Curate, connect, and discover
Materials Science In Fiction - Blog Posts
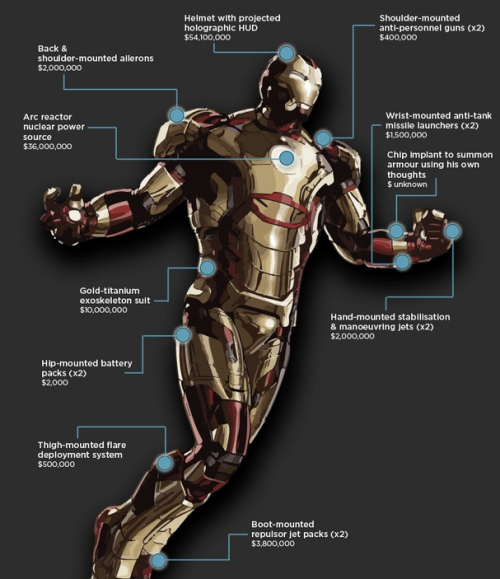
Dissecting Iron Man Suit - An Engineering Analysis
Structural, energy, and thermal analysis of Iron Man Suits specifically Mark I to Mark XLVI which have the following capabilities in common: external armor, supersonic flight, hovering, weaponry, and decoy flares.
1. STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS
Wear Resistant and Shock Absorbent Exoskeleton The physical protective value of exoskeleton is its ability to resist any penetrative loads as well as any shock loads. However, the whole thickness of exoskeleton panels should not be too hard because it will pass on the external impact load into the suit’s internal hardware, or even the human body inside it. All of this can be achieved by combining more than one materials; a hard material on the outside and the soft material on the inside
Hard Outer Layer for Penetrative Loads The materials needed for the exoskeleton’s outer layer should be hard and tactile. Titanium Alloy would be an ideal choice. Fiber glass has good tensile strength but not good shear strength, while titanium has both .Titanium Alloy is not only much stronger, but is also lighter than steel, which will provide more fluidity of movement compared to any heavy material counterparts.
Ductile Inner Layer for Shock Loads There should be a soft inner linings behind titanium panels to serve as shock absorbent. Sorbothane is a material that is extremely soft and has the ability to convert shock loads into heat transfer at a molecular level. It is a proprietary, visco-elastic polymer. Visco-elastic means that a material exhibits properties of both liquids (viscous solutions) and solids (elastic materials).
Sorbothane is a thermoset, polyether-based, polyurethane material. Sorbothane combines shock absorption, good memory, vibration isolation and vibration damping characteristics. In addition, Sorbothane is a very effective acoustic damper and absorber. Even if one drops an egg from the top of a building into a bed of sorbothane, this remarkable material is soft enough to cushion the impact and would not allow the egg to break.
This technique of having a hard material on the outside and the soft material on the inside is not new. It has been used for centuries in Japan for making samurai swords. The hardness of its outer layer give the swords its cutting edge and penetrative power, and its ductility allows it to absorb shock loads when it strikes or struck.
2. ENERGY ANALYSIS : Hovering Capability
Hovering using thrusters (aka repulsors) requires tremendous amount of energy, particularly when the suit is used for a long duration. Energy usage for hovering is dependent upon the hovering methods
Magnetic Levitation requires no energy at all, but is limited to the presence of magnetic field.
Ducted and Open Propellers (helicopter blades). Several human powered helicopters have been made overtime that have achieved flight. It has been experimentally recorded that a 78 kg person in a 58 kg copter requires only 1.1 kW to climb using helicopter blades, and only 60 Watts to maintain altitude.
Jet Thrust is the least energy-efficient method. Because thrust-to-weight ratio needs to be greater than 1 to achieve lift-off, a Jet-pack requires over 1KN of thrust force, depending on the weight of the jet and the person. If wings are attached to the jet-pack, horizontal flight can be achieved with thrust to weight ratio lower than 1, thus improving the duration of the flight and its range.There have been jet-packs made in the past, most iconic display of it was in 1994 Olympics opening ceremony. The fuel used in the jet-pack was mostly hydrogen peroxide. It provides thrust at low temperature compared to other fuels. However, it has low energy density of 810 Wh/kg, giving the jet-packs up to only 30 seconds of flight-time. Jet’s flight time is limited even by using energy-rich fossil fuel. Yves Rossy (aka Jet Man) has successfully used kerosene oil in his flight, but the thruster jets have to be pushed away from the body for safety. His suit allows only several minutes of flight. In addition, if a heavier suit (greater than 25 kg) is used, hydraulics are needed, which would require additional energy and slow down mobility. The Iron Monger suit was an example of hydraulic-driven mobility suit.
3. POWER SOURCE
Tony Stark manages the suit’s energy requirements, including thermal management and artificial intelligence system, through the fictional arc reactor. The reactor is able to provides almost limitless clean energy despite being a very small device. In real life, the only thing that has an energy density comparable to the arc reactor, and would meet all the energy requirements of the suit would be nuclear power. Uranium (fission) energy density is 80.620.000 MJ/kg. However, nuclear power is not suitable to be harnessed in a manned suit, since it generates a tremendous amount of heat.
A more practical solution would be a battery energy-storage. If lithium batteries are used on propeller blades, minutes-long flight time can be achieved. Furthermore, these batteries can readily power suit’s electrical devices / electronics requirements. Lithium ion battery has energy density of 150 Wh/kg (0.5 MJ/kg). Fossil fuel, on the other hand, have a much higher energy density than batteries, but would require a clunky generator to power the suit’s electrical requirements.
Lithium sulfur batteries have 5 times more energy density compared to lithium ion batteries. Lithium sulfur packs had already powered the longest unmanned flight for more than 30 hours. Unless we discover something like an arc-reactor, lithium sulfur batteries could be just the thing to power up the suit. The downside is, it requires hours of charging for just minutes of usage.
There is an alternative option, though not a ‘reactor’ proper. A compact and high-output generator (standard car alternators crank out 50-70 amps at 12 volts for years, and some can go as high as 150 amps) could be spun by a small and strong output electric motor (all alternators have to do is spin). That motor can be powered by a high density battery like used for electric bikes in the 1500w to 2500w range at 20 something volts. This would power a strong and small motor at 3500 to 4000 rpm for hours. That’s more than enough to create power for a number of systems, if they’re built to take advantage of the amperage. And with new constructions of carbon arrays coming out every day, one or more of those could bring a meaningful electric output increase in an otherwise standard generator, even above what we have in cars now.
4. THERMAL MANAGEMENT
The suit cannot be hermetically sealed. Human body heat evaporates water from the skin. Therefore, air ventilation is a must to remove them. It is also needed to maintain a good supply of oxygen. So, there must be a structure inside the exoskeleton that allows air flow. This would prevent any internal condensation to settle and will also remove buildup of body heat. The layer of sorbothene would act both as a thermal and an electrical insulator. This means that extreme external temperature would not be transferred to the inner layer. The suit would not get too hot or too cold from the outer environment. There should be small fans to draw and pull air from the ambient in controlled amount, and should be able to exchange hot air. With the technology available today, the thermal management of the suit is easily manageable. There are also solid state devices such as thermal pads and thermoelectric generators. Thermoelectric generators can surfaces hot or cold depending on the polarity of the electric current and thus can be an integral component of the suit for controlling the internal temperature.
Source (x)
Keep reading