
134 posts
Latest Posts by yourwriters - Page 5
Writing Tip February 26th
33 Ways to Write Stronger Characters (Part 1/3)
To Give:
1. Give them a goal. A strong goal not only gives your character purpose, it helps you map out your plot with ease.
2. Give them a motivation. Something is driving your character to chase down their goal. It could be a negative emotion like fear, guilt, or regret; a negative trait like pride, vanity, or greed; or a positive emotion like love, determination, or passion. Whatever the case, giving your character a motivation will make the actions they take to achieve their goal seem realistic and relatable.
3. Give them purpose. Consider how your character adds to the story. Do they create conflict or undergo emotional development? If not, your character will seem pointless.
4. Give them a fear. Fear is an emotion that all humans feel. It leads to insecurity, impatience, and conflict, which is why fear is the perfect emotion to include in your story. It both hooks readers and drives the plot forward. Just don’t let your characters cower in fear for long; make sure that they take action, too.
5. Give them a flaw. Perfection is boring. Imperfection is human. Write a human story by giving your character flaws. Go beyond the physical and give your character a poor personality trait, bad standing in society, or an unpleasant circumstance to live in.
6. Give them a history. Allow your character’s past to shape who they become. Give your character a rich history that will affect their present-day decisions.
7. Give them a present story. Don’t drown your novel in backstory. Give your character a present-day story, a quest or a journey that will shape and grow them.
8. Give them a personality. Don’t let your character have a dull, flat personality. Make your character complex by giving them contradictory traits and avoiding clichés at all costs.
9. Give them interests. A character that doesn’t like anything simply isn’t interesting. Give your character a passion, even if it’s one your readers will hate. Fervor breeds interest, no matter the subject.
10. Give them a quirk. Everyone has their strange habits. And strange is just as interesting as passionate. Give your character a quirk to help them stand out from the crowd.
11. Give them a name. More specifically, give your character a name with purpose. Showcase a time period, foreshadow their actions, or hint at their interests. Give your character’s name a role in your story.
12. Give them a desire. Desires are powerful motivators. Some desires may lead your character to accomplish their goal while others may lead your character away.
13. Give them a love. How can your readers love your character if your character loves no one? Your character doesn’t have to be all hugs and smiles, but they do need to hold love for at least one person if you want your readers to like them.
-She’s Novel Blog
“The bigger the issue, the smaller you write. Remember that. You don’t write about the horrors of war. No. You write about a kid’s burnt socks lying on the road. You pick the smallest manageable part of the big thing, and you work off the resonance.”
— Richard Price (via promptly-written)
Building an Unforgettable Character
Character building is one of my favorite parts of writing a novel. I love seeing where they’re going to take me and where their journey is going to end up. Even though I plot extensively before starting a new novel, I always leave room for the characters to lead me somewhere new.
So, what’s the secret to building an unforgettable character? Here are some tips to lead you in the right direction:
They need to be relatable
If your audience can’t relate to your character, that’s usually a huge problem. We relate to characters like Harry Potter not because we’ve been to Hogwarts and practiced magic, but because we can relate to his pain and to his connection with his friends. He represents emotions that a lot of us have struggled with and he doesn’t quite feel like he fits in. His struggle to find himself is relatable.
Take some time to figure out what your character ultimately represents and don’t be afraid to bring emotion into it. We want to feel connected to your characters and we want to find something in them that matches something in us.
They need to be realistic
It’s important that your character’s actions should remain realistic. Not in the sense of remaining true to our world, but to theirs. Their actions should make sense in context to what they’re going through. If you’re constantly questioning why a character would do something because it just doesn’t make logical sense, you’ll have trouble respecting that character. It’s important that we understand their actions.
They need to be proactive
A good character is a go-getter. I’m not saying they will always make the right decisions or that they’re all good people, but all main characters/protagonists should be able to do things on their own. I’m also not saying they don’t need help, but they need to overcome the big challenges on their own or through what they’ve learned. They can’t just stand around waiting for everyone else to finish things. They need to take initiative at some point, and this should be due to their personal growth throughout the story.
I understand that this point does depend on the story you’re writing. Maybe your character is an unmotivated person. Maybe they’re lazy. This usually doesn’t matter because a story isn’t interesting if that person remains inactive. They can have periods of inactivity and become unmotivated during parts of your story, but ultimately that does need to change at some point.
They need to have flaws
Flaws will humanize your character and are usually what stands in your character’s path to success. A character that does everything right all the time and doesn’t have any growth because they’re already perfect is VERY BORING. They should fail and they should learn lessons. I’m not saying all their flaws should be fixed by the end of the novel because that’s not how people operate in real life, but character flaws should help build interesting layers.
-Kris Noel
Actually
The question I get the most is how I write characters that feel like real people.
Generally when I’m designing a human being, I deconstruct them into 7 major categories:
1. Primary Drive 2. Fear: Major and Secondary 3. Physical Desires 4. Style of self expression 5. How they express affection 6. What controls them (what they are weak for) 7. What part of them will change.
1. Primary Drive: This is generally related to the plot. What are their plot related goals? How are they pulling the plot forward? how do they make decisions? What do they think they’re doing and how do they justify doing it. 2. Fear: First, what is their deep fear? Abandonment? being consumed by power? etc. Second: tiny fears. Spiders. someone licking their neck. Small things that bother them. At least 4. 3. Physical desires. How they feel about touch. What is their perceived sexual/romantic orientation. Do their physical desires match up with their psychological desires.
4. Style of self expression: How they talk. Are they shy? Do they like to joke around and if so, how? Are they anxious or confident internally and how do they express that externally. What do words mean to them? More or less than actions? Does their socioeconomic background affect the way they present themselves socially? 5. How they express affection: Do they express affection through actions or words. Is expressing affection easy for them or not. How quickly do they open up to someone they like. Does their affection match up with their physical desires. how does the way they show their friends that they love them differ from how they show a potential love interest that they love them. is affection something they struggle with?
6. What controls them (what they are weak for): what are they almost entirely helpless against. What is something that influences them regardless of their own moral code. What– if driven to the end of the wire— would they reject sacrificing. What/who would they cut off their own finger for. What would they kill for, if pushed. What makes them want to curl up and never go outside again from pain. What makes them sink to their knees from weakness or relief. What would make them weep tears of joy regardless where they were and who they were in front of.
7. WHAT PART OF THEM WILL CHANGE: people develop over time. At least two of the above six categories will be altered by the storyline–either to an extreme or whittled down to nothing. When a person experiences trauma, their primary fear may change, or how they express affection may change, etc. By the time your book is over, they should have developed. And its important to decide which parts of them will be the ones that slowly get altered so you can work on monitoring it as you write. making it congruent with the plot instead of just a reaction to the plot.
That’s it.
But most of all, you have to treat this like you’re developing a human being. Not a “character” a living breathing person. When you talk, you use their voice. If you want them to say something and it doesn’t seem like (based on the seven characteristics above) that they would say it, what would they say instead?
If they must do something that’s forced by the plot, that they wouldn’t do based on their seven options, they can still do the thing, but how would they feel internally about doing it?
How do their seven characteristics meet/ meld with someone else’s seven and how will they change each other?
Once you can come up with all the answers to all of these questions, you begin to know your character like you’d know one of your friends. When you can place them in any AU and know how they would react.
They start to breathe.
The Easiest Way to Name a Character
Nameberry.com
I have to mini-rant about this website. It’s a baby-naming site, but it is one of the best out there for authors– and I’m about to tell you why.
It’s a beautiful and organized site. And there are three main things that I love about it.
1. They have a list for everything.
Whether site-made or user-made, the list categories can range from basic to specific. Here’s a few examples: Baby Names with Animal Meanings, Biblical Place Names, Celestial Baby Names, One Syllable Baby Names, Classic Baby Names with a Twist. It’s good for when you know the country of origin of the character, you want them to have a certain tone right away, you want religious symbology, or you want something simple– whatever it is, if you have a general idea for a name, Nameberry has lists that have you covered.

2. They have THE best search engine!
For this, click on “Find A Name” in the right top corner below the search bar.

As you can see, you can get really specific. You don’t have to fill out all the boxes, so if you just want to see all names of Italian origin or all names that start with “X”, you totally can! This is especially helpful to writers with the “meaning” section. Add in that easter egg symbology!
They also have something called the Namehunter, where you put in names you like to bring up similar ones.
3. They are really in-depth with background on a name
This includes (usually): > the meaning > the origin > Commentary from “experts” (sometimes this section is BS, I ignore it.) > Famous people with that name > Pop Culture references with that name (which can include literature) > Nicknames and Variations > Variations from different languages/regions > Similar names > Popularity over the years

Trust me, if you’ve never used this website before– just try it! I love it so much, it’s so helpful. Easier than scrounging through a hundred websites for names that mean “earth” or “savior” and are also of Armenian origin.
My Personal Character Files: The 6 Box Method
This is for my science fiction WIP, so some things may need to be added/modified depending on your genre. I will also include a screenshot of an example at the bottom so y’all can see how I set it up in my Doc.
1. The Quick Ref
I use this as the first page of my “Character FIles” Doc.
I put all my important characters in a list, then add their height, age, and the page their complete file can be found on. This is helpful when I need to know if a character would have to crane their neck upward to look another character in the eyes. Comes up more than I’d have guessed.

2. The Individual Profile: 6 Box Method
I add and subtract stuff based on how important the character is. Without further ado…
Box One: Reference Photo
This is where I add in any actor, model, drawing, etc that I base the look on. When I don’t need one, sometimes I’ll put in a picture that represents the character’s style.
Box Two: The Introduction
Full Name
Nickname(s)
Age
Occupation
Current home
Situation: How do they enter this story?
Motivation: What do they want?
Favorite quote/saying
Biggest strength
Biggest issue
Strongest trait
Box Three: Behavior
Personality
Habits
Ambition/Short and Long Term Goals
Greatest fear(s)
Phobias
Biggest secret(s)
Social skills
Interior talents
Box Four: Background
Home moon/planet
Important history
Family
Friends, Enemies, Acquaintances, and Colleagues
Finances
Education
Phys. Health/Mental Health
Religion
Romantic/sexual preference
Interests/Hobbies
Box Five: Appearance & Physicality
Height
Body type
Skin tone/Ethnicity/Species
Facial description
Prominent/distinguishing features
Dress
Mannerisms
Physical talents
Box Six: Speech
Normal tone
Language & accent
Favorite phrases
3. The Example
Rey from The Force Awakens. Made in Google Docs.

Boxes 1 and 2

Boxes 3 and 4

Boxes 5 and 6
Best of luck on your writing journey!
The Ten Genres
From Save the Cat by Blake Snyder
“Take the story from ‘What is it?’ to ‘What is it most like?’”
Monster in the House
A monster, a house, and people inside the house who really want to kill the monster
House = confined space
Monster = formed from a sin committed by a character
Jaws, The Exorcist, Alien
Golden Fleece
Quest myth
A hero goes on the road for one thing and ends up with themselves
The goal is internal growth
Milestones = people and incidents that cause change within the hero
Star Wars, Back to the Future, The Road Trip
Out of the Bottle
“I wish I had a _______” + “What if?”
An underdog who does not succeed for long
Has a moral
Alternative: comeuppance in which a character with that _______ has it taken away
Bruce Almighty, Love Potion #9
Person with a Problem
An ordinary person finds themselves in unordinary circumstances
Primal problems like love or survival
An average person must solve the Problem by finding it within themselves to be the hero
The bigger the enemy, the bigger the odds to overcome and the more heroics
Terminator
Rites of Passage
Life transitions and their external conflicts
“Monster” is vague, unseen, unnamable
Ex. teenage years, vices to overcome, midlife crisis, any crisis really, old age, break up, grieving
Everybody’s in on “the joke” except the hero
Only experience can offer a solution
Victory is accepting the Problem and surrendering to it
Ladybird, Call Me By Your Name
Buddy Love
Love story in disguise
Can include romantic love, usually platonic
hate/disagreement to realizing “we need each other”
“We need each other” causes more conflict because who can tolerate needing somebody?
All is lost moment = separation, fight, goodbye-good-riddance
Resolution = surrender egos to overcome Problem
One is changed, one is the changer
Don Quixote, Thelma & Louise
Whydunit
Why over who
Does not include hero changing
Audience discovers something about human nature
Walks on dark side
All about discovery
“Are we this evil?”
Citizen Kane, Mystic River
The Fool Triumphant
Underdog and the advantages of anonymity
Set underdog against an establishment
Usually includes accomplice that’s in on the joke and gets brunt of repercussions
Outsider thrill of victory
Forrest Gump
Institutionalized
Sacrificing goals of few for the many
Groups, institutions, “families”
Honors institution AND exposes problems of losing individuality to it
Breakout character’s role is to expose group goal as a fraud
Told from newcomer’s perspective who can ask “how does this work?” and eventually: “who’s crazier: them or me?”
Group dynamic is crazy and self-destructive
Pros and cons of community over self
Loyalty can blind common sense
One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest, August: Osage County
Superhero
Extraordinary person finds themselves in an ordinary world
Foster empathy through hero being misunderstood, their pitfalls and disadvantages, and human qualities
Zoolander, X-Men, Gladiator, Dracula
Hey! Do you have any tips for people who've reached a block in their writing? I've been trying to plan out a plot for my book, but I've reached a point where I can't think of anything else
What to Do If You Get Stuck While Outlining Your Plot
Hi! Thanks for writing. Getting blocked can happen at all stages: Before writing, during writing, during outlining, in the idea stage, etc. But since you specifically said you’re reaching a block in your plot planning, I’ll address that :)
#1 Make sure your character’s motivation & conflict are “big” enough
If your character doesn’t have a book-length problem, you can get stuck trying to fill in empty space in the plot. In order to find more events to flesh out your story, you may need to make adjustments. Is their desire strong enough to fuel a book? Is the conflict big enough? Is their problem difficult to solve? If not, how can you make their problem harder? Or take longer to resolve?
You might need a combination of a fiercer desire, a bigger problem, more problems, more obstacles, and/ or a more stubborn antagonist to reveal potential scenes and events. For help with your character’s motivation and conflict, check out the PDF “Creating Character Arcs” in my Free Resource Library.
#2 Plot your story backwards
This can help you make sure you have a strong enough ending and open up new possibilities you might not have noticed while plotting forward. I have a post about it here.
#3 Use the but/therefore method
The but/therefore method is a great way to fill holes. It tests the cause-effect connections between your plot and character and almost always reveals gaps that need to be addressed with new or stronger scenes. Use this template for each scene or chapter:
Main character wants ______, but _______, therefore ______.
What comes after “wants” is the motivation for that chapter or scene. After “but” goes the conflict or obstacle. After “therefore” is the result or action the character takes, which leads into the next goal, and so on, and so on.
Chapter-by-chapter it might look something like this:
Chapter 1: Julian wants to ask Matt to the dance, but he’s scared of being rejected, therefore he slips a cryptic note into Matt’s locker.
Chapter 2: Matt doesn’t see the note. Now Julian wants to get into his locker and retrieve it, but the principal sees him trying to jimmy open the lock, therefore Julian is given detention for a week.
You can also do this scene-by-scene. My suggestion would be to start with the chapter outline, see what it reveals, then move into the scenes if you still feel stuck.
#4 Ask questions
Classic un-sticking questions start with “what if” or “why”? Asking questions can unlock new story directions you might not have noticed were there before.
What if the main character’s ex-boyfriend came back to town? What if they didn’t achieve that small goal back in chapter 4? What if they were hiding something? etc.
Why are they avoiding their sister? Why is it so difficult for them to apologize? Why haven’t they quit their job if they hate it so much? etc.
#5 Consider creating a subplot (or two or three)
A book-length story usually needs a few side stories to flesh out the main one. Look for areas of your story that could be expanded, characters that might take the story down a related tangent, and conflicts that seem small but could be bigger with some digging.
#6 Take a break
Sometimes, you just need to give it a rest. Walk away from your outline for at least a week. When you come back, you may see things you didn’t see before and be able to breathe new life into it. In the meantime, let your mind wander. It’s amazing what creative solutions writers can come up with when they aren’t “trying.”
//////////////
The Literary Architect is a writing advice blog run by me, Bucket Siler. For more writing help, check out my Free Resource Library, peruse my post guide, or hire me to edit your novel or short story. xoxo
I was wondering if you knew any basic guides to outlining a novel for the first time?
Outlining a story is very, very important. Without an outline and thorough planning, your story will veer off in wildly different directions and will cost you a ton of time editing later, like my book did.
1. Get the characters down first
Characters are like the chess pieces of the story. Their moves and strengths/weaknesses will decide what is going to happen and how it will happen. Sure, you can have a nice plot and setting, but without the characters, the story is meaningless.
Here is the character chart that I usually use:
Name (First/Middle/Last/Maiden name)
Aliases/Nicknames
Age
Race
Gender
Sexuality
Height
Weight
Eye color
Hair color
Clothing style
Religion
Political views
Personality Traits
Strengths and Weaknesses
Likes and Dislikes
Family
Friends
Enemies
Role in the story
Backstory/past
2. Choose a template
Just bulleting the events does not give the plot the dimension that it deserves and does not really accommodate side plots.
I personally use the zigzag method that I discovered from this post. I branch off of the zigzags for my side plots so it looks kind of like a graph.

You can also use the subway method, which I found on the nanowrimo website.
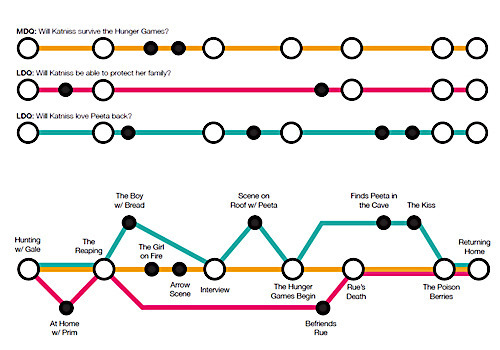
There are a whole other host of outlines to choose from if you search them up!
3. Know that you don’t have to stick to it
An outline is just that: an outline. It’s not the final decision for the plot, it’s the first draft for the plot. If you’re writing and one of the points just isn’t working anymore, you don’t have to keep it because it was a part of your outline.
Write what feels right.
Happy outlining, and good luck with your story!
I’m wondering, how do I come up with good ideas to write a sub-plot that actually fits into the story and won’t make the reader lose the connection with the main plot?
How to Write A Sub Plot

If you look back on every single bestselling book ever printed, the chances are that most, if not all of them, contain sub-plots.
A sub-plot is part of a book that develops separately from the main story, and it can serve as a tool that extends the word count and adds interest and depth into the narrative.
Sub-plots are key to making your novel a success, and, although they aren’t necessary for shorter works, are an essential aspect of story writing in general.
However, sub-plots can be difficult to weave into the main plot, so here are a few tips on how to incorporate sub-plots into your writing.
1. Know Your Kinds of Sub-Plots and Figure Out Which is Best For Your Story

Sub-plots are more common than you think, and not all of them extend for many chapters at a time.
A sub-plot doesn’t have to be one of the side characters completely venturing off from the main group to struggle with their own demons or a side quest that takes up a quarter of the book. Small things can make a big difference, and there are many of these small things that exist in literature that we completely skip over when it comes to searching for sub-plots.
Character Arcs
Character arcs are the most common sub-plot.
They show a change in a dynamic character’s physical, mental, emotional, social, or spiritual outlook, and this evolution is a subtle thing that should definitely be incorporated so that the readers can watch their favorite characters grow and develop as people.
For example, let’s say that this guy named Bob doesn’t like his partner Jerry, but the two of them had to team up to defeat the big bad.
While the main plot involves the two of them brainstorming and executing their plans to take the big bad down, the sub-plot could involve the two getting to know each other and becoming friends, perhaps even something more than that.
This brings me to the second most common sub-plot:
Romance
Romance can bolster the reader’s interest; not only do they want to know if the hero beats the big bad guy, they also want to know if she ends up with her love interest in the end or if the warfare and strife will keep them apart.
How to Write Falling in Love
How to Write a Healthy Relationship
How to Write a Romance
Like character arcs, romance occurs simultaneously with the main plot and sometimes even influences it.
Side-Quests
There are two types of side-quest sub-plots, the hurtles and the detours.
Hurdle Sub-Plots
Hurdle sub-plots are usually complex and can take a few chapters to resolve. Their main purpose is to put a barrier, or hurdle, between the hero and the resolution of the main plot. They boost word count, so be careful when using hurdle sub-plots in excess.
Think of it like a video game.
You have to get into the tower of a fortress to defeat the boss monster.
However, there’s no direct way to get there; the main door is locked and needs to have three power sources to open it, so you have to travel through a monster-infested maze and complete all of these puzzles to get each power source and unlock the main door.
Only, when you open the main door, you realize that the bridge is up and you have to find a way to lower it down and so forth.
Detour Sub-Plot
Detour sub-plots are a complete break away from the main plot. They involve characters steering away from their main goal to do something else, and they, too, boost word count, so be careful not too use these too much.
Taking the video game example again.
You have to get to that previously mentioned fortress and are on your way when you realize there is an old woman who has lost her cattle and doesn’t know what to do.
Deciding the fortress can wait, you spend harrowing hours rounding up all of the cows and steering them back into their pen for the woman.
Overjoyed, the woman reveals herself to be a witch and gives you a magical potion that will help you win the fight against the big bad later.
**ONLY USE DETOUR SUB-PLOTS IF THE OUTCOME HELPS AID THE PROTAGONISTS IN THE MAIN PLOT**
If they’d just herded all of the cows for no reason and nothing in return, sure it would be nice of them but it would be a complete waste of their and the readers’ time!
2. Make Sure Not to Introduce or Resolve Your Sub-Plots Too Abruptly

This goes for all sub-plots. Just like main plots, they can’t be introduced and resolved with a snap of your fingers; they’re a tool that can easily be misused if placed into inexperienced hands.
Each sub-plot needs their own arc and should be outlined just like how you outlined your main plot.
How to Outline Your Plot
You could use my methods suggested in the linked post, or you could use the classic witch’s hat model if you feel that’s easier for something that’s less important than your main storyline.

3. Don’t Push It

If you don’t think your story needs a sub-plot, don’t add a sub-plot! Unneeded sub-plots can clutter up your narrative and make it unnecessarily winding and long.
You don’t have to take what I’m saying to heart ever!
It’s your story, you write it how you think it should be written, and no one can tell you otherwise!
Hope this Helped!
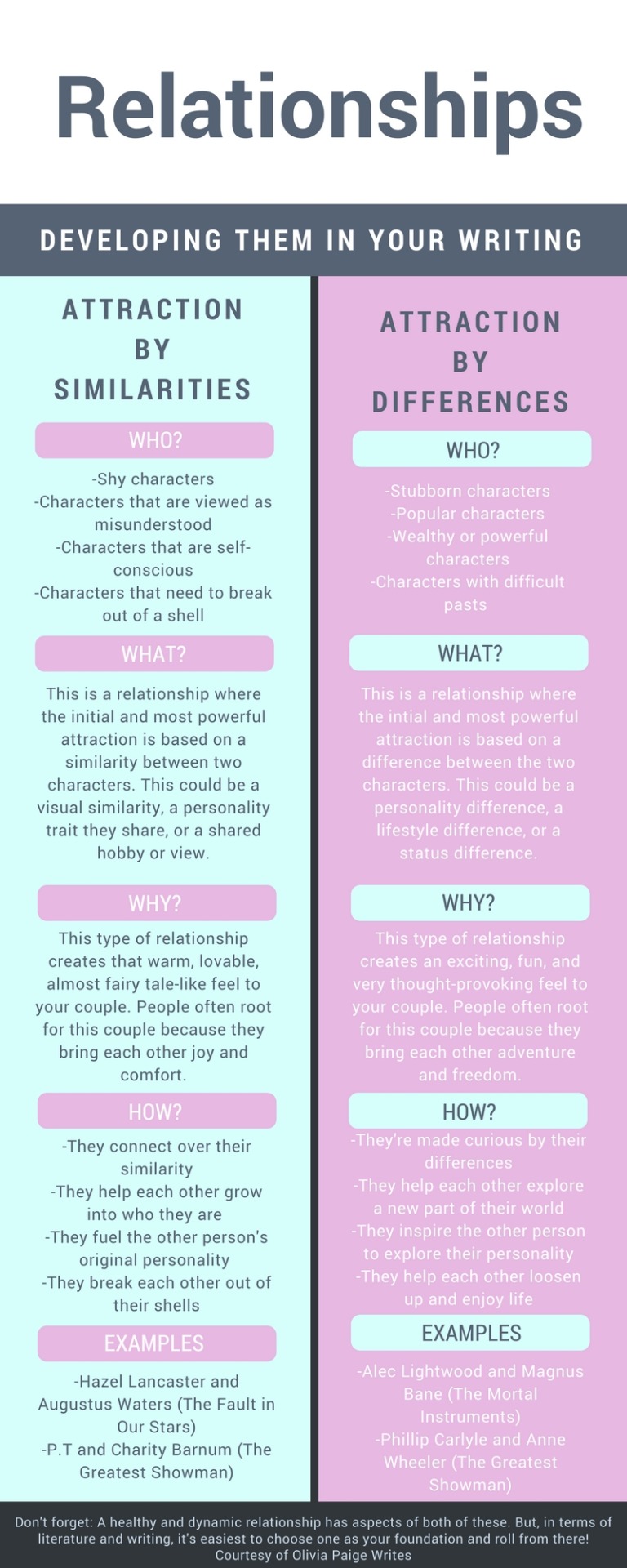
Writing great friendships
Some of the best chemistry/relationships in fiction exist between characters who are/become friends. Here are some tips for making friendships come alive on the page:
1. Banter
One of the most interesting aspects of fictional friendships is the way the characters interact with each other whilst important plot points are occurring.
If your characters have easy banter, teasing one another without missing a beat and managing to bounce off each other even in the toughest circumstances, it will be clear to the reader that these two are/should be good friends.
Friends know each other well. They know the other’s character so well that they can easily find something to tease each other over. However, this also means knowing which topics are off-limits.
If you want to write a good, healthy friendship, your characters shouldn’t use humour/sarcasm as a way to hurt the other. It should be good-natured and understood as such from both sides.
Different friendships will have different types of chemistry. Some friends may tease each other with facial expressions. Others may already anticipate a snarky remark and counter it before it’s been spoken. Others will have physical ways of goofing around.
Some friends might not tease each other at all. Banter isn’t necessary; it’s just a good way to make your characters come alive and make their friendship one that is loved by readers.
What’s important is chemistry - the way they automatically react to each other.
Think Sam and Dean in Supernatural or Juliette and Kenji in the Shatter Me series.
2. Mutual support
Unless you purposefully want to write an unhealthy/toxic friendship, your characters should both be supportive of the other.
This means that, even if one is the MC and the other the side-kick, both should be cognisant of the other’s feelings and problems, and should be considerate in this regard.
Few things will make your MC as likable as remembering to check in and be there for their best friend even when they are in the thick of a crisis.
You need to show your characters being vulnerable in front of each other and being supportive in ways that are tailored to the needs of each friend.
So, if one of the characters really responds to physical comfort, the other should know to give hugs/rub their back when they’re not feeling well. Similarly, if one of them doesn’t like being touched and responds to material comfort, have the other bring them ice cream and join them for a movie marathon. Whatever works for your characters.
What gets me every time is when a character is falling apart and won’t listen to/be consoled by anyone but their best friend (but this is just personal preference).
3. Knowing the other’s past/family life
This really only applies to characters who have been friends for quite a while.
Good friends know each other’s backstory - the highs and lows and mundane details. They know they layout of their family home and they probably know their family members well.
Friends will often talk about these things, only having to mention a few words for the other to know what they’re talking about i.e. “The ‘09 Thanksgiving disaster” or “You know how Uncle Fred is”
This will instantly make it clear that your characters are close and have come a long way together.
Perhaps there are issues at home/trauma from the past that the other character will immediately understand. So, if one character appears with a black eye, their friend might know that the father was probably drunk the night before and got violent. Or if the character has a nightmare, the friend might know that it was about childhood abuse etc.
This can also apply to good things i.e. if one of the characters gets a nice note in their lunchbox, the other might know that their grandma is in town.
Whatever works for your story should be used to indicate the level of unspoken understanding the friends have.
4. Being protective
Few things will make your readers love a friendship more than the friends being fiercely protective of each other (in a healthy, non-territorial way).
Has someone hurt one of the characters? The other should be furious and want to exact revenge. Does someone say something demeaning to one of the friends? The other should defend them immediately and vehemently.
This can also take on a humorous twist if one of the characters starts dating someone. The friend can make extra sure that said date is sincere and promise to exact vengeance if their friend is hurt.
This can also be a great plot device, since it could explain why the MC’s best friend joins the quest/goes along on the journey. Perhaps this is the main plot point: a character seeking to protect/avenge their friend.
If you want to go in a toxic direction, this can be taken too far i.e. a friend who never lets the other spend time with anyone else/stalks the other/is patronising etc.
5. Common interest(s)
Even if the two characters are vastly different, there should be something that keeps them together besides loyalty.
This is especially important for characters who become friends throughout the course of the novel.
This doesn’t have to mean that both of them go hiking every weekend or want to become pilots one day. It could be something small, like a love of cheesy movies or a shared taste in music. Maybe they both enjoy silence/don’t like other people. Maybe they are both social justice warriors, but for different causes.
This could also be common characteristics instead of interests. Perhaps both are very ambitious/funny/social.
There should just be some factor that ignited the friendship and brings the two of them together.
This doesn’t necessarily have to be a big part of your story, but you should at least have it mentioned to make the friendship appear more authentic.
Reblog if you found these tips useful. Comment if you would like a Part 2. Follow me for similar content.

About Conflict by Sacha Black
Hey, a chart! This is inspired by an ask I got (I’m gonna be honest, I promised the person I’d tag them, but then sent the reply before I wrote down the URL. So, if I told you I was gonna tag you in this, tag yourself!!)
