How We’re Accelerating Our Missions To The Moon
How We’re Accelerating Our Missions to the Moon

Our Space Launch System isn’t your average rocket. It is the only rocket that can send our Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies to the Moon. To accomplish this mega-feat, it has to be the most powerful rocket ever built. SLS has already marked a series of milestones moving it closer to its first launch, Artemis.
Here are four highlights you need to know about — plus one more just on the horizon.
Counting Down

Earlier this month, Boeing technicians at our Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans successfully joined the top part to the core stage with the liquid hydrogen tank. The core stage will provide the most of the power to launch Artemis 1. Our 212-foot-tall core stage, the largest the we have ever built, has five major structural parts. With the addition of the liquid hydrogen tank to the forward join, four of the five parts have been bolted together. Technicians are finishing up the final part — the complex engine section — and plan to bolt it in place later this summer.
Ready to Rumble

This August, to be exact. That’s when the engines for Artemis 1 will be added to the core stage. Earlier this year, all the engines for the first four SLS flights were updated with controllers, tested and officially cleared “go” for launch. We’ve saved time and money by modifying 16 RS-25 engines from the space shuttle and creating a more powerful version of the solid rocket boosters that launched the shuttle. In April, the last engine from the shuttle program finished up a four-year test series that included 32 tests at our Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. These acceptance tests proved the engines could operate at a higher thrust level necessary for deep space travel and that new, modernized flight controllers —the “brains” of the engine — are ready to send astronauts to the Moon in 2024.
Getting a Boost

Our industry partners have completed the manufacture and checkout of 10 motor segments that will power two of the largest propellant boosters ever built. Just like the engines, these boosters are designed to be fast and powerful. Each booster burns six tons of propellant every second, generating a max thrust of 3.6 million pounds for two minutes of pure awesome. The boosters will finish assembly at our Kennedy Space Center in Florida and readied for the rocket’s first launch in 2020. In the meantime, we are well underway in completing the boosters for SLS and Orion’s second flight in 2022.
Come Together

Meanwhile, other parts of the rocket are finished and ready for the ride to the Moon. The final piece of the upper part of the rocket, the launch vehicle stage adapter, will soon head toward Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Two other pieces, including the interim cryogenic propulsion stage that will provide the power in space to send Orion on to the Moon, have already been delivered to Kennedy.
Looking to the Future

Our engineers evaluated thousands of designs before selecting the current SLS rocket design. Now, they are performing critical testing and using lessons learned from current assembly to ensure the initial and future designs are up to the tasks of launching exploration missions for years to come. This real-time evaluation means engineers and technicians are already cutting down on assembly time for future mission hardware, so that we and our partners can stay on target to return humans to the Moon by 2024 — to stay so we can travel on to Mars.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Will there be a livestream to the solar eclipse on the NASA website?
Yup! We’ll have a live stream up https://eclipse2017.nasa.gov/eclipse-live-stream They I believe will also be covering events that are happening across the US. A bunch of my office mates here are going across the US to help with the coverage and to collect data! It should be incredibly exciting!
Build a Rover, Race a Rover!

Have you ever wanted to drive a rover across the surface of the Moon?
This weekend, students from around the world will get their chance to live out the experience on Earth! At the Human Exploration Rover Challenge, managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, high schoolers and college students operate human-powered rovers that they designed and built as they traverse a simulated world, making decisions and facing obstacles that replicate what the next generation of explorers will face in space.

Though the teams that build the rover can be a few people or a few dozen, in the end, two students (one male, one female) will end up navigating their rover through a custom-built course at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center. Each duo will push their rover to the limit, climbing up hills, bumping over rocky and gravelly grounds, and completing mission objectives (like retrieving soil samples and planting their team flag) for extra points -- all in less than seven minutes.

2019 will mark the 25th year of Rover Challenge, which started life as the Great Moonbuggy Race on July 16, 1994. Six teams braved the rain and terrain (without a time limit) in the Rocket City that first year -- and in the end, the University of New Hampshire emerged victorious, powering through the moon craters, boulder fields and other obstacles in eighteen minutes and fifty-five seconds.

When it came time to present that year's design awards, though, the honors went to the University of Puerto Rico at Humacao, who have since become the only school to compete in every Great Moonbuggy Race and Rover Challenge hosted by NASA Marshall. The second-place finishers in 1994, the hometown University of Alabama in Huntsville, are the only other school to compete in both the first race and the 25th anniversary race in 2019.

Since that first expedition, the competition has only grown: the race was officially renamed the Human Exploration Rover Challenge for 2014, requiring teams to build even more of their rover from the wheels up, and last year, new challenges and tasks were added to better reflect the experience of completing a NASA mission on another planet. This year, almost 100 teams will be competing in Rover Challenge, hailing from 24 states, Washington, D.C., Puerto Rico, and countries from Bolivia to Bangladesh.

Rover Challenge honors the legacy of the NASA Lunar Roving Vehicle, which made its first excursion on the moon in 1971, driven by astronauts David Scott and James Irwin on Apollo 15. Given the competition's space race inspiration, it's only appropriate that the 25th year of Rover Challenge is happening in 2019, the 50th anniversary of Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin's historic Apollo 11 moon landing.

Interested in learning more about Rover Challenge? Get the details on the NASA Rover Challenge site -- then join us at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center (entrance is free) or watch live on the Rover Challenge Facebook Page starting at 7 AM CT, this Friday, April 12 and Saturday, April 13. Happy roving!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

It's almost launch day! On Monday, June 24, the launch window opens for the Department of Defense's Space Test Program-2 launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy. Among the two dozen satellites on board are four NASA payloads whose data will help us improve satellite design and performance.
Our experts will be live talking about the launch and NASA's missions starting this weekend.
🛰 Tune in on Sunday, June 23, at 12 p.m. EDT (9 a.m. PDT) for a live show diving into the technology behind our projects.
🚀 Watch coverage of the launch starting at 11 p.m. EDT (8 p.m. PDT) on Monday, June 24
Join us at nasa.gov/live, and get updates on the launch at blogs.nasa.gov/spacex.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Space toilet, Radishes, and a Spacewalk in Virtual Reality
A rocket is launching to the International Space Station next week, carrying tons of science and supplies to the orbiting laboratory. It’s Northrop Grumman’s 14th (NG-14) commercial resupply cargo mission, and includes plant research, a new space toilet, and a special virtual reality camera designed to immerse you in a spacewalk. Let’s take a closer look at what’s on board, and how you can ask some of the scientists anything.

A new way to “boldly go” in space

A new space toilet is heading to the space station. It’s smaller than the current toilets aboard the station, and includes a 3D printed titanium cover for its dual fan separator. These are just some of the upgrades that make it better suited for our deep space exploration missions. Engineers also gathered feedback from astronauts and set out to design more comfortable attachments that would make “boldly going” in space a more enjoyable experience. The toilet is being tested on the space station, and will also be used on a future Artemis mission. The new design will allow us to increase how much water we recover for use, because yep … yesterday’s coffee becomes tomorrow’s drinking water. See below for an opportunity to speak with the folks who made the new space toilet happen.
Space plants are rad(ish)!

Astronauts traveling to the Moon and Mars will need to grow food to supplement their diets. The latest in plant studies aboard the space station hopes to pack a crunch in that research. We’ll be growing radishes in a special plant chamber, and learning how light, water, atmosphere, and soil conditions affect the bulbous vegetables. Radishes are nutritious, grow quickly (roughly four weeks from sowing to harvest), and are genetically similar to Arabidopsis, a plant frequently studied in microgravity. What we learn could help optimize growth of the plants in space as well as provide an assessment of their nutrition and taste. See below for an opportunity to ask anything of the scientist and engineer behind this new crop.
Immerse yourself in a spacewalk

If going to space is on your bucket list, you might be closer than you think to checking that box. Felix & Paul Studios is creating an immersive 360 virtual reality film of a spacewalk that will put you right next to the astronauts as they go about their work on the outside of the space station … at 17,500 miles per hour. The new camera, specially designed to withstand the incredibly harsh environment of space, will be mounted on the station’s robotic arm so it can be maneuvered around the outside of the space station. Félix Lajeunesse and Paul Raphaël are the co-founders of the immersive entertainment studio, and have been producing a film aboard the space station – from Earth – for more than a year already. See below for a chance to ask them anything about what filming in space takes.

You can join in the NG-14 Reddit Ask Me Anything on Friday, Sept. 25 to ask anything of these folks and their projects. Here’s the schedule:
Space toilet (a.k.a the Universal Waste Management System): Melissa McKinley with NASA’s Advanced Exploration Systems and Jim Fuller of Collins Aerospace, and program manager for UWMS at 12 p.m. EDT at https://www.reddit.com/r/space.
Radishes in space (a.k.a. Plant Habitat-02): Dr. Karl Hasenstein is the scientist behind the Plant Habitat-02, and Dave Reed knows the ins and outs of the Advanced Plant Habitat of the space station. Their Reddit AMA begins at 3 p.m. EDT at https://www.reddit.com/r/gardening.
Virtual reality spacewalk camera: Félix Lajeunesse and Paul Raphaël co-founders and creative directors of Felix & Paul Studios will be taking questions at 5 p.m. EDT on https://www.reddit.com/r/filmmakers.
These are just a few of the payloads launching aboard the NG-14 Cygnus cargo vehicle to the space station next week. Read about the cancer research, and new commercial products also heading to space and watch the video above to learn more. Launch is targeted for Tuesday, Sept. 29, with a five-minute launch window opening at approximately 10:26 p.m. EDT. Live coverage begins on NASA TV at 10 p.m. EDT.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Learn more about our Deep Space Network, where to watch the Ursid meteor shower, Cassini’s ring-grazing at Saturn and more.

1. A Deep Space Anniversary
On Dec. 24, 1963, the Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Deep Space Information Facility was renamed the Deep Space Network. And, it’s been humanity's ear to the skies ever since.
+ History of the Deep Space Network
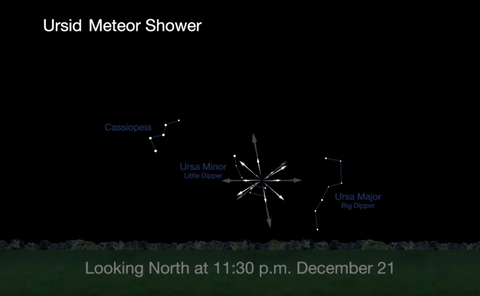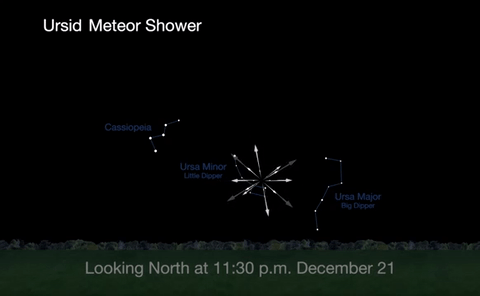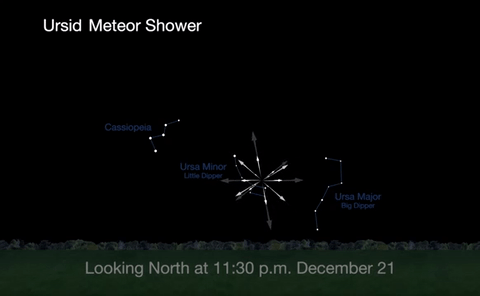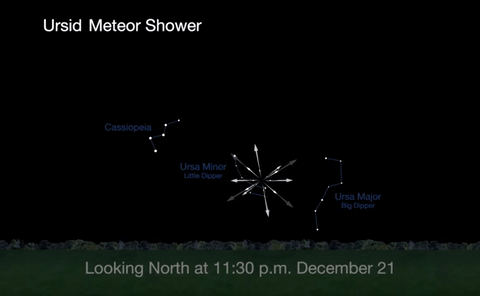
2. Ursid Meteor Shower
The best time to view the Ursids, radiating from Ursa Minor, or the little Dipper, will be from midnight on December 21 until about 1a.m. on December 22, before the moon rises.

3. At Saturn, the Ring-Grazing Continues
Our Cassini spacecraft has completed several orbits that take it just outside Saturn’s famous rings. The first ring-grazing orbit began on November 30. The spacecraft will repeat this feat 20 times, with only about a week between each ring-plane crossing.
+ Learn more

4. Preparing for the 2017 Total Solar Eclipse
Next year North America will see one of the most rare and spectacular of all sky events. Learn how to prepare.
+ 2017 Solar Eclipse Toolkit

5. Searching for Rare Asteroids
Our first mission to return an asteroid sample to Earth will be multitasking during its two-year outbound cruise to the asteroid Bennu. On February 9-20, OSIRIS-REx (Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, and Security-Regolith Explorer) will activate its onboard camera suite and begin its search for elusive “Trojan,” asteroids, constant companions to planets in our solar system as they orbit the sun, remaining near a stable point 60 degrees in front of or behind the planet. Because they constantly lead or follow in the same orbit, they will never collide with their companion planet.
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com


In Roman mythology, the god Jupiter drew a veil of clouds around himself to hide his mischief. It was only Jupiter's wife, the goddess Juno, who could peer through the clouds and reveal Jupiter's true nature. Our @NASAJuno spacecraft is looking beneath the clouds of the massive gas giant, not seeking signs of misbehavior, but helping us to understand the planet's structure and history... Now, @NASAJuno just published its first findings on the amount of water in the gas giant’s atmosphere. The Juno results estimate that at the equator, water makes up about 0.25% of the molecules in Jupiter's atmosphere — almost three times that of the Sun. An accurate total estimate of this water is critical to solving the mystery of how our solar system formed.
The JunoCam imager aboard Juno captured this image of Jupiter's southern equatorial region on Sept. 1, 2017. The bottom image is oriented so Jupiter's poles (not visible) run left-to-right of frame.
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS/Kevin M. Gill
What would be the ideal discovery to make with the Webb Telescope? Or what would you love to find with it?
NASA Technology in Your Life
How does NASA technology benefit life on Earth? It probably has an impact in more ways than you think! Since 1976, our Spinoff program has profiled nearly 2,000 space technologies that have transformed into commercial products and services. In celebration of Spinoff’s 40th year of publication, we’ve assembled a collection of spinoffs that have had the greatest impact on Earth.
Take a look and see how many you utilize on a regular basis:
Digital Image Sensors

Whether you take pictures and videos with a DSLR camera or a cell phone, or even capture action on the go with a device like a GoPro Hero, you’re using NASA technology. The CMOS active pixel sensor in most digital image- capturing devices was invented when we needed to miniaturize cameras for interplanetary missions. This technology is also widely used in medical imaging and dental X-ray devices.
Enriched Baby Formula

While developing life support for Mars missions, NASA-funded researchers discovered a natural source for an omega-3 fatty acid previously found primarily in breast milk that plays a key role in infant development. The ingredient has since been added to more than 90% of infant formula on the market and is helping babies worldwide develop healthy brains, eyes and hearts.
NASTRAN Software

NASTRAN is a software developed by our engineers that performs structural analysis in the 1960s. Still popular today, it’s been used to help design everything from airplanes and cars to nuclear reactors and even Disney’s Space Mountain roller coaster.
Food Safety Standards

Looking to ensure the absolute safety of prepackaged foods for spaceflight, we partnered with the Pillsbury Company to create a new, systematic approach to quality control. Now known as Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), the method has become an industry standard that benefits consumers worldwide by keeping food free from a wide range of potential chemical, physical and biological hazards.
Neutral Body Posture Specifications

What form does the human body naturally assume when all physical influences, including the pull of gravity, stop affecting it? We conducted research to find out using Skylab, America’s first space station, and later published specifications for what it called neutral body posture. The study has informed seat designs in everything from airplanes and office chairs to several models of Nissan automobiles.
Advanced Water Filtration

We recently discovered unexpected sources of water on the moon and Mars, but even so, space remains a desert for human explorers, and every drop must be recycled and reused. A nano filter devised to purify water in orbit is currently at work on Earth, in devices that supply water to remote villages as well as in a water bottle that lets hikers and adventurers stay hydrated using streams and lakes.
Swimsuit Designs

Wind-tunnel testing at our Langley Research Center played a key role in the development of Speedo’s LZR Racer swimsuit, proving which materials and seams best reduced drag as a swimmer cuts through the water. The swimsuit made a splash during its Olympic debut in 2008, as nearly every medal winner and world-record breaker wore the suit.
Air Purifier

When plants grow, they release a gas called ethylene that accelerates decay, hastening the wilting of flowers and the ripening of fruits and vegetables. Air circulation on Earth keeps the fumes from building up, but in the hermetically sealed environment of a spacecraft, ethylene poses a real challenge to the would-be space farmers. We funded the development of an ethylene scrubber for the International Space Station that has subsequently proved capable of purifying air on Earth from all kinds of pathogens and particulates. Grocery stores use it to keep produce fresh longer. It’s also been marketed for home use and has even been embraced by winemakers, who employ the scrubber to keep aging wine in barrels free from mold, mildew and musty odors.
Scratch-Resistant, UV-Reflective Lenses

Some of the earliest research into effective scratch-resistant coatings for prescription and sunglass lenses drew from work done at Ames Research Center on coatings for astronaut helmet visors and plastic membranes used in water purification systems. In the 1980s, we developed sunlight-filtering lenses to provide eye protection and enhance colors, and these lenses have found their way into sunglasses, ski goggles and safety masks for welders.
Dustbuster

An Apollo-era partnership with Black & Decker to build battery-operated tools for moon exploration and sample collection led to the development of a line of consumer, medical and industrial hand-held cordless tools. This includes the popular Dustbuster cordless vacuum.
To see even more of our spinoff technologies, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/offices/oct/40-years-of-nasa-spinoff
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Andre Douglas
A Virginia native, Andre Douglas served in the U.S. Coast Guard as a naval architect and salvage engineer. Douglas later worked as an engineer for Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory on NASA's DART mission to redirect an asteroid. https://go.nasa.gov/48FBlam
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
I am interested in learning how to grow plants in space. How can I be involved in this as a college student, or independently?
-
 millerman1969 liked this · 1 year ago
millerman1969 liked this · 1 year ago -
 fdavid02 liked this · 1 year ago
fdavid02 liked this · 1 year ago -
 io-robirobot liked this · 2 years ago
io-robirobot liked this · 2 years ago -
 pareidoliaonthemove liked this · 2 years ago
pareidoliaonthemove liked this · 2 years ago -
 blueunknowninfluencer liked this · 3 years ago
blueunknowninfluencer liked this · 3 years ago -
 wyanton liked this · 3 years ago
wyanton liked this · 3 years ago -
 metalzoic liked this · 3 years ago
metalzoic liked this · 3 years ago -
 artemis2021-blog liked this · 3 years ago
artemis2021-blog liked this · 3 years ago -
 lolagonnamakeit liked this · 4 years ago
lolagonnamakeit liked this · 4 years ago -
 craigory-tucker liked this · 4 years ago
craigory-tucker liked this · 4 years ago -
 solousuf liked this · 4 years ago
solousuf liked this · 4 years ago -
 noboru-k liked this · 4 years ago
noboru-k liked this · 4 years ago -
 just-a-random-guy liked this · 4 years ago
just-a-random-guy liked this · 4 years ago -
 steve51world liked this · 4 years ago
steve51world liked this · 4 years ago -
 torukmakto69 liked this · 4 years ago
torukmakto69 liked this · 4 years ago -
 tbearjc liked this · 4 years ago
tbearjc liked this · 4 years ago -
 alexbyrth liked this · 4 years ago
alexbyrth liked this · 4 years ago -
 frostedwheat liked this · 4 years ago
frostedwheat liked this · 4 years ago -
 usafphantom2 reblogged this · 4 years ago
usafphantom2 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 usafphantom2 liked this · 4 years ago
usafphantom2 liked this · 4 years ago -
 mama1943 reblogged this · 4 years ago
mama1943 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 cosmicstars13 liked this · 4 years ago
cosmicstars13 liked this · 4 years ago -
 ask-henrymiller-onvariousshit liked this · 4 years ago
ask-henrymiller-onvariousshit liked this · 4 years ago -
 hauntedbouquetchild reblogged this · 4 years ago
hauntedbouquetchild reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 hauntedbouquetchild liked this · 4 years ago
hauntedbouquetchild liked this · 4 years ago -
 hauntedbouquetchild reblogged this · 4 years ago
hauntedbouquetchild reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 bitter1stuff reblogged this · 5 years ago
bitter1stuff reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 miasmaskyy liked this · 5 years ago
miasmaskyy liked this · 5 years ago -
 undead0-0love liked this · 5 years ago
undead0-0love liked this · 5 years ago -
 agentpinebutoldandirrelevant reblogged this · 5 years ago
agentpinebutoldandirrelevant reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 witchfindertable liked this · 5 years ago
witchfindertable liked this · 5 years ago -
 grbghost reblogged this · 5 years ago
grbghost reblogged this · 5 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts