-of-carrot-flowers7 reblogged this · 5 years ago
king-of-carrot-flowers7 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 prince-of-places liked this · 5 years ago
prince-of-places liked this · 5 years ago -
 shoshaz36-blog liked this · 5 years ago
shoshaz36-blog liked this · 5 years ago
For more content, Click Here and experience this XYHor in its entirety!Space...the Final Frontier. Let's boldly go where few have gone before with XYHor: Space: Astronomy & Spacefaring: the collection of the latest finds and science behind exploring our solar system, how we'll get there and what we need to be prepared for!
128 posts