🌊🌊🌊 This Natural-color Image Captured May 17 Near The Coast Of Guinea-Bissau In West Africa

🌊🌊🌊 This natural-color image captured May 17 near the coast of Guinea-Bissau in West Africa shows estuaries branching out like a network of roots from a plant. Crossfading to a data visualization helps reveals water clarity due to dissolved organic matter in Guinea-Bissau.
With their long tendrils, the rivers meander through the country’s lowland plains to join the Atlantic Ocean. On the way, they carry water, nutrients, but also sediments out from the land. These estuaries play an important role in agriculture for this small country that is mostly made up of flat terrain. While the coastal valleys can flood often during the rainiest part of the year in the summer, the rain makes the valleys good locations for farming, especially rice cultivation. Using satellite data, researchers continue to observe the country's change in terrain and as a result, they're documenting a regrowth of previously eroded coastal areas.
Learn more
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Going the Distance... In Space
On April 17, NASA's New Horizons crossed a rare deep-space milestone – 50 astronomical units from the Sun, or 50 times farther from the Sun than Earth is. New Horizons is just the fifth spacecraft to reach this great distance, following the legendary Voyagers 1 and 2 and Pioneers 10 and 11. It’s almost 5 billion miles (7.5 billion kilometers) away; a remote region where a signal radioed from NASA's largest antennas on Earth, even traveling at the speed of light, needs seven hours to reach the far-flung spacecraft.
To celebrate reaching 50 AU, the New Horizons team compiled a list of 50 facts about the mission. Here are just a few of them; you'll find the full collection at: http://pluto.jhuapl.edu/News-Center/Fifty-Facts.php.

New Horizons is the first – and so far, only – spacecraft to visit Pluto. New Horizons sped through the Pluto system on July 14, 2015, providing a history-making close-up view of the dwarf planet and its family of five moons.
New Horizons is carrying some of the ashes of Pluto’s discoverer, Clyde Tombaugh. In 1930, the amateur astronomer spotted Pluto in a series of telescope images at Lowell Observatory in Arizona, making him the first American to discover a planet.

The “Pluto Not Yet Explored” U.S. stamp that New Horizons carries holds the Guinness World Record for the farthest traveled postage stamp. The stamp was part of a series created in 1991, when Pluto was the last unexplored planet in the solar system.

Dispatched at 36,400 miles per hour (58, 500 kilometers per hour) on January 19, 2006, New Horizons is still the fastest human-made object ever launched from Earth.
As the spacecraft flew by Jupiter’s moon Io, in February 2007, New Horizons captured the first detailed movie of a volcano erupting anywhere in the solar system except Earth.

New Horizons’ radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) – its nuclear battery – will provide enough power to keep the spacecraft operating until the late-2030s.

Measurements of the universe’s darkness using New Horizons data found that the universe is twice as bright as predicted – a major extragalactic astronomy discovery!

New Horizons’ Venetia Burney Student Dust Counter is the first student-built instrument on any NASA planetary mission – and is providing unprecedented insight into the dust environment in the outer solar system.

New Horizons is so far away, that even the positons of the stars look different than what we see from Earth. This view of an "alien sky" allowed scientists to make stereo images of the nearest stars against the background of the galaxy.

Arrokoth – the official name the mission team proposed for the Kuiper Belt object New Horizons explored in January 2019 – is a Native American term that means “sky” in the Powhatan/Algonquin language.

Stay tuned in to the latest New Horizons updates on the mission website and follow NASA Solar System on Twitter and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Planes, Trains and Barges: How We’re Moving Our Artemis 1 Rocket to the Launchpad
Our Space Launch System rocket is on the move this summer — literally. With the help of big and small businesses in all 50 states, various pieces of hardware are making their way to Louisiana for manufacturing, to Alabama for testing, and to Florida for final assembly. All of that work brings us closer to the launch of Artemis 1, SLS and Orion’s first mission to the Moon.

By land and by sea and everywhere in between, here’s why our powerful SLS rocket is truly America’s rocket:
Rollin’ on the River

The SLS rocket will feature the largest core stage we have ever built before. It’s so large, in fact, that we had to modify and refurbish our barge Pegasus to accommodate the massive load. Pegasus was originally designed to transport the giant external tanks of the space shuttles on the 900-mile journey from our rocket factory, Michoud Assembly Facility, in New Orleans to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Now, our barge ferries test articles from Michoud along the river to Huntsville, Alabama, for testing at Marshall Space Flight Center. Just a week ago, the last of four structural test articles — the liquid oxygen tank — was loaded onto Pegasus to be delivered at Marshall for testing. Once testing is completed and the flight hardware is cleared for launch, Pegasus will again go to work — this time transporting the flight hardware along the Gulf Coast from New Orleans to Cape Canaveral.
Chuggin’ along

The massive, five-segment solid rocket boosters each weigh 1.6 million pounds. That’s the size of four blue whales! The only way to move the components for the powerful boosters on SLS from Promontory, Utah, to the Booster Fabrication Facility and Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy is by railway. That’s why you’ll find railway tracks leading from these assembly buildings and facilities to and from the launch pad, too. Altogether, we have about 38-mile industrial short track on Kennedy alone. Using a small fleet of specialized cars and hoppers and existing railways across the US, we can move the large, bulky equipment from the Southwest to Florida’s Space Coast. With all the motor segments complete in January, the last booster motor segment (pictured above) was moved to storage in Utah. Soon, trains will deliver all 10 segments to Kennedy to be stacked with the booster forward and aft skirts and prepared for flight.
It’s a bird, it’s a plane, no, it’s super Guppy!

A regular passenger airplane doesn’t have the capacity to carry the specialized hardware for SLS and our Orion spacecraft. Equipped with a unique hinged nose that can open more than 200 degrees, our Super Guppy airplane is specially designed to carry the hulking hardware, like the Orion stage adapter, to the Cape. That hinged nose means cargo is actually loaded from the front, not the back, of the airplane. The Orion stage adapter, delivered to Kennedy in 2018, joins to the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage, which will give our spacecraft the push it needs to go to the Moon on Artemis 1. It fit perfectly inside the Guppy’s cargo compartment, which is 25 feet tall and 25 feet wide and 111 feet long.
All roads lead to Kennedy

In the end, all roads lead to Kennedy, and the star of the transportation show is really the “crawler.” Rolling along at a delicate 1 MPH when it’s loaded with the mobile launcher, our two crawler-transporters are vital in bringing the fully assembled rocket to the launchpad for each Artemis mission. Each the size of a baseball field and powered by locomotive and large power generator engines, one crawler-transporter is able to carry 18 million pounds on the nine-mile journey to the launchpad. As of June 27, 2019, the mobile launcher atop crawler-transporter 2 made a successful final test roll to the launchpad, clearing the transporter and mobile launcher ready to carry SLS and Orion to the launchpad for Artemis 1.
Dream Team

It takes a lot of team work to launch Artemis 1. We are partnering with Boeing, Northrop Grumman and Aerojet Rocketdyne to produce the complex structures of the rocket. Every one of our centers and more than 1,200 companies across the United States support the development of the rocket that will launch Artemis 1 to the Moon and, ultimately, to Mars. From supplying key tools to accelerate the development of the core stage to aiding the transportation of the rocket closer to the launchpad, companies like Futuramic in Michigan and Major Tool & Machine in Indiana, are playing a vital role in returning American astronauts to the Moon. This time, to stay. To stay up to date with the latest SLS progress, click here.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Small Tissue Chips in Space a Big Leap Forward for Research
Tissue chips, thumb-drive sized devices that contain human cells in a 3D matrix, represent a giant leap in science.
They can test cells’ response to:
•stresses
•drugs
•genetic changes

The Tissue Chips in Space initiative seeks to better understand the role of microgravity on human health and disease and to translate that understanding to improved human health on Earth.
This series of investigations to test tissue chips in microgravity aboard the International Space Station is planned through a collaboration between the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) at the National Institutes for Health (NIH) and the National Laboratory in partnership with NASA.

Many of the changes in the human body caused by microgravity resemble the onset and progression of diseases associated with aging on Earth, but in space, changes occur much faster. Scientists may be able to use tissue chips in space to model changes that take months or years to happen on Earth.
A tissue chip needs three properties, according to Lucie Low, scientific program manager at NCATS. “It has to be 3D,” she explained. “It must have multiple different types of cells, and it must have microfluidic channels. Essentially, you get a functional unit of what human tissues are like, outside of the body,” said Low.

As accurate models of the structure and function of human organs, tissue chips provide a model for predicting whether a drug, vaccine or biologic agent is safe in humans more quickly and effectively than current methods.

This first phase of Tissue Chips in Space includes five investigations. An investigation of immune system aging is planned for launch on the SpaceX CRS-16 flight, scheduled for mid-November. The other four, scheduled to launch on subsequent flights, include lung host defense, the blood-brain barrier, musculoskeletal disease and kidney function. This phase tests the effects of microgravity on the tissue chips and demonstrates the capability of the automated system.
All five investigations make a second flight about 18 months later to confirm use of the model, such as testing potential drugs on the particular organs. Four more projects are scheduled for launch in summer 2020, including two on engineered heart tissue to understand cardiovascular health, one on muscle wasting and another on gut inflammation.
Ultimately, the technology could allow astronauts going into space to take along personalized chips that could be used to monitor changes in their bodies and to test possible countermeasures and therapies. That would be a major leap forward in keeping astronauts healthy on missions to deep space!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Anonymous asked:
What is the best about being mission control?
25 Years of Exploring the Universe with NASA's Chandra Xray Observatory

Illustration of the Chandra telescope in orbit around Earth. Credit: NASA/CXC & J. Vaughan
On July 23, 1999, the space shuttle Columbia launched into orbit carrying NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory. August 26 marked 25 years since Chandra released its first images.
These were the first of more than 25,000 observations Chandra has taken. This year, as NASA celebrates the 25th anniversary of this telescope and the incredible data it has provided, we’re taking a peek at some of its most memorable moments.
About the Spacecraft
The Chandra telescope system uses four specialized mirrors to observe X-ray emissions across the universe. X-rays that strike a “regular” mirror head on will be absorbed, so Chandra’s mirrors are shaped like barrels and precisely constructed. The rest of the spacecraft system provides the support structure and environment necessary for the telescope and the science instruments to work as an observatory. To provide motion to the observatory, Chandra has two different sets of thrusters. To control the temperatures of critical components, Chandra's thermal control system consists of a cooling radiator, insulators, heaters, and thermostats. Chandra's electrical power comes from its solar arrays.
Learn more about the spacecraft's components that were developed and tested at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Fun fact: If the state of Colorado were as smooth as the surface of the Chandra X-ray Observatory mirrors, Pike's Peak would be less than an inch tall.

Engineers in the X-ray Calibration Facility at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, integrating the Chandra X-ray Observatory’s High-Resolution Camera with the mirror assembly, in this photo taken March 16, 1997. Credit: NASA
Launch
When space shuttle Columbia launched on July 23, 1999, Chandra was the heaviest and largest payload ever launched by the shuttle. Under the command of Col. Eileen Collins, Columbia lifted off the launch pad at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Chandra was deployed on the mission’s first day.

Reflected in the waters, space shuttle Columbia rockets into the night sky from Launch Pad 39-B on mission STS-93 from Kennedy Space Center. Credit: NASA
First Light Images
Just 34 days after launch, extraordinary first images from our Chandra X-ray Observatory were released. The image of supernova remnant Cassiopeia A traces the aftermath of a gigantic stellar explosion in such captivating detail that scientists can see evidence of what is likely the neutron star.
“We see the collision of the debris from the exploded star with the matter around it, we see shock waves rushing into interstellar space at millions of miles per hour,” said Harvey Tananbaum, founding Director of the Chandra X-ray Center at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory.

Cassiopeia A is the remnant of a star that exploded about 300 years ago. The X-ray image shows an expanding shell of hot gas produced by the explosion colored in bright orange and yellows. Credit: NASA/CXC/SAO
A New Look at the Universe
NASA released 25 never-before-seen views to celebrate the telescopes 25th anniversary. This collection contains different types of objects in space and includes a new look at Cassiopeia A. Here the supernova remnant is seen with a quarter-century worth of Chandra observations (blue) plus recent views from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (grey and gold).

This image features deep data of the Cassiopeia A supernova, an expanding ball of matter and energy ejected from an exploding star in blues, greys and golds. The Cassiopeia A supernova remnant has been observed for over 2 million seconds since the start of Chandra’s mission in 1999 and has also recently been viewed by the James Webb Space Telescope. Credit: NASA/CXC/SAO
Can You Hear Me Now?
In 2020, experts at the Chandra X-ray Center/Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) and SYSTEM Sounds began the first ongoing, sustained effort at NASA to “sonify” (turn into sound) astronomical data. Data from NASA observatories such as Chandra, the Hubble Space Telescope, and the James Webb Space Telescope, has been translated into frequencies that can be heard by the human ear.
SAO Research shows that sonifications help many types of learners – especially those who are low-vision or blind -- engage with and enjoy astronomical data more.
Click to watch the “Listen to the Universe” documentary on NASA+ that explores our sonification work: Listen to the Universe | NASA+

An image of the striking croissant-shaped planetary nebula called the Cat’s Eye, with data from the Chandra X-ray Observatory and Hubble Space Telescope. NASA’s Data sonification from Chandra, Hubble and/or Webb telecopes allows us to hear data of cosmic objects. Credit: NASA/CXO/SAO
Celebrate With Us!
Dedicated teams of engineers, designers, test technicians, and analysts at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are celebrating with partners at the Chandra X-ray Center and elsewhere outside and across the agency for the 25th anniversary of the Chandra X-ray Observatory. Their hard work keeps the spacecraft flying, enabling Chandra’s ongoing studies of black holes, supernovae, dark matter, and more.
Chandra will continue its mission to deepen our understanding of the origin and evolution of the cosmos, helping all of us explore the Universe.

The Chandra Xray Observatory, the longest cargo ever carried to space aboard the space shuttle, is shown in Columbia’s payload bay. This photo of the payload bay with its doors open was taken just before Chandra was tilted upward for release and deployed on July 23, 1999. Credit: NASA
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Pick Your Favorite Findings From Fermi’s First Decade
The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope has been observing some of the most extreme objects and events in the universe — from supermassive black holes to merging neutron stars and thunderstorms — for 10 years. Fermi studies the cosmos using gamma rays, the highest-energy form of light, and has discovered thousands of new phenomena for scientists.
Here are a few of our favorite Fermi discoveries, pick your favorite in the first round of our “Fermi Science Playoff.”
Colliding Neutron Stars

In 2017, Fermi detected a gamma ray burst at nearly the same moment ground observatories detected gravitational waves from two merging neutron stars. This was the first time light and ripples in space-time were detected from the same source.
The Sun and Moon in Gamma Rays

In 2016, Fermi showed the Moon is brighter in gamma rays than the Sun. Because the Moon doesn’t have a magnetic field, the surface is constantly pelted from all directions by cosmic rays. These produce gamma rays when they run into other particles, causing a full-Moon gamma-ray glow.
Record Rare from a Blazar

The supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy 3C 279 weighs a billion times the mass of our Sun. In June 2015, this blazar became the brightest gamma-ray source in the sky due to a record-setting flare.
The First Gamma-Ray Pulsar in Another Galaxy

In 2015, for the first time, Fermi discovered a gamma-ray pulsar, a kind of rapidly spinning superdense star, in a galaxy outside our own. The object, located on the outskirts of the Tarantula Nebula, also set the record for the most luminous gamma-ray pulsar we’ve seen so far.
A Gamma-Ray Cycle in Another Galaxy

Many galaxies, including our own, have black holes at their centers. In active galaxies, dust and gas fall into and “feed” the black hole, releasing light and heat. In 2015 for the first time, scientists using Fermi data found hints that a galaxy called PG 1553+113 has a years-long gamma-ray emission cycle. They’re not sure what causes this cycle, but one exciting possibility is that the galaxy has a second supermassive black hole that causes periodic changes in what the first is eating.
Gamma Rays from Novae

A nova is a fairly common, short-lived kind of explosion on the surface of a white dwarf, a type of compact star not much larger than Earth. In 2014, Fermi observed several novae and found that they almost always produce gamma-rays, giving scientists a new type of source to explore further with the telescope.
A Record-Setting Cosmic Blast

Gamma-ray bursts are the most luminous explosions in the universe. In 2013, Fermi spotted the brightest burst it’s seen so far in the constellation Leo. In the first three seconds alone, the burst, called GRB 130427A, was brighter than any other burst seen before it. This record has yet to be shattered.
Cosmic Rays from Supernova Leftovers

Cosmic rays are particles that travel across the cosmos at nearly the speed of light. They are hard to track back to their source because they veer off course every time they encounter a magnetic field. In 2013, Fermi showed that these particles reach their incredible speed in the shockwaves of supernova remains — a theory proposed in 1949 by the satellite’s namesake, the Italian-American physicist Enrico Fermi.
Discovery of a Transformer Pulsar

In 2013, the pulsar in a binary star system called AY Sextanis switched from radio emissions to high-energy gamma rays. Scientists think the change reflects erratic interaction between the two stars in the binary.
Gamma-Ray Measurement of a Gravitational Lens

A gravitational lens is a kind of natural cosmic telescope that occurs when a massive object in space bends and amplifies light from another, more distant object. In 2012, Fermi used gamma rays to observe a spiral galaxy 4.03 billion light-years away bending light coming from a source 4.35 billion light-years away.
New Limits on Dark Matter

We can directly observe only 20 percent of the matter in the universe. The rest is invisible to telescopes and is called dark matter — and we’re not quite sure what it is. In 2012, Fermi helped place new limits on the properties of dark matter, essentially narrowing the field of possible particles that can describe what dark matter is.
‘Superflares’ in the Crab Nebula

The Crab Nebula supernova remnant is one of the most-studied targets in the sky — we’ve been looking at it for almost a thousand years! In 2011, Fermi saw it erupt in a flare five times more powerful than any previously seen from the object. Scientists calculate the electrons in this eruption are 100 times more energetic than what we can achieve with particle accelerators on Earth.
Thunderstorms Hurling Antimatter into Space

Terrestrial gamma-ray flashes are created by thunderstorms. In 2011, Fermi scientists announced the satellite had detected beams of antimatter above thunderstorms, which they think are a byproduct of gamma-ray flashes.
Giant Gamma-Ray Bubbles in the Milky Way

Using data from Fermi in 2010, scientists discovered a pair of “bubbles” emerging from above and below the Milky Way. These enormous bubbles are half the length of the Milky Way and were probably created by our galaxy’s supermassive black hole only a few million years ago.
Hint of Starquakes in a Magnetar

Neutron stars have magnetic fields trillions of times stronger than Earth’s. Magnetars are neutron stars with magnetic fields 1,000 times stronger still. In 2009, Fermi saw a storm of gamma-ray bursts from a magnetar called SGR J1550-5418, which scientists think were related to seismic waves rippling across its surface.
A Dark Pulsar

We observe many pulsars using radio waves, visible light or X-rays. In 2008, Fermi found the first gamma-ray only pulsar in a supernova remnant called CTA 1. We think that the “beam” of gamma rays we see from CTA 1 is much wider than the beam of other types of light from that pulsar. Those other beams never sweep across our vision — only the gamma-rays.

Have a favorite Fermi discovery or want to learn more? Cast your vote in the first of four rounds of the Fermi Science Playoff to help rank Fermi’s findings. Or follow along as we celebrate the mission all year.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Spectacular death. Spectacular star. Your crushed heart remains bright from afar. You’re looking at a composite image of the Crab Nebula, located 6,500 light-years away. The white dot in the center — an extremely dense ball of neutrons just 12 miles across but with the same mass as our Sun — is all that remains from a star that exploded in 1054 A.D. Had the blast occurred 50 light-years away, its intense radiation would have wiped out most life forms on Earth. Spectacular death. Spectacular star. We’re grateful we can admire you from afar.
7 Sports Astronauts Love Without Gravity (Including Football)
Astronauts onboard the International Space Station spend most of their time doing science, exercising and maintaining the station. But they still have time to shoot hoops and toss around a football.
From chess to soccer, there’s a zero-gravity spin to everything.
1. Baseball



Baseball: America’s favorite pastime. JAXA astronaut, Satoshi Furukawa shows us how microgravity makes it possible to be a one-man team. It would be a lot harder to hit home runs if the players could jump that high to catch the ball.
2. Chess

Yes, it’s a sport, and one time NASA astronaut Greg Chamitoff (right) played Earth on a Velcro chess board. An elementary school chess team would pick moves that everyone could vote for online. The winning move would be Earth’s play, and then Chamitoff would respond. About every two days, a move would be made. But who won the historic Earth vs. Space match? Earth! Chamitoff resigned after Earth turned its pawn into a queen, but it was game well played.
3. Soccer


NASA astronaut Steve Swanson put a new spin on soccer by juggling the ball upside down. However, he might not have considered himself upside down. On the space station, up and down are relative.
4. Gymnastics
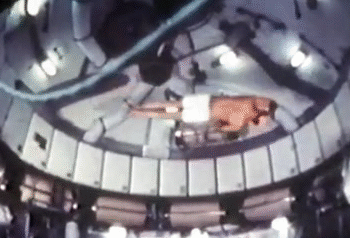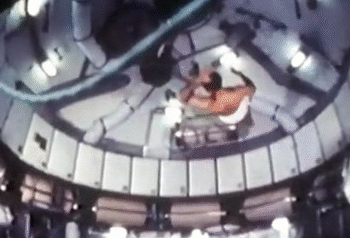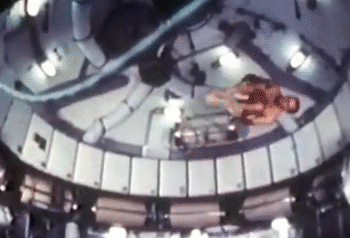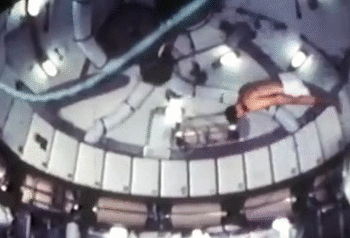
NASA astronauts usually sign off their videos with a zero-gravity somersault (either forwards or backwards). But astronauts are also proficient in handstands, flips and twists. The predecessor to the International Space Station, the Skylab, had the best space for the moves. The current space station is a bit tight in comparison.
5. Basketball

Objects that aren’t heavy don’t move very well on the space station. They kind of just float. It’s like Earth, but exaggerated. For example, on Earth a beach ball wouldn’t go as far as a basketball. The same is true in space, which is why playing with a basketball in space is more fun than playing with a beach ball.
6. Golf

People talk about hitting golf balls off skyscrapers, but what about off the International Space Station? While golf isn’t a normal occurrence on the station, it’s been there. One golf company even sent an experiment to the station to find out how to make better golf clubs.
7. Football

Zero gravity doesn’t make everything easier. Astronauts need to relearn how to throw things because their brains need to relearn how to interpret sensory information. A bowling ball on the space station no longer feels as heavy as a bowling ball on Earth. When astronauts first throw things on the space station, everything keeps going too high. That would put a wrench in your spiral for a couple of months. But once you adjust, the perfect spiral will just keep spiraling!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Meet Our New Flight Directors!
We just hired six new flight directors to join a unique group of individuals who lead human spaceflights from mission control at our Johnson Space Center in Houston.

A flight director manages all human spaceflight missions and related test flights, including International Space Station missions, integration of new American-made commercial spacecraft and developing plans for future Orion missions to the Moon and beyond.
Only 97 people have served as flight directors, or are in training to do so, in the 50-plus years of human spaceflight. That’s fewer than the over 300 astronauts! We talked with the new class about their upcoming transitions, how to keep calm in stressful situations, the importance of human spaceflight and how to best learn from past mistakes. Here’s what they had to say…
Allison Bollinger

Allison is from Lancaster, Ohio and received a BS in Aerospace Engineering from Purdue University. She wanted to work at NASA for as long as she can remember. “I was four-and-a-half when Challenger happened,” she said. “It was my first childhood memory.” Something in her clicked that day. “After, when people asked what I wanted to be when I grew up, I said an astronaut.”
By high school a slight fear of heights, a propensity for motion sickness and an aptitude for engineering shifted her goal a bit. She didn’t want to be an astronaut. “I wanted to train astronauts,” she said. Allison has most recently worked at our Neutral Buoyancy Lab managing the daily operations of the 40-ft-deep pool the astronauts use for spacewalk training! She admits she’ll miss “the smell of chlorine each day. Coming to work at one of the world’s largest pools and training astronauts is an incredible job,” she says. But she’s excited to be back in mission control, where in a previous role she guided astronauts through spacewalks.
She’s had to make some tough calls over the years. So we asked her if she had any tips for when something… isn’t going as planned. She said, “It’s so easy to think the sky is falling. Take a second to take a deep breath, and then you’ll realize it’s not as bad as you thought.”
Adi Boulos

Adi is from Chicago, Illinois and graduated from the University of Illinois Urbana Champaign with a BS in Aerospace Engineering. He joined us in 2008 as a member of the very first group of flight controllers that specialize in data handling and communications and tracking systems aboard the space station.
Most recently he served as the group lead in the Avionics Trainee group, which he loved. “I was managing newer folks just coming to NASA from college and getting to become flight controllers,” he said. “I will miss getting to mentor them from day one.” But he’s excited to start his new role alongside some familiar faces already in mission control. “It’s a great group of people,” he said of his fellow 2018 flight director class. “The six of us, we mesh well together, and we are all from very diverse backgrounds.”
As someone who has spent most of his career supporting human spaceflight and cargo missions from mission control, we asked him why human spaceflight is so important. He had a practical take. “It allows us to solve problems we didn’t know we had,” he said. “For example, when we went to the moon, we had to solve all kinds of problems on how to keep humans alive for long-duration flights in space which directly impacts how we live on the ground. All of the new technology we develop for living in space, we also use on the ground.”
Marcos Flores

Marcos is from Caguas, Puerto Rico and earned a BS in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Puerto Rico and an MS in Aerospace Engineering from Purdue University. Spanish is his first language; English is his second.
The first time he came to the Continental US was on a trip to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida as a kid! “I always knew I wanted to work for NASA,” he said. “And I knew I wanted to be an engineer because I liked to break things to try to figure out how they worked.” He joined us in 2010 as an intern in a robotics laboratory working on conceptual designs for an experimental, autonomous land rover. He later transitioned to the space station flight control team, where he has led various projects, including major software transitions, spacewalks and commercial cargo missions!
He shares his new coworkers’ thoughts on the practical aspects of human spaceflight and believes it’s an expression of our “drive to explore” and our “innate need to know the world and the universe better.” But for him, “It’s more about answering the fundamental questions of where we come from and where we’re headed.”
Pooja Jesrani

Pooja graduated from The University of Texas at Austin with a BS in Aerospace Engineering. She began at NASA in 2007 as a flight controller responsible for the motion control system of the International Space Station. She currently works as a Capsule Communicator, talking with the astronauts on the space station, and on integration with the Boeing Starliner commercial crew spacecraft.
She has a two-year-old daughter, and she’s passionate about motherhood, art, fashion, baking, international travel and, of course, her timing as a new flight director! “Not only have we been doing International Space Station operations continuously, and we will continue to do that, but we are about to launch U.S. crewed vehicles off of U.S. soil for the first time since the space shuttle in 2011. Exploration is ramping up and taking us back to the moon!” she said.” “By the time we get certified, a lot of the things we will get to do will be next-gen.”
We asked her if she had any advice for aspiring flight directors who might want to support such missions down the road. “Work hard every day,” she said. “Every day is an interview. And get a mentor. Or multiple mentors. Having mentorship while you progress through your career is very important, and they really help guide you in the right direction.”
Paul Konyha

Paul was born in Manhasset, NY, and has a BS in Mechanical Engineering from Louisiana Tech University, a Master’s of Military Operational Arts and Science from Air University, and an MS in Astronautical Engineering from the University of Southern California. He began his career as an officer in the United States Air Force in 1996 and authored the Air Force’s certification guide detailing the process through which new industry launch vehicles (including SpaceX’s Falcon 9) gain approval to launch Department of Defense (DoD) payloads.
As a self-described “Star Wars kid,” he has always loved space and, of course, NASA! After retiring as a Lieutenant Colonel in 2016, Paul joined Johnson Space Center as the Deputy Director of the DoD Space Test Program Human Spaceflight Payloads Office. He’s had a rich career in some pretty high-stakes roles. We asked him for advice on handling stress and recovering from life’s occasional setbacks. “For me, it’s about taking a deep breath, focusing on the data and trying not to what if too much,” he said. “Realize that mistakes are going to happen. Be mentally prepared to know that at some point it’s going to happen—you’re going to have to do that self-reflection to understand what you could’ve done better and how you’ll fix it in the future. That constant process of evaluation and self-reflection will help you get through it.”
Rebecca Wingfield

Rebecca is from Princeton, Kentucky and has a BS in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Kentucky and an MS in Systems Engineering from the University of Houston, Clear Lake. She joined us in 2007 as a flight controller responsible for maintenance, repairs and hardware installations aboard the space station.
Since then, she’s worked as a capsule communicator for the space station and commercial crew programs and on training astronauts. She’s dedicated her career to human spaceflight and has a special appreciation for the program’s long-term benefits. “As our human race advances and we change our planet in lots of different ways, we may eventually need to get off of it,” she said. “There’s no way to do that until we explore a way to do it safely and effectively for mass numbers of people. And to do that, you have to start with one person.” We asked her if there are any misconceptions about flight directors. She responded, “While they are often steely-eyed missile men and women, and they can be rough around the edges, they are also very good mentors and teachers. They’re very much engaged in bringing up the next generation of flight controllers for NASA.”

Congrats to these folks on leading the future of human spaceflight!
You can learn more about each of them HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Signs You Might Be Ready to Apply to be a NASA Astronaut
Have you heard the news? Astronaut applications are opening soon (March 2), and there’s never been a better time to apply then now. Here are a few signs that might mean you’re ready to take to the stars:
1. You Don’t Mind Having Roommates

When you’re an astronaut, you have to work and live with your crew mates for extended periods of time. It’s important to the mission and your safety that everyone can collaborate and work together.
2. You LOVE Space

If the Milky Way, planets and space travel doesn’t excite you then this might not be the perfect job for you. But if you love galaxies, space station research and deep space exploration, then maybe you should take a look at our application.
3. Adventure Doesn’t Scare You

Being an astronaut means that you get to take part in adventures that most people will never experience. Imagine: sitting on the launch pad in the Orion spacecraft, atop a rocket that’s getting ready to launch. You’ll travel farther into space than any other humans have been and help push the boundaries of technology in the proving ground of deep space lunar orbits, leading the way for future missions to Mars.
4. You Want to be on the Cutting Edge of Science

Not only do astronauts get to travel to space, but they also get to conduct really cool research in microgravity. Did you know that right now they’re monitoring veggie growth on the International Space Station? This research could help with our future deep space exploration and could teach us a few things about growing plants on Earth. Learn more about all the awesome research on the space station HERE.
5. You’re Not Afraid of Heights

One of the coolest things about being an astronaut, is that you get to go to SPACE! At the very least, you’ll travel to the International Space Station, which is 250 miles above Earth. Or, you could be one of the first astronauts to travel to a distant asteroid or even Mars!
6. You Like Meeting New People

Space is a place where people from all around the world come together to push the boundaries of human exploration. Whether you’re living on the space station with an international crew, or embarking on Artemis missions to the Moon – you’re sure to make new friendships wherever you go.
7. Pizza is Life

Meal time is family time aboard the space station, and what better way to bond than pizza night! Getting to know your crew mates AND channelling your inner chef is always a win win.
8. World Traveling is on Your Bucket List

The International Space Station orbits Earth 16 times a day, so get ready to rack up those frequent flyer miles! A favorite past time of many astronauts is Earth watching from the station’s cupola observatory. Get lost in the Pacific Ocean’s blue hue, gaze at the Himalayas or photograph your favorite cities all from a bird’s eye view. Get assigned to an Artemis Moon mission? Even better! Have fun expanding your travels to the solar system.
9. You’ve Dreamed of Flying

Perk about the job? Your childhood dreams to fly finally come true. Whether you’re floating around the International Space Station or getting adjusted to our new spaceship, Gateway, your inner superhero will be beaming.
10. You Like Helping Others

Astronauts don’t just push the boundaries of human exploration, they also help pave the way for scientific breakthroughs back at home. Thanks to the microgravity environment of space, discoveries not possible on Earth are able to be unlocked. Investigations into Parkinson’s Disease, cancer and more have been conducted on the orbital lab.
Interested in applying to become an astronaut? You’re in luck, applications are open from March 2- 31! Learn about some common myths about becoming an astronaut HERE.
Get more info on applying to be one of our astronauts HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 good-lobster reblogged this · 1 year ago
good-lobster reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 good-lobster liked this · 1 year ago
good-lobster liked this · 1 year ago -
 malandrosxx liked this · 3 years ago
malandrosxx liked this · 3 years ago -
 comeoffage reblogged this · 4 years ago
comeoffage reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 bunni-bunny liked this · 5 years ago
bunni-bunny liked this · 5 years ago -
 desertorange liked this · 5 years ago
desertorange liked this · 5 years ago -
 spaxey reblogged this · 5 years ago
spaxey reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 muttonch0p liked this · 5 years ago
muttonch0p liked this · 5 years ago -
 lorelaymoony-blog liked this · 5 years ago
lorelaymoony-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 summerbrookereding liked this · 5 years ago
summerbrookereding liked this · 5 years ago -
 po4yb reblogged this · 6 years ago
po4yb reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 po4yb liked this · 6 years ago
po4yb liked this · 6 years ago -
 karimomega liked this · 6 years ago
karimomega liked this · 6 years ago -
 hersongblizzard-blog liked this · 6 years ago
hersongblizzard-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 gyozana reblogged this · 6 years ago
gyozana reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 whiterabbitwithclaws liked this · 6 years ago
whiterabbitwithclaws liked this · 6 years ago -
 redsector-a reblogged this · 6 years ago
redsector-a reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 lunareel liked this · 6 years ago
lunareel liked this · 6 years ago -
 itsalexiskr reblogged this · 6 years ago
itsalexiskr reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 bienemaia-blog liked this · 6 years ago
bienemaia-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 ravengreystone liked this · 6 years ago
ravengreystone liked this · 6 years ago -
 fenix-minerva liked this · 6 years ago
fenix-minerva liked this · 6 years ago -
 fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 6 years ago
fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 doomcathedral reblogged this · 6 years ago
doomcathedral reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 doomcathedral liked this · 6 years ago
doomcathedral liked this · 6 years ago -
 lovelyyaliengirl liked this · 6 years ago
lovelyyaliengirl liked this · 6 years ago -
 van1ties reblogged this · 6 years ago
van1ties reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 theonlycedrica reblogged this · 6 years ago
theonlycedrica reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 theonlycedrica liked this · 6 years ago
theonlycedrica liked this · 6 years ago -
 thehappymediumsteapot reblogged this · 6 years ago
thehappymediumsteapot reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 thehappymediumsteapot liked this · 6 years ago
thehappymediumsteapot liked this · 6 years ago -
 lavenderlundi liked this · 6 years ago
lavenderlundi liked this · 6 years ago -
 woolfpuppy liked this · 6 years ago
woolfpuppy liked this · 6 years ago -
 unwoven-words reblogged this · 6 years ago
unwoven-words reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 lint-lickeeerrrr liked this · 6 years ago
lint-lickeeerrrr liked this · 6 years ago -
 guayabadequeso reblogged this · 6 years ago
guayabadequeso reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 awesomeeverysingleday liked this · 6 years ago
awesomeeverysingleday liked this · 6 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts