Messier 82

Messier 82
Messier 82 is a starburst galaxy about 12 million light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major. A member of the M81 Group, it is about five times more luminous than the whole Milky Way and has a center one hundred times more luminous than our galaxy’s center.
Image credit: NASA/ESA & Hubble
More Posts from Xyhor-astronomy and Others

Saturn photographed by the Cassini spacecraft in 2014
Image credit: NASA/JPL/Cassini; precessed by: Ian Regan
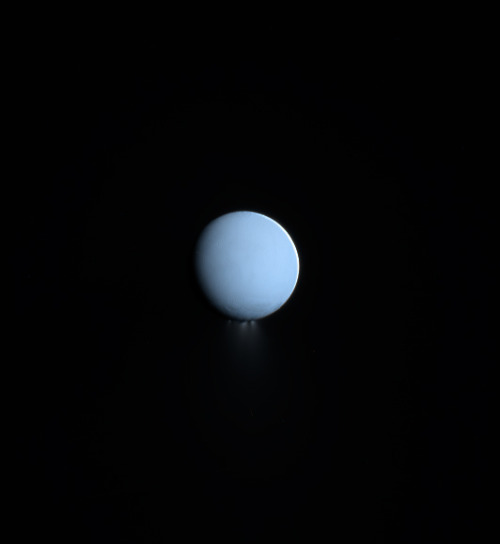
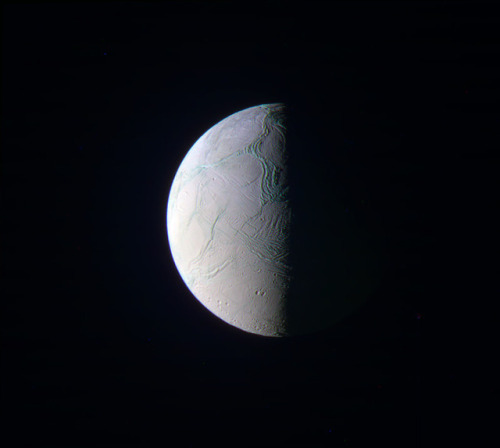









Enceladus
Enceladus is one of the major inner moons of Saturn along with Dione, Tethys, and Mimas. It orbits Saturn at a distance of 148,000 miles (238,000 km), falling between the orbits of Mimas and Tethys. It is tidally locked with Saturn, keeping the same face toward the planet. It completes one orbit every 32.9 hours within the densest part of Saturn’s E Ring, the outermost of its major rings, and is its main source.
Enceladus is, like many moons in the extensive systems of the giant planets, trapped in an orbital resonance. Its resonance with Dione excites its orbital eccentricity, which is damped by tidal forces, tidally heating its interior, and possibly driving the geological activity.
Enceladus is Saturn’s sixth largest moon, only 157 miles (252 km) in mean radius, but it’s one of the most scientifically compelling bodies in our solar system. Hydrothermal vents spew water vapor and ice particles from an underground ocean beneath the icy crust of Enceladus. This plume of material includes organic compounds, volatile gases, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, salts and silica.
With its global ocean, unique chemistry and internal heat, Enceladus has become a promising lead in our search for worlds where life could exist.

In 2005, Cassini’s multiple instruments discovered that this icy outpost is gushing water vapor geysers out to a distance of three times the radius of Enceladus. The icy water particles are roughly one ten-thousandth of an inch, or about the width of a human hair. The particles and gas escape the surface at jet speed at approximately 800 miles per hour (400 meters per second). The eruptions appear to be continuous, refreshing the surface and generating an enormous halo of fine ice dust around Enceladus, which supplies material to one of Saturn’s rings, the E-ring.
Several gases, including water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, perhaps a little ammonia and either carbon monoxide or nitrogen gas make up the gaseous envelope of the plume.
Read more at: solarsystem.nasa.gov
Image credit: NASA/JPL/Cassini & Kevin Gill
![Andromeda [x]](https://64.media.tumblr.com/aa70ce40e59ba0f9da6e334afac731fe/tumblr_ox11noOQXn1tuy5mao1_500.jpg)
Andromeda [x]
js
How to Discover a Planet: A short step-by-step guide on how each of our planetary neighbors were originally discovered.

An irregular island
This image, courtesy of the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope’s Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), captures the glow of distant stars within NGC 5264, a dwarf galaxy located just over 15 million light-years away in the constellation of Hydra (The Sea Serpent).
Dwarf galaxies like NGC 5264 typically possess around a billion stars — just one per cent of the number of stars found within the Milky Way. They are usually found orbiting other, larger, galaxies such as our own, and are thought to form from the material left over from the messy formation of their larger cosmic relatives.
NGC 5264 clearly possesses an irregular shape — unlike the more common spiral or elliptical galaxies — with knots of blue star formation. Astronomers believe that this is due to the gravitational interactions between NGC 5264 and other galaxies nearby. These past flirtations sparked the formation of new generations of stars, which now glow in bright shades of blue.
https://www.spacetelescope.org/images/potw

Composed of gas and dust, the pictured pillar resides in a tempestuous stellar nursery called the Carina Nebula, located 7500 light-years away in the southern constellation of Carina.
Credit: NASA, ESA and the Hubble SM4 ERO Team
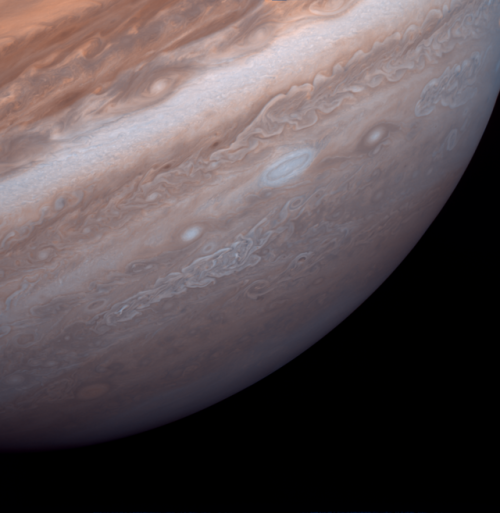
South pole of Jupiter photographed by Voyager 1 on March 1, 1979
Credit: NASA / Voyager 1


NGC 7635, also known as the bubble Nebula.
Chasing the Shadow of Neptune’s Moon Triton
Our Flying Observatory

Our flying observatory, called SOFIA, carries a 100-inch telescope inside a Boeing 747SP aircraft. Scientists onboard study the life cycle of stars, planets (including the atmosphere of Mars and Jupiter), nearby planetary systems, galaxies, black holes and complex molecules in space.
AND in just a few days SOFIA is going on a special flight to chase the shadow of Neptune’s moon Triton as it crosses Earth’s surface!
In case you’re wondering, SOFIA stands for: Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy.
Triton

Triton is 1,680 miles (2,700 km) across, making it the largest of the 13 moons orbiting Neptune. Unlike most large moons in our solar system, Triton orbits in the opposite direction of Neptune, called a retrograde orbit. This backward orbit leads scientists to believe that Triton formed in an area past Neptune, called the Kuiper Belt, and was pulled into its orbit around Neptune by gravity.
The Voyager 2 spacecraft flew past Neptune and Triton in 1989 and found that Triton’s atmosphere is made up of mostly nitrogen…but it has not been studied in nearly 16 years!
Occultations are Eclipse-Like Events

An occultation occurs when an object, like a planet or a moon, passes in front of a star and completely blocks the light from that star. As the object blocks the star’s light, it casts a faint shadow on Earth’s surface.
But unlike an eclipse, these shadows are not usually visible to the naked eye because the star and object are much smaller and not nearly as bright as our sun. Telescopes with special instruments can actually see these shadows and study the star’s light as it passes near and around the object – if they can be in the right place on Earth to catch the shadow.
Chasing Shadows

Scientists have been making advanced observations of Triton and a background star. They’ve calculated exactly where Triton’s faint shadow will fall on Earth! Our SOFIA team has designed a flight path that will put SOFIA (the telescope and aircraft) exactly in the center of the shadow at the precise moment that Triton and the star will align.
This is no easy feat because the shadow is moving at more than 53,000 mph while SOFIA flies at Mach 0.85 (652 mph), so we only have about two minutes to catch the shadow!! But our SOFIA team has previously harnessed the aircraft’s mobility to study Pluto from inside the center of its occultation shadow, and is ready to do it again to study Triton!
What We Learn From Inside the Shadow

From inside the shadow, our team on SOFIA will study the star’s light as it passes around and through Triton’s atmosphere. This allows us to learn more about Triton’s atmosphere, including its temperature, pressure, density and composition!
Our team will use this information to examine if Triton’s atmosphere has changed since our Voyager 2 spacecraft flew past it in 1989. That’s a lot of information from a bit of light inside a shadow! Similar observations of Uranus in 1977, from our previous flying observatory, led to the discovery of rings around that planet!
International Ground-Based Support

Ground-based telescopes across the United States and Europe – from Scotland to the Canary Islands – will also be studying Triton’s occultation. Even though most of these telescopes will not be in the center of the shadow, the simultaneous observations, from different locations on Earth, will give us information about how Triton’s atmosphere varies across its latitudes.
This data from across the Earth and from onboard SOFIA will help researchers understand how Triton’s atmosphere is distorted at different locations by its high winds and its strong tides!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

While stuck in traffic in 1961, James Powell, a young researcher at Brookhaven National Laboratory came up with the idea of using powerful magnets to lift and propel massive passenger-carrying cars. Over the next seven years, he and his colleague Gordon Danby spent their spare time piecing together a concept. They obtained a patent for the breakthrough in 1968. Powell and Danby’s magnetic levitation, or maglev, technology must have seemed like magic back then, but it is now being used to move large trains at speeds up to 375 miles per hour!
Not content to rest on this sole accomplishment, the 84-year-old Powell now has grander ambitions for his maglev breakthrough. In 2001, he teamed up with George Maise, an aeronautical engineer and 23-year veteran of Brookhaven National Laboratory, to put forth an idea to revolutionize space launches: StarTram.
Continue Reading.
-
 reminiscent-smile liked this · 8 months ago
reminiscent-smile liked this · 8 months ago -
 xxluna-team-galacticxx reblogged this · 11 months ago
xxluna-team-galacticxx reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 zurgy-space reblogged this · 11 months ago
zurgy-space reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 zurgy liked this · 11 months ago
zurgy liked this · 11 months ago -
 sssccrr liked this · 2 years ago
sssccrr liked this · 2 years ago -
 atomsmegablast liked this · 3 years ago
atomsmegablast liked this · 3 years ago -
 daughter-of-hades123 liked this · 4 years ago
daughter-of-hades123 liked this · 4 years ago -
 jimalim reblogged this · 4 years ago
jimalim reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 cynicallysweetposts liked this · 4 years ago
cynicallysweetposts liked this · 4 years ago -
 celamity reblogged this · 4 years ago
celamity reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 celamity liked this · 4 years ago
celamity liked this · 4 years ago -
 wolfsong-the-bloody-beast reblogged this · 4 years ago
wolfsong-the-bloody-beast reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 foolofmadness reblogged this · 4 years ago
foolofmadness reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 kenny-wind-yt reblogged this · 4 years ago
kenny-wind-yt reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 kenny-wind-yt liked this · 4 years ago
kenny-wind-yt liked this · 4 years ago -
 reasonpeason liked this · 4 years ago
reasonpeason liked this · 4 years ago -
 chungarll reblogged this · 4 years ago
chungarll reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 chungarll liked this · 4 years ago
chungarll liked this · 4 years ago -
 mothmansslut reblogged this · 4 years ago
mothmansslut reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 jack-first-ofher-name liked this · 4 years ago
jack-first-ofher-name liked this · 4 years ago -
 aloofloafcat19 liked this · 4 years ago
aloofloafcat19 liked this · 4 years ago -
 polypyrite liked this · 4 years ago
polypyrite liked this · 4 years ago -
 hypocriticalbonehead liked this · 4 years ago
hypocriticalbonehead liked this · 4 years ago -
 kapitaali liked this · 4 years ago
kapitaali liked this · 4 years ago -
 foolofmadness liked this · 4 years ago
foolofmadness liked this · 4 years ago -
 i-need-glitter reblogged this · 4 years ago
i-need-glitter reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 dozywrld reblogged this · 4 years ago
dozywrld reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 pitirres reblogged this · 4 years ago
pitirres reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 fortunebow reblogged this · 4 years ago
fortunebow reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 pumkpkin reblogged this · 4 years ago
pumkpkin reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 creator-indy liked this · 4 years ago
creator-indy liked this · 4 years ago -
 macieisnotreal reblogged this · 4 years ago
macieisnotreal reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 agrumina reblogged this · 4 years ago
agrumina reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 silverlindcn reblogged this · 4 years ago
silverlindcn reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 journeythroughtherain reblogged this · 4 years ago
journeythroughtherain reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 nxmy reblogged this · 4 years ago
nxmy reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 trinns liked this · 4 years ago
trinns liked this · 4 years ago -
 esoterismomagico liked this · 4 years ago
esoterismomagico liked this · 4 years ago
For more content, Click Here and experience this XYHor in its entirety!Space...the Final Frontier. Let's boldly go where few have gone before with XYHor: Space: Astronomy & Spacefaring: the collection of the latest finds and science behind exploring our solar system, how we'll get there and what we need to be prepared for!
128 posts