The Planet Saturn, Observed By The Hubble Space Telescope.


The planet Saturn, observed by the Hubble Space Telescope.
More Posts from Xnzda and Others

Hubble’s Bubble
To celebrate 26 years in space, Hubble has captured this magnificent view of NGC 7635, better known as the Bubble Nebula. The “bubble” is created by the stellar wind from a hot, young central star that is 10-20 times the mass of our Sun.
Charting the slow death of the Universe
Paris (SPX) Aug 12, 2015 The study, which is part of the Galaxy And Mass Assembly (GAMA) project, the largest multi-wavelength survey ever put together, involved many of the world’s most powerful telescopes [1]. “We used as many space and ground-based telescopes as we could get our hands on to measure the energy output of over 200 000 galaxies across as broad a wavelength range as possible,” says Simon Driver ICRA Full article

M94: Bursting With Stars
Located about 16 million light-years away, this new Hubble image shows the sparkling galaxy Messier 94. You’ll notice the bright ring (or starburst ring) around Messier 94 where new stars are forming at a high rate. The cause of this star-forming region is thought to be a pressure wave going outwards from the galactic center, compressing the gas and dust in the outer region. The compression of material means the gas starts to collapse into denser clouds. Inside these dense clouds, gravity pulls the gas and dust together until temperature and pressure are high enough for stars to be born. (Image credit: NASA / ESA / Hubble)
Black holes

Perseus Black hole
Black holes are objects that have collapsed under their own weight to a point, creating an object that is very small but enormously dense. It is a region of space that has a gravitational pull so strong that no imminent particle or electromagnetic radiation can escape from it. This astonishing concept of black hole was first given by John Michell in 1783.He proposed that if you take the sun and compress it to a very small volume it would have a gravitational pull so strong that you have to travel at speeds greater than the speed of light to escape it.At first black holes are thought to be theoretical concepts which do not exist. But later they turned out to be very real. So how do these giant suckers form?
In order to understand the formation of a black hole we need to understand the formation and the life cycle of stars. A star is formed when large amounts of dust and gases, mainly hydrogen gas condense and collapse under its own gravitational force. As the gas collapses, the atoms of the gas collide with each other at higher and higher speeds resulting in the heating of the gas. Ultimately the gas becomes so hot that when the hydrogen atoms collide they don’t bounce off, but fuse together to form helium atoms, same as in the hydrogen bomb. As a result a large amount of heat is released which is the reason why stars shine. This heat increases the pressure of the gas until it balances out the gravitational pull and the gas stops contracting. Hence a star is formed.
The stars are usually stable as long as they have hydrogen in them. As the hydrogen runs out, the fusion reaction stops. To keep the fusion reaction going the star turns to its helium reserve. After it runs out of helium, it switches to carbon, and then oxygen. Stars with the mass of our Sun stop at this point as they don’t have enough energy to continue the fusion process and become white dwarfs. But stars with about 5 times the mass of our sun continue further to produce silicon, aluminum, potassium so on up to iron. No further energy can be produced by fusing iron atoms so the star starts to cool down. Once the external force of radiation stops acting the gravitational pull takes over and the star begins to contract. The entire mass of the star collapses into smaller and smaller volume of space. Eventually when the star has contracted to a certain critical radius, the gravitational field at the surface becomes so strong that even light cannot escape it. And this is how a black hole is formed.
Another way of formation of black hole is when two neutron stars collide with each other. When they collide their combined mass results in a very high gravitational force that leads to a collapse and a black hole is formed.

In this image, information from the Chandra X-ray Observatory is combined with images from the Hubble Space Telescope. NASA believes these two black holes are spiraling toward each other and have been doing so for 30 years.
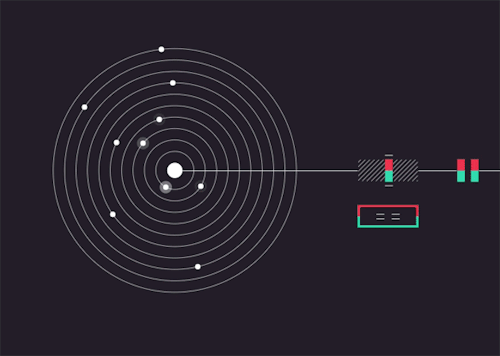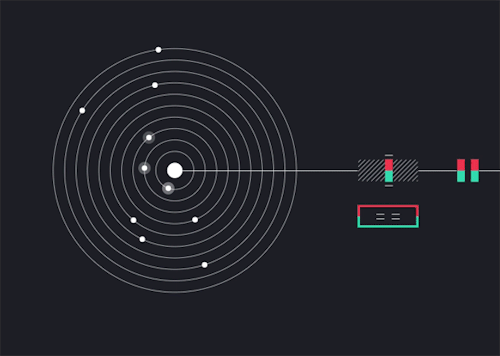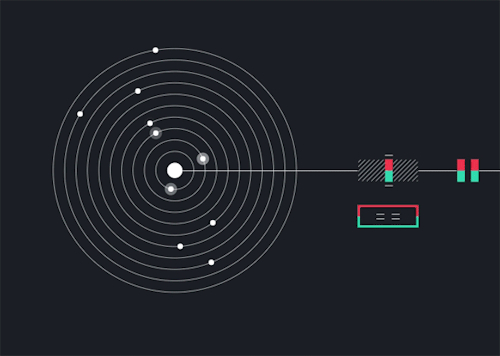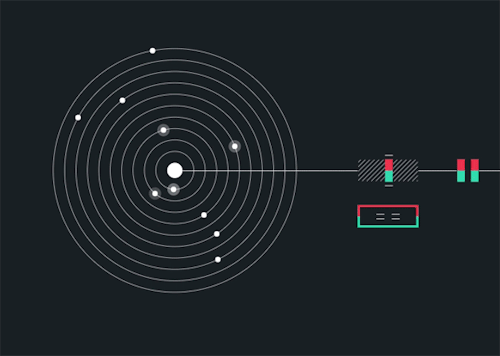
Solarbeat
This is magical. whitevinyldesign.com/solarbeat
via wired
Because every planet has its own orbital period, “it ends up generating this unending, interesting pattern,” Twyman says. For example, Mercury, which has an orbit of 88 Earth days, is the backbeat to the sound, while Pluto, which takes approximately 248 years to orbit the sun, rarely makes an appearance in the music. “It really lends itself to generating ambient music,” he says. You can tweak the speed of orbit, slowing it down to make a soothing tinkle of a child’s mobile or speeding it up to orchestrate a chaotic planetary choir. New features allow you to add sound effects like echo, flutter and bass, and you can choose from eight different chords to personalize the sound. READ MORE

In this amazing Hubble Space Telescope image, a blue bubble-like nebula surrounds a Wolf–Rayet star WR 31a, located about 30,000 light-years away in the constellation of Carina (The Keel). Wolf–Rayet stars are the most massive and brightest stars known, and their lifecycle is only a few hundred thousand years — a blink of an eye in cosmic terms.
Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt
-
 junkoabe reblogged this · 4 months ago
junkoabe reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 she-is-art-to-me liked this · 7 months ago
she-is-art-to-me liked this · 7 months ago -
 frei-nah reblogged this · 7 months ago
frei-nah reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 dotglobal liked this · 1 year ago
dotglobal liked this · 1 year ago -
 tenigam liked this · 2 years ago
tenigam liked this · 2 years ago -
 pleaselovemeliketrust liked this · 2 years ago
pleaselovemeliketrust liked this · 2 years ago -
 manyarchives reblogged this · 2 years ago
manyarchives reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 mariposible reblogged this · 2 years ago
mariposible reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 caserosblog liked this · 3 years ago
caserosblog liked this · 3 years ago -
 indosilver reblogged this · 3 years ago
indosilver reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 noelle--in--wonderland liked this · 3 years ago
noelle--in--wonderland liked this · 3 years ago -
 the-image-file reblogged this · 3 years ago
the-image-file reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 theseandi liked this · 3 years ago
theseandi liked this · 3 years ago -
 water-peony reblogged this · 3 years ago
water-peony reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 0613s liked this · 3 years ago
0613s liked this · 3 years ago -
 rctrogroove reblogged this · 3 years ago
rctrogroove reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 edgesolar liked this · 3 years ago
edgesolar liked this · 3 years ago -
 ovrystie reblogged this · 3 years ago
ovrystie reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 lemonsharkpie reblogged this · 3 years ago
lemonsharkpie reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 cotton--dandy reblogged this · 3 years ago
cotton--dandy reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 is-there-someone-else-or-not liked this · 3 years ago
is-there-someone-else-or-not liked this · 3 years ago -
 ashaaaante reblogged this · 3 years ago
ashaaaante reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 ashaaaante liked this · 3 years ago
ashaaaante liked this · 3 years ago -
 yf-21 liked this · 3 years ago
yf-21 liked this · 3 years ago -
 salvatoreroses reblogged this · 3 years ago
salvatoreroses reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 hija-de-marte reblogged this · 3 years ago
hija-de-marte reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 the-soft-parade-has-now-begun reblogged this · 3 years ago
the-soft-parade-has-now-begun reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 sorrowful-mess liked this · 3 years ago
sorrowful-mess liked this · 3 years ago -
 linapavlina liked this · 3 years ago
linapavlina liked this · 3 years ago -
 the-soft-parade-has-now-begun reblogged this · 3 years ago
the-soft-parade-has-now-begun reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 p-u-t-a-l-a-w-e-aa reblogged this · 3 years ago
p-u-t-a-l-a-w-e-aa reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 goldenshibe liked this · 3 years ago
goldenshibe liked this · 3 years ago -
 delirium-et-ratio reblogged this · 3 years ago
delirium-et-ratio reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 delirium-et-ratio liked this · 3 years ago
delirium-et-ratio liked this · 3 years ago



