The Search For Starless Planets
The Search for Starless Planets
While it’s familiar to us, our solar system may actually be a bit of an oddball. Our Milky Way galaxy is home to gigantic worlds with teeny-tiny orbits and planets that circle pairs of stars. We’ve even found planets that don’t orbit stars at all! Instead, they drift through the galaxy completely alone (unless they have a moon to keep them company). These lonely island worlds are called rogue planets.

Where do rogue planets come from?
The planet-building process can be pretty messy. Dust and gas around a star clump together to form larger and larger objects, like using a piece of play-dough to pick up other pieces.
Sometimes collisions and close encounters can fling a planet clear out of the gravitational grip of its parent star. Rogue planets may also form out in space on their own, like the way stars grow.

Seeing the invisible
We’ve discovered more than 4,000 exoplanets, but only a handful are rogue planets. That’s because they’re superhard to find! Rogue planets are almost completely invisible to us because they don’t shine like stars and space is inky black. It’s like looking for a black cat in a dark room without a flashlight.
Some planet-finding methods involve watching to see how orbiting planets affect their host star, but that doesn’t work for rogue planets because they’re off by themselves. Rogue planets are usually pretty cold too, so infrared telescopes can’t use their heat vision to spot them either.
So how can we find them? Astronomers use a cool cosmic quirk to detect them by their effect on starlight. When a rogue planet lines up with a more distant star from our vantage point, the planet bends and magnifies light from the star. This phenomenon, called microlensing, looks something like this:

Imagine you have a trampoline, a golf ball, and an invisible bowling ball. If you put the bowling ball on the trampoline, you could see how it made a dent in the fabric even if you couldn’t see the ball directly. And if you rolled the golf ball near it, it would change the golf ball’s path.

A rogue planet affects space the way the bowling ball warps the trampoline. When light from a distant star passes by a rogue planet, it curves around the invisible world (like how it curves around the star in the animation above). If astronomers on Earth were watching the star, they’d notice it briefly brighten. The shape and duration of this brightness spike lets them know a planet is there, even though they can’t see it.

Telescopes on the ground have to look through Earth’s turbulent atmosphere to search for rogue planets. But when our Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope launches in the mid-2020s, it will give us a much better view of distant stars and rogue planets because it will be located way above Earth’s atmosphere — even higher than the Moon!
Other space telescopes would have to be really lucky to spot these one-in-a-million microlensing signals. But Roman will watch huge patches of the sky for months to catch these fleeting events.

Lessons from cosmic castaways
Scientists have come up with different models to explain how different planetary systems form and change over time, but we still don’t know which ones are right. The models make different predictions about rogue planets, so studying these isolated worlds can help us figure out which models work best.
When Roman spots little microlensing starlight blips, astronomers will be able to get a pretty good idea of the mass of the object that caused the signal from how long the blip lasts. Scientists expect the mission to detect hundreds of rogue planets that are as small as rocky Mars — about half the size of Earth — up to ones as big as gas giants, like Jupiter and Saturn.

By design, Roman is only going to search a small slice of the Milky Way for rogue planets. Scientists have come up with clever ways to use Roman’s future data to estimate how many rogue planets there are in the whole galaxy. This information will help us better understand whether our solar system is pretty normal or a bit of an oddball compared to the rest of our galaxy.

Roman will have such a wide field of view that it will be like going from looking at the cosmos through a peephole to looking through a floor-to-ceiling window. The mission will help us learn about all kinds of other cool things in addition to rogue planets, like dark energy and dark matter, that will help us understand much more about our place in space.
Learn more about the Roman Space Telescope at: https://roman.gsfc.nasa.gov/

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
What’s Up for April 2016?

Jupiter, Mars, the Lyrid meteor shower and 2016’s best views of Mercury are all visible in the sky this month.

Jupiter, where our Juno mission will begin orbiting on July 4, continues to shine almost as brightly this month as last. And eagle-eyed telescope viewers will see a transit, a shadow transit, an occultation and an eclipse of Jupiter’s moons- all in one night: April 6-7.

Io transits first, crossing the planet beginning at 9:52 p.m. EDT. It’s shadow can be seen less than an hour later.

Next Jupiter occults, or eclipses, Europa as Europa slips behind the giant planet at 10:48 p.m. EDT. At 3 a.m. Europa reappears from its eclipse, dramatically leaving the shadow of Jupiter.

Ganymede transits the planet beginning at 1:01 EDT April 7.
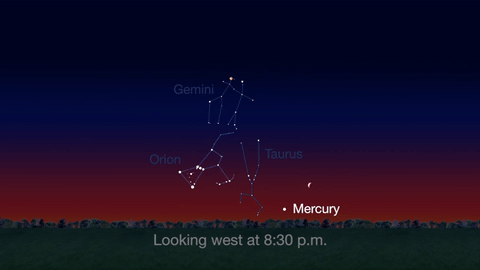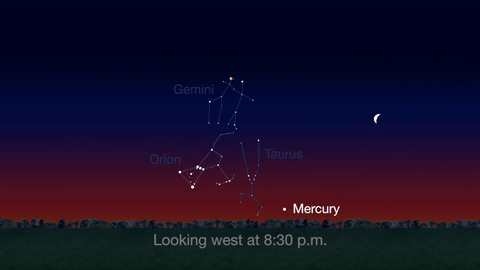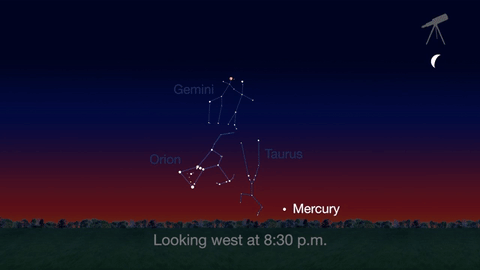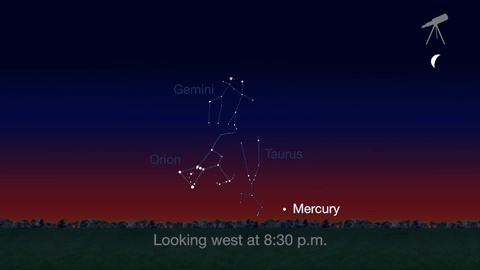
Check out the other planets in April, too! Mercury is always a challenging object to view, but this month you can spot it after sunset about 10 degrees above the horizon. Through a telescope you can see its phase. It will appear like a tiny crescent moon, with about 1/3 of its disk illuminated.

Mars is finally visible before midnight this month. It rises in the southeast at about 10 p.m. by the end of April. The best observing of Mars will be when it is highest in the sky. This means a few hours before dawn. Its brightness and apparent size increase dramatically this month. By month’s end, Mars appears nearly twice as bright as at the beginning of the month.

About mid-month you’ll see Mars near its rival in the sky: the similar-colored red supergiant star Antares. The name “Antares” means “equal to or rival of Mars”.
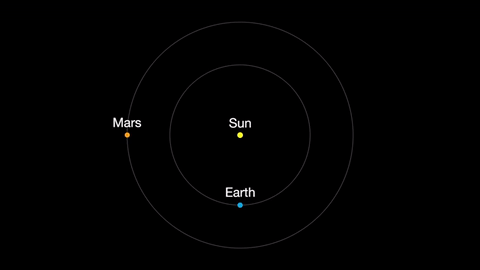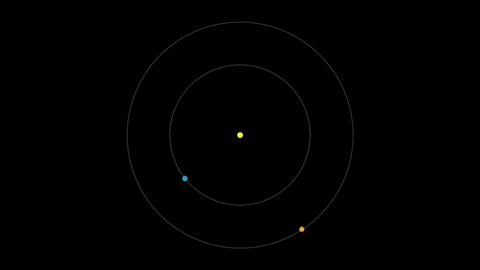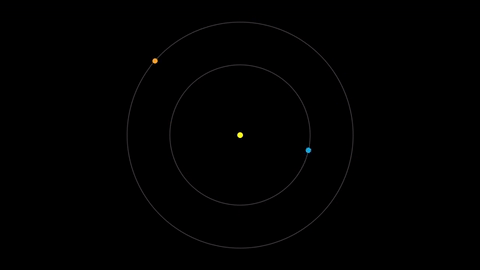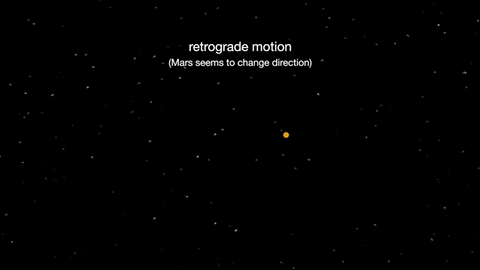
Earth moves almost twice as fast as Mars does, so it often passes Mars in their race around the sun. This causes “retrograde motion”: an illusion we see from our viewpoint on Earth.
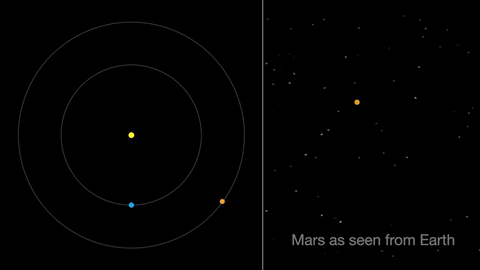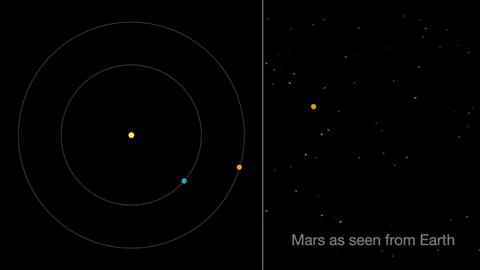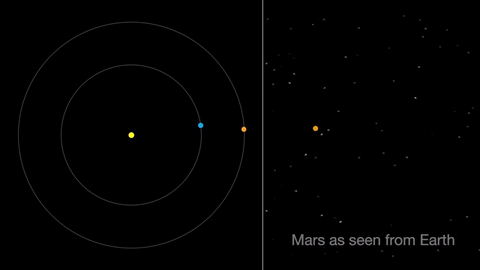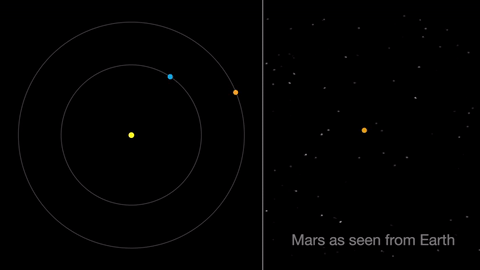
Retrograde motion happens as Earth catches up to Mars, causing Mars to appear slow to slow its eastward motion against the stars. After a few days, when Earth has overtaken Mars, the Red Planet seems to move westward. Eventually, Earth moves far enough around its orbit that Mars appears to be moving eastward again.
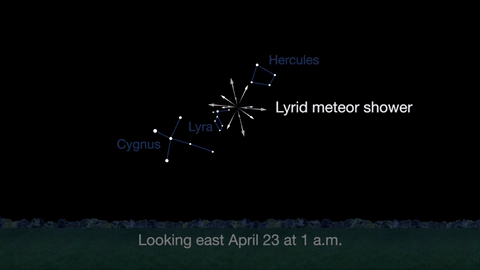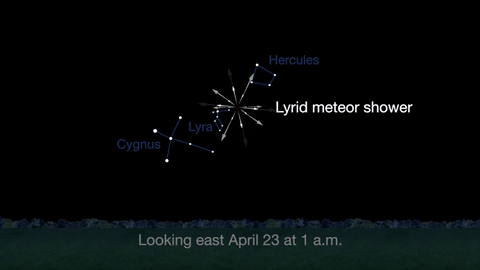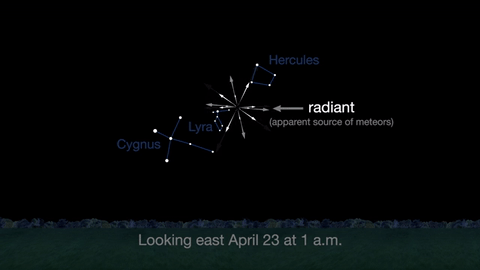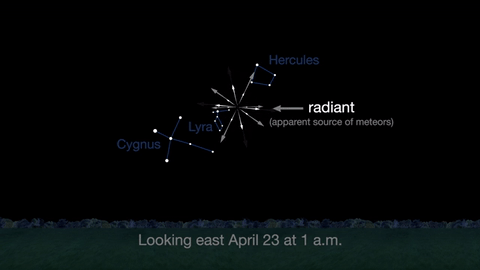
April features one meteor shower, the Lyrids. This year the Lyrids are marred by the full moon. The best time to view will be just before dawn on April 23, when the constellation Lyra is overhead and the moon will be near to setting.
With all of these great things to spot in the sky this month, be sure to get outside and look up!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: What to Know This Week
Let us lead you on a journey of our solar system. Here are some things to know this week:
1. Readying OSIRIS-REx for Launch

Our OSIRIS-REx asteroid mission will launch one month from now, and engineers are getting the spacecraft and its rocket ready for action. One major step will be encasing OSIRIS-REx in its fairing, the protective shield where the spacecraft will ride into space.
Learn more about OSIRIS-REx.
2. Be a Planetary Ambassador

Our Solar System Ambassadors Program is a public outreach program for volunteers across the nation, who share the excitement of our space exploration missions and information about recent discoveries with their communities. Think you have what it takes to be a Solar System Ambassador?
Apply starting September 1
3. Cassini’s Grand Adventure

This week, Cassini prepares for the final phase of its grand adventure at Saturn, which will include orbits that take the robotic spacecraft just outside the planet's spectacular rings. Already, Cassini's orbital inclination is increasing, and it has sent home some striking photos taken from above the north pole.
See the latest sights.
4. Watch Peak Perseids

August's Perseid meteor shower peaks for U.S. observers just after sunrise on Friday morning, Aug. 12. Some experts' predictions include an outburst of up to 150 or 200 meteors per hour at the peak. Will there be an outburst, or even a second peak, as in some past years?
Watch and see
5. Eye in the Sky

Our Mars Reconnaissance Obiter continues its eagle-eye watch on the Red Planet from above. The MRO team released a massive new collection of super-high-resolution images of the Martian surface.
Take a look.
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Prepare to be mesmerized… 😵💫

Feast your eyes on the magnificent galaxy M51, also known as the Whirlpool Galaxy! This hypnotic spiral galaxy was captured in visible light with Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys. Living up to its nickname, the Whirlpool Galaxy has the traits of a typical spiral galaxy, like beautifully curving arms, pink star-forming regions, and brilliant blue strands of star clusters.
The Whirlpool Galaxy is located about 31 million light-years away in the constellation Canes Venatici.
Discover more about the Whirlpool Galaxy here.
Right now, the Hubble Space Telescope is exploring #GalaxiesGalore! Find more galaxy content and spectacular new images by following along on Hubble’s Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram.
Credit: NASA, ESA, S. Beckwith (STScI), and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
Celebrate Earth Day with NASA

"We came all this way to explore the Moon, and the most important thing is that we discovered the Earth." - Apollo 8 astronaut Bill Anders
On Dec. 24, 1968, Anders snapped this iconic photo of "Earthrise" during the historic Apollo 8 mission. As he and fellow astronauts Frank Borman and Jim Lovell became the first humans to orbit the Moon, they witnessed Earth rising over the Moon's horizon. The image helped spark the first #EarthDay on April 22, 1970.
Anders sat down with Dr. Kate Calvin, our chief scientist and senior climate advisor, to chat about the photo, and NASA’s role in studying our home.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Exploring Our National Parks…from Space!
The United States has nearly 84 million acres of historic and scenic land in its national parks system. In celebration of National Park Week, here are some satellite views of a few of those national treasures.
Throughout National Park Week, you can #FindYourPark and visit for free.
Yosemite National Park – California

Naked summits alternate with forested lowlands in Yosemite Valley, part of California’s Yosemite National Park. Our Landsat 7 satellite captured this true-color image of part of the Yosemite Valley on Aug. 8, 2001.
Yellowstone National Park – Wyoming, Idaho and Montana

Established in 1872, it was the first national park in the United States, and the world! Its geological and biological wonders have led international groups to declare it a world heritage site and a biosphere reserve. Yellowstone National Park captures the spirit and purpose of the National Park Service, blending modern and ancient human history with nature in its raw complexity.
Hot Springs National Park – Arkansas

National Parks usually make us think of pristine landscapes untouched by human civilization. Most of the 59 national parks in the United States fit that mold, but there are a few exceptions. Arkansas’s Hot Springs National Park, the country’s smallest and most urban, is one of them. Hot Springs, a city of 96,000 people, lies at the southern edge of the park and partly within its boarders.
Shenandoah National Park – Virginia

This long, narrow park in the Blue Ridge Mountains spans more than 179,000 acres, with 40% of the land protected as wilderness. More than 95% of the park is forested, sheltering 1,300 plant species and 267 types of trees and shrubs. The park contains 577 archeological sites, more than 100 cemeteries, and some rocks that date back a billion years.
Olympic National Park – Washington

Possibly one of America’s most diverse national landscapes, Olympic National Park is situated on the Olympic Peninsula in northwestern Washington. If you walked from west to east across the park, you would start at the rocky Pacific shoreline, move into rare temperate rainforests and lush river valleys, ascend glaciers and rugged mountain peaks, and then descend into a comparatively dry rain shadow and alpine forest. From beach to the top of Mount Olympus, you would rise 7,980 feet above sea level.
Colorado National Monument – Colorado

Along the Interstate 70 corridor in western Colorado, well-watered croplands, residential properties and urbanized areas create a broad stripe of green and gray. Away from the interstate, dry climate conditions color the landscape shades of beige, brick and tan. Yet these arid regions offer treasures of their own, including stunning vistas and wildlife both living and extinct. The varied landscapes of this park show the effects of tens of millions of years of erosion.
The images above were produced by our Earth Observatory as part of its 2016 series featuring the National Park Service properties. Check out more HERE.
Want to see more of our nation’s parks from space? Visit our Flickr gallery HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What’s Up - February 2018
What’s Up For February?

This month, in honor of Valentine's Day, we'll focus on celestial star pairs and constellation couples.

Let's look at some celestial pairs!

The constellations Perseus and Andromeda are easy to see high overhead this month.

According to lore, the warrior Perseus spotted a beautiful woman--Andromeda--chained to a seaside rock. After battling a sea serpent, he rescued her.

As a reward, her parents Cepheus and Cassiopeia allowed Perseus to marry Andromeda.

The great hunter Orion fell in love with seven sisters, the Pleiades, and pursued them for a long time. Eventually Zeus turned both Orion and the Pleiades into stars.

Orion is easy to find. Draw an imaginary line through his belt stars to the Pleiades, and watch him chase them across the sky forever.

A pair of star clusters is visible on February nights. The Perseus Double Cluster is high in the sky near Andromeda's parents Cepheus and Cassiopeia.

Through binoculars you can see dozens of stars in each cluster. Actually, there are more than 300 blue-white supergiant stars in each of the clusters.

There are some colorful star pairs, some visible just by looking up and some requiring a telescope. Gemini's twins, the brothers Pollux and Castor, are easy to see without aid.

Orion's westernmost, or right, knee, Rigel, has a faint companion. The companion, Rigel B, is 500 times fainter than the super-giant Rigel and is visible only with a telescope.

Orion's westernmost belt star, Mintaka, has a pretty companion. You'll need a telescope.

Finally, the moon pairs up with the Pleiades on the 22nd and with Pollux and Castor on the 26th.
Watch the full What’s Up for February Video:
There are so many sights to see in the sky. To stay informed, subscribe to our What’s Up video series on Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Smoke Gets In Your Eyes…and Our Instruments
Fires are some of the most dynamic and dramatic natural phenomena. They can change rapidly, burning natural landscapes and human environments alike. Fires are a natural part of many of Earth’s ecosystems, necessary to replenish soil and for healthy plant growth. But, as the planet warms, fires are becoming more intense, burning longer and hotter.

Right now, a fleet of vehicles and a team of scientists are in the field, studying how smoke from those fires affects air quality, weather and climate. The mission? It’s called FIREX-AQ. They’re working from the ground up to the sky to measure smoke, find out what’s in it, and investigate how it affects our lives.

Starting on the ground, the Langley Aerosol Research Group Experiment (LARGE) operates out of a large van. It’s one of two such vans working with the campaign, along with some other, smaller vans. It looks a little like a food truck, but instead of a kitchen, the inside is packed full of science instruments.

The team drives the van out into the wilderness to take measurements of smoke and tiny particles in the air at the ground level. This is important for a few reasons: First of all, it’s the stuff we’re breathing! It also gives us a look at smoke overnight, when the plumes tend to sink down out of the atmosphere and settle near the ground until temperatures heat back up with the Sun. The LARGE group camps out with their van full of instruments, taking continuous measurements of smoke…and not getting much sleep.

Just a little higher up, NOAA’s Twin Otter aircraft can flit down close to where the fires are actually burning, taking measurements of the smoke and getting a closer look at the fires themselves. The Twin Otters are known as “NOAA’s workhorses” because they’re easily maneuverable and can fly nice and slow to gather measurements, topping out at about 17,000 feet.

Then, sometimes flying at commercial plane height (30,000 feet) and swooping all the way down to 500 feet above the ground, NASA’s DC-8 is packed wing to wing with science instruments. The team onboard the DC-8 is looking at more than 500 different chemicals in the smoke.

The DC-8 does some fancy flying, crisscrossing over the fires in a maneuver called “the lawnmower” and sometimes spiraling down over one vertical column of air to capture smoke and particles at all different heights. Inside, the plane is full of instrument racks and tubing, capturing external air and measuring its chemical makeup. Fun fact: The front bathroom on the DC-8 is closed during science flights to make sure the instruments don’t accidentally measure anything ejected from the plane.

Finally, we make it all the way up to space. We’ve got a few different mechanisms for studying fires already mounted on satellites. Some of the satellites can see where active fires are burning, which helps scientists and first responders keep an eye on large swaths of land.

Some satellites can see smoke plumes, and help researchers track them as they move across land, blown by wind.

Other satellites help us track weather and forecast how the fires might behave. That’s important for keeping people safe, and it helps the FIREX-AQ team know where to fly and drive when they’ll get the most information. These forecasts use computer models, based on satellite observations and data about how fires and smoke behave. FIREX-AQ’s data will be fed back into these models to make them even more accurate.

Learn more about how NASA is studying fires from the field, here.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Thank you for joining! It’s time to find out how YOU can get involved with NASA as a student or send your experiments to the International Space Station.
One of our experts today is Hannah Johnson, the team lead of a student group sending their experiment to the space station! She is joined by Becky Kamas, our lead for STEM on Station activities for students.
Between 12-1 p.m. EDT today, our experts will talk about about designing an experiment for microgravity, working with NASA to launch it to space, how you can join this initiative, and more!
View all answers HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
The One-Year Mission
First off, what is the One-Year Crew? Obviously, they’re doing something for a year, but what, and why?
Two crew members on the International Space Station have just met the halfway point of their year in space. NASA Astronaut Scott Kelly and Russian Cosmonaut Mikhail Kornienko are living in space for 342 days and will help us better understand the effects of microgravity on the human body.
Why 342 days and not 365? Thought you might ask. Due to crew rotation schedules, which involve training timelines and dictate when launches and landings occur, the mission was confined to 342 days. Plenty of time to conduct great research though!

The studies performed throughout their stay will yield beneficial knowledge on the medical, psychological and biomedical challenges faced by astronauts during long-duration spaceflight.
The weightlessness of the space environment has various effects on the human body, including: Fluid shifts that cause changes in vision, rapid bone loss, disturbances to sensorimotor ability, weakened muscles and more.
The goal of the One-Year Mission is to understand and minimize these effects on humans while in space.
The Twins Study

A unique investigation that is being conducted during this year in space is the Twins Study. NASA Astronaut Scott Kelly’s twin brother Mark Kelly will spend the year on Earth while Scott is in space. Since their genetic makeup is as close to identical as we can get, this allows a unique research perspective. We can now compare all of the results from Scott Kelly in space to his brother Mark on Earth.
But why are we studying all of this? If we want to move forward with our journey to Mars and travel into deep space, astronauts will need to live in microgravity for long periods of time. In order to mitigate the effects of long duration spaceflight on the human body, we need to understand the causes. The One-Year mission hopes to find these answers.
Halfway Point

Today, September 15 marks the halfway point of their year in space, and they now enter the final stretch of their mission.
Here are a few fun tidbits on human spaceflight to put things in perspective:
1) Scott Kelly has logged 180 days in space on his three previous flights, two of which were Space Shuttle missions.
2) The American astronaut with the most cumulative time in space is Mkie Fincke, with 382 days in space on three flights. Kelly will surpass this record for most cumulative time in space by a U.S. astronaut on October 16.
3) Kelly will pass Mike Lopez-Alegria’s mark for most time on a single spaceflight (215 days) on October 29.
4) By the end of this one-year mission, Kelly will have traveled for 342 days, made 5,472 orbits and traveled 141.7 million miles in a single mission.
Have you seen the amazing images that Astronaut Scott Kelly has shared during the first half of his year in space? Check out this collection, and also follow him on social media to see what he posts for the duration of his #YearInSpace: Facebook, Twitter, Instagram.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Planets: As Seen by Voyager
The Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft explored Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune before starting their journey toward interstellar space. Here you’ll find some of those images, including “The Pale Blue Dot” – famously described by Carl Sagan – and what are still the only up-close images of Uranus and Neptune.
These twin spacecraft took some of the very first close-up images of these planets and paved the way for future planetary missions to return, like the Juno spacecraft at Jupiter, Cassini at Saturn and New Horizons at Pluto.
Jupiter

Photography of Jupiter began in January 1979, when images of the brightly banded planet already exceeded the best taken from Earth. They took more than 33,000 pictures of Jupiter and its five major satellites.

Findings:
Erupting volcanoes on Jupiter's moon Io, which has 100 times the volcanic activity of Earth.
Better understanding of important physical, geological, and atmospheric processes happening in the planet, its satellites and magnetosphere.
Jupiter's turbulent atmosphere with dozens of interacting hurricane-like storm systems.
Saturn

The Saturn encounters occurred nine months apart, in November 1980 and August 1981. The two encounters increased our knowledge and altered our understanding of Saturn. The extended, close-range observations provided high-resolution data far different from the picture assembled during centuries of Earth-based studies.

Findings:
Saturn’s atmosphere is almost entirely hydrogen and helium.
Subdued contrasts and color differences on Saturn could be a result of more horizontal mixing or less production of localized colors than in Jupiter’s atmosphere.
An indication of an ocean beneath the cracked, icy crust of Jupiter's moon Europa.
Winds blow at high speeds in Saturn. Near the equator, the Voyagers measured winds about 1,100 miles an hour.
Uranus

The Voyager 2 spacecraft flew closely past distant Uranus, the seventh planet from the Sun. At its closest, the spacecraft came within 50,600 miles of Uranus’s cloud tops on Jan. 24, 1986. Voyager 2 radioed thousands of images and voluminous amounts of other scientific data on the planet, its moons, rings, atmosphere, interior and the magnetic environment surrounding Uranus.

Findings:
Revealed complex surfaces indicative of varying geologic pasts.
Detected 11 previously unseen moons.
Uncovered the fine detail of the previously known rings and two newly detected rings.
Showed that the planet’s rate of rotation is 17 hours, 14 minutes.
Found that the planet’s magnetic field is both large and unusual.
Determined that the temperature of the equatorial region, which receives less sunlight over a Uranian year, is nevertheless about the same as that at the poles.
Neptune

Voyager 2 became the first spacecraft to observe the planet Neptune in the summer of 1989. Passing about 3,000 miles above Neptune’s north pole, Voyager 2 made its closest approach to any planet since leaving Earth 12 years ago. Five hours later, Voyager 2 passed about 25,000 miles from Neptune’s largest moon, Triton, the last solid body the spacecraft had the opportunity to study.

Findings:
Discovered Neptune’s Great Dark Spot
Found that the planet has strong winds, around 1,000 miles per hour
Saw geysers erupting from the polar cap on Neptune’s moon Triton at -390 degrees Fahrenheit
Solar System Portrait
This narrow-angle color image of the Earth, dubbed ‘Pale Blue Dot’, is a part of the first ever ‘portrait’ of the solar system taken by Voyager 1.

The spacecraft acquired a total of 60 frames for a mosaic of the solar system from a distance of more than 4 billion miles from Earth and about 32 degrees above the ecliptic.

From Voyager’s great distance, Earth is a mere point of light, less than the size of a picture element even in the narrow-angle camera.

“Look again at that dot. That's here. That's home. That's us. On it everyone you love, everyone you know, everyone you ever heard of, every human being who ever was, lived out their lives.” - Carl Sagan
Both spacecraft will continue to study ultraviolet sources among the stars, and their fields and particles detectors will continue to search for the boundary between the Sun's influence and interstellar space. The radioisotope power systems will likely provide enough power for science to continue through 2025, and possibly support engineering data return through the mid-2030s. After that, the two Voyagers will continue to orbit the center of the Milky Way.
Learn more about the Voyager spacecraft HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
-
 itreallyissunset liked this · 1 month ago
itreallyissunset liked this · 1 month ago -
 vhincent liked this · 1 month ago
vhincent liked this · 1 month ago -
 littleghostwitch liked this · 2 months ago
littleghostwitch liked this · 2 months ago -
 foreverangelica liked this · 6 months ago
foreverangelica liked this · 6 months ago -
 return2zero liked this · 6 months ago
return2zero liked this · 6 months ago -
 mysticangel123 liked this · 6 months ago
mysticangel123 liked this · 6 months ago -
 ladyparamount reblogged this · 6 months ago
ladyparamount reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 ladyparamount liked this · 6 months ago
ladyparamount liked this · 6 months ago -
 deepspacexavier reblogged this · 6 months ago
deepspacexavier reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 deepspacexavier liked this · 7 months ago
deepspacexavier liked this · 7 months ago -
 tineyearthling reblogged this · 8 months ago
tineyearthling reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 tineyearthling liked this · 8 months ago
tineyearthling liked this · 8 months ago -
 justatiredhuman liked this · 8 months ago
justatiredhuman liked this · 8 months ago -
 hkdroids liked this · 1 year ago
hkdroids liked this · 1 year ago -
 blackdranzer liked this · 1 year ago
blackdranzer liked this · 1 year ago -
 tisgroovy reblogged this · 1 year ago
tisgroovy reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 fractalusurper liked this · 1 year ago
fractalusurper liked this · 1 year ago -
 almostloudstarfish liked this · 1 year ago
almostloudstarfish liked this · 1 year ago -
 giant-sequoia reblogged this · 1 year ago
giant-sequoia reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 giant-sequoia liked this · 1 year ago
giant-sequoia liked this · 1 year ago -
 ganthritorchic reblogged this · 1 year ago
ganthritorchic reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 ganthritorchic liked this · 1 year ago
ganthritorchic liked this · 1 year ago -
 dandenbo liked this · 1 year ago
dandenbo liked this · 1 year ago -
 247reader liked this · 1 year ago
247reader liked this · 1 year ago -
 joasakura reblogged this · 1 year ago
joasakura reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 burnitalldowndarling reblogged this · 1 year ago
burnitalldowndarling reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 sweagen liked this · 1 year ago
sweagen liked this · 1 year ago -
 unabashedmoonhideout6969 liked this · 1 year ago
unabashedmoonhideout6969 liked this · 1 year ago -
 silviapasqua reblogged this · 1 year ago
silviapasqua reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 silviapasqua liked this · 1 year ago
silviapasqua liked this · 1 year ago -
 ljpumpernickle liked this · 1 year ago
ljpumpernickle liked this · 1 year ago -
 revans liked this · 2 years ago
revans liked this · 2 years ago -
 lazygizka reblogged this · 2 years ago
lazygizka reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 beneath-a-thousand-stars liked this · 2 years ago
beneath-a-thousand-stars liked this · 2 years ago -
 iamnotinyourworld liked this · 2 years ago
iamnotinyourworld liked this · 2 years ago -
 voidexiia liked this · 2 years ago
voidexiia liked this · 2 years ago -
 musume-no-suoh liked this · 2 years ago
musume-no-suoh liked this · 2 years ago -
 intellectualhedonist liked this · 3 years ago
intellectualhedonist liked this · 3 years ago -
 ladytisane liked this · 3 years ago
ladytisane liked this · 3 years ago -
 deceterumrerum reblogged this · 3 years ago
deceterumrerum reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 thisismytrashcanv20 reblogged this · 3 years ago
thisismytrashcanv20 reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 scintulla reblogged this · 3 years ago
scintulla reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 aeschylated reblogged this · 3 years ago
aeschylated reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 grandecappoccinu liked this · 3 years ago
grandecappoccinu liked this · 3 years ago -
 dclcq liked this · 3 years ago
dclcq liked this · 3 years ago -
 jawanaka reblogged this · 3 years ago
jawanaka reblogged this · 3 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts