Solar System: Things To Know This Week
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Earlier this month, Mars was at opposition, which is the point in their orbits when Mars, Earth and the sun all line up, making for good conditions to view the Red Planet from Earth.
Now, it’s Saturn’s turn. The ringed planet will be at opposition on June 3, and this week is a great time to see it — both in the sky as well as up close, thanks to our spacecraft. Here are a few things to know about Saturn exploration this week:
1. Group Portrait

Thanks to their current orbital positions, our sun-observing spacecraft STEREO-A was recently able to capture the sun, Saturn, Mars and Earth in one image. Take a closer look HERE. Discover more about the STEREO mission HERE.
2. Likable, Lick-able Saturn

Saturn’s handsome visage is featured among the new stamps that the US Postal Service is releasing this week to highlight our adventures in planetary exploration.
3. Do You Even Know Saturn?

Yes, yes, it’s the one with the rings. But did you know Saturn has winds that can exceed 1000 miles per hour? Or that its magnetic field is hundreds of times as powerful as the Earth’s? Or that its day is just 10 hours long? How well do you really know the sixth planet?
4. Picking Up Signals

One thing you many not know about the planet is that it’s loud, at least if you listen to its radio signals. When our robotic Cassini spacecraft first approached Saturn, it detected the powerful fields that surround it. Engineers turned those signals into beautiful, eerie sounds. Listen to them HERE.
5. Not All Who Wander Are Lost

The Cassini mission’s explorations of the Saturn system are very much ongoing. In the next few days, the spacecraft will be touring many locations, including the giant moon Titan, Saturn’s turbulent clouds, the tiny moon Albiorix and more! Get the full itinerary HERE.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Learn more about our Deep Space Network, where to watch the Ursid meteor shower, Cassini’s ring-grazing at Saturn and more.

1. A Deep Space Anniversary
On Dec. 24, 1963, the Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Deep Space Information Facility was renamed the Deep Space Network. And, it’s been humanity's ear to the skies ever since.
+ History of the Deep Space Network
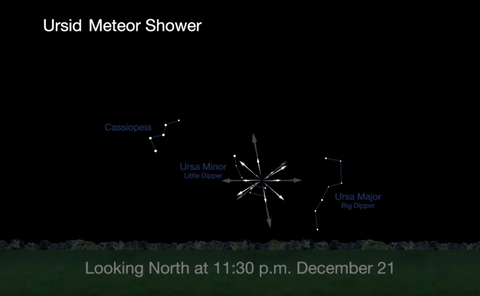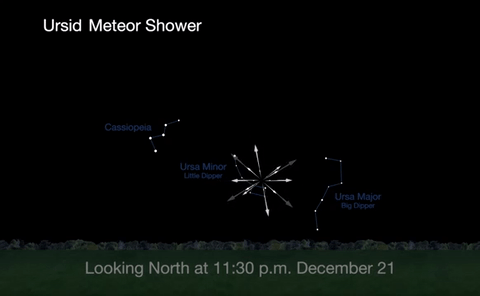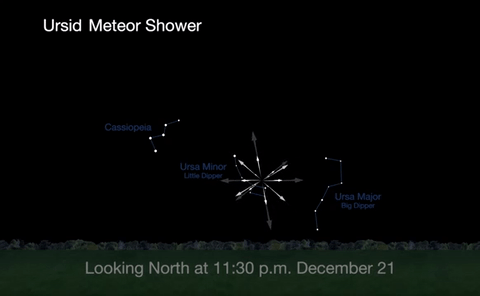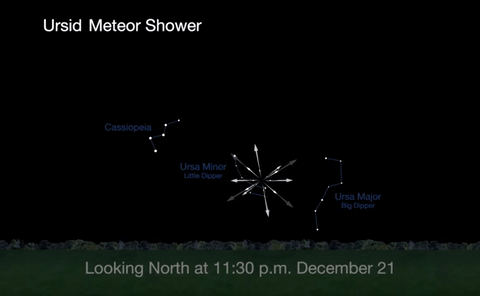
2. Ursid Meteor Shower
The best time to view the Ursids, radiating from Ursa Minor, or the little Dipper, will be from midnight on December 21 until about 1a.m. on December 22, before the moon rises.

3. At Saturn, the Ring-Grazing Continues
Our Cassini spacecraft has completed several orbits that take it just outside Saturn’s famous rings. The first ring-grazing orbit began on November 30. The spacecraft will repeat this feat 20 times, with only about a week between each ring-plane crossing.
+ Learn more

4. Preparing for the 2017 Total Solar Eclipse
Next year North America will see one of the most rare and spectacular of all sky events. Learn how to prepare.
+ 2017 Solar Eclipse Toolkit

5. Searching for Rare Asteroids
Our first mission to return an asteroid sample to Earth will be multitasking during its two-year outbound cruise to the asteroid Bennu. On February 9-20, OSIRIS-REx (Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, and Security-Regolith Explorer) will activate its onboard camera suite and begin its search for elusive “Trojan,” asteroids, constant companions to planets in our solar system as they orbit the sun, remaining near a stable point 60 degrees in front of or behind the planet. Because they constantly lead or follow in the same orbit, they will never collide with their companion planet.
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week

It’s the time of year for summer break, swimming, and oh, yes storms. June 1 marks the beginning of hurricane season on the Atlantic coast, but we’re not alone. Our neighboring planets have seen their fair share of volatile weather, too (like the Cassini spacecraft’s view of the unique six-sided jet stream at Saturn’s north pole known as “the hexagon”).
This week, we present 10 of the solar system’s greatest storms.

1. Jupiter’s Great Red Spot
With tumultuous winds peaking at 400 mph, the Great Red Spot has been swirling wildly over Jupiter’s skies for at least 150 years and possibly much longer. People saw a big spot on Jupiter as early as the 1600s when they started stargazing through telescopes, though it’s unclear whether they were looking at a different storm. Today, scientists know the Great Red Spot has been there for a while, but what causes its swirl of reddish hues remains to be discovered. More >

2. Jupiter’s Little Red Spot
Despite its unofficial name, the Little Red Spot is about as wide as Earth. The storm reached its current size when three smaller spots collided and merged in the year 2000. More >

3. Saturn’s Hexagon
The planet’s rings might get most of the glory, but another shape’s been competing for attention: the hexagon. This jet stream is home to a massive hurricane tightly centered on the north pole, with an eye about 50 times larger than the average hurricane eye on Earth. Numerous small vortices spin clockwise while the hexagon and hurricane spin counterclockwise. The biggest of these vortices, seen near the lower right corner of the hexagon and appearing whitish, spans about 2,200 miles, approximately twice the size of the largest hurricane on Earth. More>
4. Monster Storm on Saturn
A tempest erupted in 2010, extending approximately 9,000 miles north-south large enough to eventually eat its own tail before petering out. The storm raged for 200 days, making it the longest-lasting, planet-encircling storm ever seen on Saturn. More >

5. Mars’ Dust Storm
Better cover your eyes. Dust storms are a frequent guest on the Red Planet, but one dust storm in 2001 larger by far than any seen on Earth raised a cloud of dust that engulfed the entire planet for three months. As the Sun warmed the airborne dust, the upper atmospheric temperature rose by about 80 degrees Fahrenheit. More >

6. Neptune’s Great Dark Spot
Several large, dark spots on Neptune are similar to Jupiter’s hurricane-like storms. The largest spot, named the “Great Dark Spot” by its discoverers, contains a storm big enough for Earth to fit neatly inside. And, it looks to be an anticyclone similar to Jupiter’s Great Red Spot. More >

7. Sun Twister
Not to be confused with Earth’s tornadoes, a stalk-like prominence rose up above the Sun, then split into about four strands that twisted themselves into a knot and dispersed over a two-hour period. This close-up shows the effect is one of airy gracefulness. More >

8. Titan’s Arrow-shaped Storm
The storm blew across the equatorial region of Titan, creating large effects in the form of dark and likely “wet” from liquid hydrocarbons areas on the surface of the moon. The part of the storm visible here measures 750 miles in length east-to-west. The wings of the storm that trail off to the northwest and southwest from the easternmost point of the storm are each 930 miles long. More >

9. Geomagnetic Storms
On March 9, 1989, a huge cloud of solar material exploded from the sun, twisting toward Earth. When this cloud of magnetized solar material called a coronal mass ejection reached our planet, it set off a chain of events in near-Earth space that ultimately knocked out an entire power grid area to the Canadian province Quebec for nine hours. More >
10. Super Typhoon Tip
Back on Earth, Typhoon Tip of 1979 remains the biggest storm to ever hit our planet, making landfall in Japan. The tropical cyclone saw sustained winds peak at 190 mph and the diameter of circulation spanned approximately 1,380 miles. Fortunately, we now have plans to better predict future storms on Earth. NASA recently launched a new fleet of hurricane-tracking satellites, known as the Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS), which will use the same GPS technology you and I use in our cars to measure wind speed and ultimately improve how to track and forecast hurricanes. More >
Discover more lists of 10 things to know about our solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What was your reaction to getting selected for the Air Force Fellows program?
NASA’s Fleet of Planet-hunters and World-explorers
Around every star there could be at least one planet, so we’re bound to find one that is rocky, like Earth, and possibly suitable for life. While we’re not quite to the point where we can zoom up and take clear snapshots of the thousands of distant worlds we’ve found outside our solar system, there are ways we can figure out what exoplanets light years away are made of, and if they have signs of basic building blocks for life. Here are a few current and upcoming missions helping us explore new worlds:
Kepler

Launched in 2009, the Kepler space telescope searched for planets by looking for telltale dips in a star’s brightness caused by crossing, or transiting, planets. It has confirmed more than 1,000 planets; of these, fewer than 20 are Earth-size (therefore possibly rocky) and in the habitable zone -- the area around a star where liquid water could pool on the surface of an orbiting planet. Astronomers using Kepler data found the first Earth-sized planet orbiting in the habitable zone of its star and one in the habitable zone of a sun-like star.
In May 2013, a second pointing wheel on the spacecraft broke, making it not stable enough to continue its original mission. But clever engineers and scientists got to work, and in May 2014, Kepler took on a new job as the K2 mission. K2 continues the search for other worlds but has introduced new opportunities to observe star clusters, young and old stars, active galaxies and supernovae.
Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS)

Revving up for launch around 2017-2018, NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) will find new planets the same way Kepler does, but right in the stellar backyard of our solar system while covering 400 times the sky area. It plans to monitor 200,000 bright, nearby stars for planets, with a focus on finding Earth and Super-Earth-sized planets.
Once we’ve narrowed down the best targets for follow-up, astronomers can figure out what these planets are made of, and what’s in the atmosphere. One of the ways to look into the atmosphere is through spectroscopy.
As a planet passes between us and its star, a small amount of starlight is absorbed by the gas in the planet’s atmosphere. This leaves telltale chemical “fingerprints” in the star’s light that astronomers can use to discover the chemical composition of the atmosphere, such as methane, carbon dioxide, or water vapor.
James Webb Space Telescope

Launching in 2018, NASA’s most powerful telescope to date, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), will not only be able to search for planets orbiting distant stars, its near-infrared multi-object spectrograph will split infrared light into its different colors- spectrum- providing scientists with information about an physical properties about an exoplanet’s atmosphere, including temperature, mass, and chemical composition.
Hubble Space Telescope

Hubble Space Telescope is better than ever after 25 years of science, and has found evidence for atmospheres bleeding off exoplanets very close to their stars, and even provided thermal maps of exoplanet atmospheres. Hubble holds the record for finding the farthest exoplanets discovered to date, located 26,000 light-years away in the hub of our Milky Way galaxy.
Chandra X-ray Observatory

Chandra X-ray Observatory can detect exoplanets passing in front of their parent stars. X-ray observations can also help give clues on an exoplanet’s atmosphere and magnetic fields. It has observed an exoplanet that made its star act much older than it actually is.
Spitzer Space Telescope

Spitzer Space Telescope has been unveiling hidden cosmic objects with its dust-piercing infrared vision for more than 12 years. It helped pioneer the study of atmospheres and weather on large, gaseous exoplanets. Spitzer can help narrow down the sizes of exoplanets, and recently confirmed the closest known rocky planet to Earth.
SOFIA

The Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) is an airplane mounted with an infrared telescope that can fly above more than 99 percent of Earth's atmospheric water vapor. Unlike most space observatories, SOFIA can be routinely upgraded and repaired. It can look at planetary-forming systems and has recently observed its first exoplanet transit.
What’s Coming Next?
Analyzing the chemical makeup of Earth-sized, rocky planets with thin atmospheres is a big challenge, since smaller planets are incredibly faint compared to their stars. One solution is to block the light of the planets' glaring stars so that we can directly see the reflected light of the planets. Telescope instruments called coronagraphs use masks to block the starlight while letting the planet's light pass through. Another possible tool is a large, flower-shaped structure known as the starshade. This structure would fly in tandem with a space telescope to block the light of a star before it enters the telescope.
All images (except SOFIA) are artist illustrations.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Ever want to ask a real life astronaut a question? Here’s your chance!
Astronauts Drew Feustel & Ricky Arnold will be taking your questions in a Video Answer Time session. We’ll collect your questions and send them to space to be answered by the astronauts on Friday, May 18. We’ll record their answers and post them on Wednesday, May 23 here on NASA’s Tumblr. Make sure to ask your question now by visiting http://nasa.tumblr.com/ask!
Andrew J. Feustel was selected by NASA in 2000. He has been assigned to Expedition 55/56, which launched in March 2018. The Lake Orion, Michigan native has a Ph.D. in the Geological Sciences, specializing in Seismology, and is a veteran of two spaceflights. Follow Feustel on Twitter and Instagram.
Richard R. Arnold II was selected as an astronaut by NASA in May 2004. The Maryland native worked in the marine sciences and as a teacher in his home state, as well as in countries such as Morocco, Saudi Arabia, and Indonesia. Follow Arnold on Twitter and Instagram.
And don’t forget to submit your questions by 5 p.m. EDT on Tuesday, May 15 at http://nasa.tumblr.com/ask!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Hello. I'm curious what new feature the james webb brings to the table, like its ability to detect in infrared, that you are most excited about? What are you most interested to look into with this new telescope?
You’ve Heard “Houston, we’ve had a problem,” But Do You Know The Mission It’s From?
It’s the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 13 mission! NASA’s “successful failure,”Apollo 13 was to be the third lunar landing attempt, but the mission was aborted mid-flight after the rupture of a service module oxygen tank. The crew never landed on the moon, but due to the dedication and ingenuity of Mission Control, made it back to Earth safely. We’ve put some of the most important numbers of the Apollo 13 mission in perspective. Check it out!









Listen to the mission in real time, HERE.
Follow NASA History on Twitter and Facebook for more interesting information about aerospace history!
Check out the stats of all the Apollo Missions in the free e-book Apollo by the Numbers, HERE.
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Our Psyche mission to a metal world, which will explore a giant metal asteroid known as 16 Psyche, is getting a new, earlier launch date. Psyche is now expected to launch from the Kennedy Space Center in 2022, cruise through the solar system for 4.6 years, and arrive at the Psyche asteroid in 2026, four years earlier than planned.
Below are 10 things to know about this mission to a completely new and unexplored type of world.
1. Psyche, Squared

Psyche is the name of the NASA space mission and the name of the unique metal asteroid orbiting the sun between Mars and Jupiter. The asteroid was discovered in 1852 by Italian astronomer Annibale de Gasparis and named after the Greek mythological figure Psyche, whom Cupid fell in love with. "Psyche" in Greek also means "soul."
2. Mission: Accepted

The Psyche Mission was selected for flight earlier this year under NASA's Discovery Program. And it will take a village to pull off: The spacecraft is being built by Space Systems Loral in Palo Alto, California; the mission is led by Arizona State University; and NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory will be responsible for mission management, operations and navigation.
3. An Unusual Asteroid

For the very first time, this mission will let us examine a world made not of rock and ice, but metal. Scientists think Psyche is comprised mostly of metallic iron and nickel, similar to Earth's core - which means Psyche could be an exposed core of an early planet as large as Mars.
4. Sweet 16

Psyche the asteroid is officially known as 16 Psyche, since it was the 16th asteroid to be discovered. It lies within the asteroid belt, is irregularly shaped, about the size of Massachusetts, and is about three times farther away from the sun than Earth.
5. Discoveries Abound

The Psyche mission will observe the asteroid for 20 months. Scientists hope to discover whether Psyche is the core of an early planet, how old it is, whether it formed in similar ways to Earth's core, and what its surface is like. The mission will also help scientists understand how planets and other bodies separated into their layers including cores, mantles and crusts early in their histories. "Psyche is the only known object of its kind in the solar system and this is the only way humans will ever visit a core," said Principal Investigator Lindy Elkins-Tanton of Arizona State University.
6. Think Fast

The mission launch and arrival were moved up because Psyche's mission design team were able to plot a more efficient trajectory that no longer calls for an Earth gravity assist, ultimately shortening the cruise time. The new trajectory also stays farther from the sun, reducing the amount of heat protection needed for the spacecraft, and will still include a Mars flyby in 2023.
7. Gadgets Galore
The Psyche spacecraft will be decked out with a multispectral imager, gamma ray and neutron spectrometer, magnetometer, and X-band gravity science investigation. More: https://sese.asu.edu/research/psyche
8. Stunning Solar Panels

In order to support the new mission trajectory, the solar array system was redesigned from a four-panel array in a straight row on either side of the spacecraft to a more powerful five-panel x-shaped design, commonly used for missions requiring more capability. Much like a sports car, combining a relatively small spacecraft body with a very high-power solar array design means the Psyche spacecraft will be able to speed to its destination much faster. Check out this artist's-concept illustration here: https://www.nasa.gov/image-feature/artists-concept-of-psyche-spacecraft-with-five-panel-array
9. See For Yourself
Watch the planned Psyche mission in action.
10. Even More Asteroids

Our missions to asteroids began with the orbiter NEAR of asteroid Eros, which arrived in 2000, and continues with Dawn, which orbited Vesta and is now in an extended mission at Ceres. The mission OSIRIS-REx, which launched on Sept. 8, 2016, is speeding toward a 2018 rendezvous with the asteroid Bennu, and will deliver a sample back to Earth in 2023. The Lucy mission is scheduled to launch in October 2021 and will explore six Jupiter Trojan asteroids. More: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=6713
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Stop. Drop. And Apply to #BeAnAstronaut!

Feel like your place is in the stars? Are you an adventure seeker, an explorer, a person passionate about science and space? We need you!!

Applications are OPEN for our newest class of #Artemis astronauts. Once chosen, you could be the next person to step foot on the Moon and eventually embark on missions to Mars!

Do you have a friend who should apply? Tag them. Do you know someone who's still in school? Encourage them to follow their dreams and aim high.

To give you a sneak peak of what life will be like if you decide to #BeAnAstronaut, we’re taking you behind-the-scenes of astronaut life over the course of March.

APPLY NOW AND GET MORE INFORMATION HERE!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
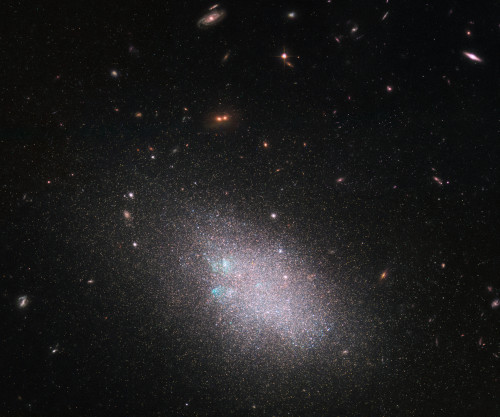

Look! A cosmic block party 🥳 In this Hubble image, you’ll find 50 spiral and dwarf galaxies hanging out in our cosmic neighborhood. The main focal point of stars is actually a dwarf galaxy. Dwarf galaxies often show a hazy structure, an ill-defined shape and an appearance somewhat akin to a swarm or cloud of stars — and UGC 685 is no exception to this. These data were gathered under Hubble’s Legacy ExtraGalactic UV Survey (LEGUS) program, the sharpest and most comprehensive ultraviolet survey of star-forming galaxies in the nearby universe. Image Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA; the LEGUS team, B. Tully, D. Calzetti
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 laurie-hoot599842-blog liked this · 2 years ago
laurie-hoot599842-blog liked this · 2 years ago -
 thegentlemansnarker liked this · 7 years ago
thegentlemansnarker liked this · 7 years ago -
 sergio338 liked this · 7 years ago
sergio338 liked this · 7 years ago -
 luntian-berdengguhit liked this · 7 years ago
luntian-berdengguhit liked this · 7 years ago -
 usafphantom2 reblogged this · 7 years ago
usafphantom2 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 peachican liked this · 7 years ago
peachican liked this · 7 years ago -
 081098 reblogged this · 8 years ago
081098 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 gothvergilstan liked this · 8 years ago
gothvergilstan liked this · 8 years ago -
 oniwoolf-blog liked this · 8 years ago
oniwoolf-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 suki-tora liked this · 8 years ago
suki-tora liked this · 8 years ago -
 thefloatingbitch liked this · 8 years ago
thefloatingbitch liked this · 8 years ago -
 yozoshimada liked this · 8 years ago
yozoshimada liked this · 8 years ago -
 psilocybin-dreams reblogged this · 8 years ago
psilocybin-dreams reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 8 years ago
fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 edge-of-the-sword reblogged this · 8 years ago
edge-of-the-sword reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 gamingonethings liked this · 8 years ago
gamingonethings liked this · 8 years ago -
 frozen-heart-in-a-summer-da-blog liked this · 8 years ago
frozen-heart-in-a-summer-da-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 frozen-heart-in-a-summer-da-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
frozen-heart-in-a-summer-da-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 modernrenaissancewoman-blog1 liked this · 8 years ago
modernrenaissancewoman-blog1 liked this · 8 years ago -
 lululuvs-blog1 liked this · 8 years ago
lululuvs-blog1 liked this · 8 years ago -
 mizzsweet1 reblogged this · 8 years ago
mizzsweet1 reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 miomckittykatofthegreatdinosaur liked this · 8 years ago
miomckittykatofthegreatdinosaur liked this · 8 years ago -
 chickencat8 liked this · 8 years ago
chickencat8 liked this · 8 years ago -
 quitebizarre liked this · 8 years ago
quitebizarre liked this · 8 years ago -
 poetcc-things liked this · 8 years ago
poetcc-things liked this · 8 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts