Curate, connect, and discover
Solar System - Blog Posts
What range/area will Perseverance be able to cover on the Martian surface? I'm assuming it's greater than the other rovers but by how much?
Do you have any messages or tips for other girls who want to study and work in STEM fields?
Why do scientists think there could have been life on Mars?
What were some of the biggest challenges in this project and how did you overcome them?
How have you used the experience gained from Curiosity to make Perseverance better? Like, Curiosity's wheels are showing wear and tear, so is there something different about Perseverance's wheels?
What is the most exciting thing you hope to learn?
What, in your opinion, is Perseverance's most groundbreaking experiment/ instrument?
Will Perseverance be near any other Rovers?
What will scientists do if Perseverance does find signs of life on Mars?
Why does it take so long for the rover to reach Mars?


The answers are IN for your questions about our Perseverance rover and her upcoming mission to Mars!
Sit back, relax, and get ready to learn some science and engineering! Experts Sarah Stewart Johnson and Lauren DuCharme are here to talk about the July 30 launch of our Perseverance mission, women in STEM, and much more.
Our Answer Time starts now!
See the Closest Ever Images of the Sun
Solar Orbiter just released its first scientific data — including the closest images ever taken of the Sun.
Launched on February 9, 2020, Solar Orbiter is a collaboration between the European Space Agency and NASA, designed to study the Sun up close. Solar Orbiter completed its first close pass of the Sun on June 15, flying within 48 million miles of the Sun’s surface.
This is already closer to the Sun than any other spacecraft has taken pictures (our Parker Solar Probe mission has flown closer, but it doesn’t take pictures of the Sun). And over the next seven years, Solar Orbiter will inch even closer to the Sun while tilting its orbit above the plane of the planets, to peek at the Sun’s north and south poles, which have never been imaged before.
Here’s some of what Solar Orbiter has seen so far.
The Sun up close

Solar Orbiter’s Extreme Ultraviolet Imager, or EUI, sees the Sun in wavelengths of extreme ultraviolet light that are invisible to our eyes.

EUI captured images showing “campfires” dotting the Sun. These miniature bright spots are over a million times smaller than normal solar flares. They may be the nanoflares, or tiny explosions, long thought to help heat the Sun’s outer atmosphere, or corona, to its temperature 300 times hotter than the Sun’s surface. It will take more data to know for sure, but one thing’s certain: In EUI’s images, these campfires are all over the Sun.

The Polar and Helioseismic Imager, or PHI, maps the Sun’s magnetic field in a variety of ways. These images show several of the measurements PHI makes, including the magnetic field strength and direction and the speed of flow of solar material.
PHI will have its heyday later in the mission, as Solar Orbiter gradually tilts its orbit to 24 degrees above the plane of the planets, giving it a never-before-seen view of the poles. But its first images reveal the busy magnetic field on the solar surface.
Studying space
Solar Orbiter’s instruments don’t just focus on the Sun itself — it also carries instruments that study the space around the Sun and surrounding the spacecraft.

The Solar and Heliospheric Imager, or SoloHi, looks out the side of the Solar Orbiter spacecraft to see the solar wind, dust, and cosmic rays that fill the space between the Sun and the planets. SoloHi captured the relatively faint light reflecting off interplanetary dust known as the zodiacal light, the bright blob of light in the right of the image. Compared to the Sun, the zodiacal light is extremely dim – to see it, SoloHi had to reduce incoming sunlight by a trillion times. The straight bright feature on the very edge of the image is a baffle illuminated by reflections from the spacecraft’s solar array.

This first data release highlights Solar Orbiter’s images, but its in situ instruments also revealed some of their first measurements. The Solar Wind Analyser, or SWA instrument, made the first dedicated measurements of heavy ions — carbon, oxygen, silicon, and iron — in the solar wind from the inner heliosphere.
Read more about Solar Orbiter’s first data and see all the images on ESA’s website.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How to See Comet NEOWISE
Observers all over the world are hoping to catch a glimpse of Comet NEOWISE before it speeds away into the depths of space, not to be seen again for another 6,800 years.
For those that are, or will be, tracking Comet NEOWISE there will be a few particularly interesting observing opportunities this week.

Over the coming days it will become increasingly visible shortly after sunset in the northwest sky.

The object is best viewed using binoculars or a small telescope, but if conditions are optimal, you may be able to see it with the naked eye. If you’re looking in the sky without the help of observation tools, Comet NEOWISE will likely look like a fuzzy star with a bit of a tail. Using binoculars will give viewers a good look at the fuzzy comet and its long, streaky tail.
Here’s what to do:
Find a spot away from city lights with an unobstructed view of the sky
Just after sunset, look below the Big Dipper in the northwest sky
Each night, the comet will continue rising increasingly higher above the northwestern horizon.

There will be a special bonus for viewers observing comet NEOWISE from the northeast United States near Washington, DC. For several evenings, there will be a brief conjunction as the International Space Station will appear to fly near the comet in the northeast sky. Approximate times and locations of the conjunctions are listed below (the exact time of the conjunction and viewing direction will vary slightly based on where you are in the Washington, DC area):
July 17 : ~10:56 p.m. EDT = NEOWISE elevation: ~08° Space Station elevation: ~14°
July 18 : ~10:08 p.m. EDT = NEOWISE elevation: ~13° Space Station elevation: ~18°
July 19 : ~10:57 p.m. EDT = NEOWISE elevation: ~10° Space Station elevation: ~08°
July 20 : ~10:09 p.m. EDT = NEOWISE elevation: ~17° Space Station elevation: ~07°
It will be a late waning Moon, with the New Moon on July 20, so the viewing conditions should be good as long as the weather cooperates.
Comet NEOWISE is about 3 miles across and covered in soot left over from its formation near the birth of our solar system 4.6 billion years ago - a typical comet.

Comets are frozen leftovers from the formation of the solar system composed of dust, rock and ices. They range from a few miles to tens of miles wide, but as they orbit closer to the sun, they heat up and spew gases and dust into a glowing head that can be larger than a planet. This material forms a tail that stretches millions of miles.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Clouds swirling in the coffee colored atmosphere of Jupiter, looks more like a familiar morning beverage of champions.
This image from our Juno spacecraft was captured in North North Temperate Belt. Image Credit: Enhanced Image by Gerald Eichstädt and Sean Doran (CC BY-NC-SA)/NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Excited about the #CountdownToMars? We've got you covered.
We've created a virtual Mars photo booth, 3D rover experience and more for you to put your own creative touch on wishing Perseverance well for her launch to the Red Planet! Check it out, HERE.
Don’t forget to mark the July 30 launch date on your calendars!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com


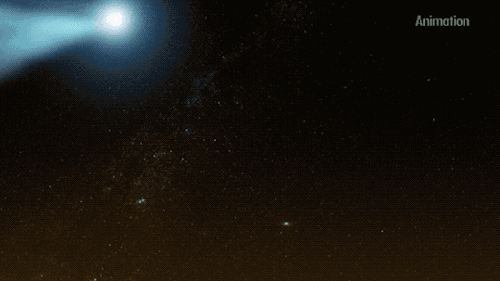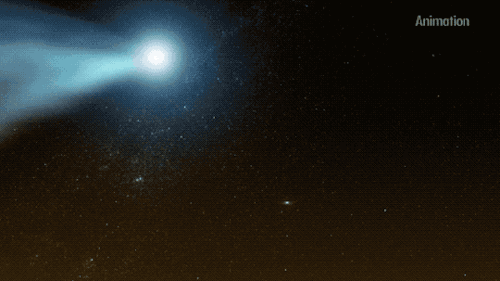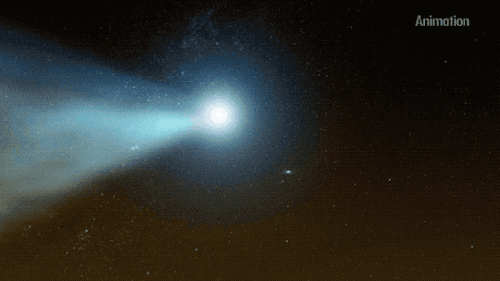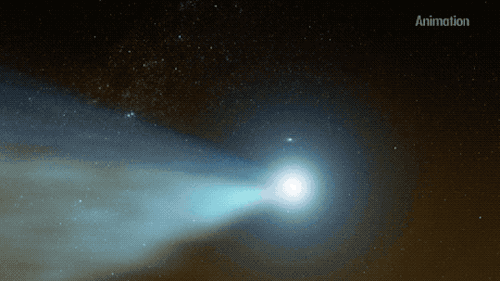
Whilst practicing solar distancing, Parker Solar Probe caught this rare glimpse of the twin tails on comet NEOWISE.☄
The twin tails are seen more clearly in this WISPR instrument processed image, which increased contrast and removed excess brightness from scattered sunlight, revealing more de-"tails". C/2020 F3 NEOWISE was discovered by our Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (NEOWISE), on March 27. Since it's discovery the comet has been spotted by several NASA spacecraft, including Parker Solar Probe, NASA’s Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory, the ESA/NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, and astronauts aboard the International Space Station.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Our friend - the Moon - is putting on a show tonight!
Look to the sky at 12:44 a.m. EDT to see the first full Moon of summer in the Northern Hemisphere and a partial penumbral eclipse, visible from most of North America. Want more info on this special occurrence? click HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Today we celebrate the mission that piqued our curiosities, and drove NASA’s perseverance to pursue further exploration of the Red Planet. The Sojourner rover landed on July 4, 1997, after hitching a ride aboard the Mars Pathfinder mission. Its innovative design became the template for future missions. The rover, named after civil rights pioneer Sojourner Truth, outlived its design life 12 times. This panoramic view of Pathfinder's Ares Vallis landing site shows Sojourner rover is the distance. Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Have You Ever Seen An Eclipse From Space? Check It Out
On June 21, 2020 an annular solar eclipse passed over parts of Asia and Africa. Eclipses happen when the Moon lines up just right between the Sun and Earth, allowing it to block out part or all of the Sun’s bright face and cast a shadow on Earth.

On that day, the International Space Station was orbiting over Kazakhstan and into China when this picture of the solar eclipse shadowing a portion of the Asian continent was captured by an external high definition camera. In the left foreground, is the H-II Transfer Vehicle-9 from Japan.

Here is another angle as seen from the orbital lab. In the left foreground, is the Progress 74 resupply ship from Russia.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Meet the people behind our next Mars rover – Perseverance.
Sending a rover to the Red Planet is more than just 3…2…1… Liftoff 🚀
It takes thousands of people and years of hard work to get a spacecraft from Earth to Mars. So when our Perseverance (Percy) rover touches down on the Martian surface, it will be because of the talented minds that helped to make it happen.
The team is on track to launch Perseverance on July 20 and land in Mars’ Jezero Crater in February 2021. Each week leading up to launch, learn not only what it’s like to work on this mission but also about the diverse background and career trajectories of the team members at our Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Want to stay up to date on Percy’s mission? Follow her on Twitter and Facebook. For more information, visit the official mission site, HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Our water-seeking robotic Moon rover just booked a ride to the Moon’s South Pole. Astrobotic of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, has been selected to deliver the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, or VIPER, to the Moon in 2023. During its 100-Earth-day mission, the approximately 1,000-pound rover will roam several miles and use its four science instruments to sample various soil environments in search of water ice. Its survey will help pave the way for a new era of human missions to the lunar surface and will bring us a step closer to developing a sustainable, long-term robotic and human presence on the Moon as part of the Artemis program.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How is it like to be a NASA Earth Scientist? What Subjects are you required to excel at to become one? Were you really good in your studies, when you were a young teenager?
Hi there! Does the study of Earth Science teach us much about the science of other planets? Can much be assumed to be similar, or is the geology/biology incomparable? Thank you!
Are there any parts of the Earth still left unexplored?
Is Earth your favorite planet? Why or why not?

Participate in the 50th anniversary of Earth Day by asking our experts anything about NASA’s role in Earth Science!
This year marks the 50th anniversary of Earth Day, and to commemorate the big day we’re bringing you exclusive access our Acting Director of Earth Sciences, Sandra Cauffman, and Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate, Dr. Thomas Zurbuchen! They will be teaming up to take your questions in an Answer Time session on Earth Day, April 22, from 12-1pm EDT here on NASA’s Tumblr! Make sure to ask your question now by visiting http://nasa.tumblr.com/ask!
Our investment in space – both the unique Earth science we conduct from orbit and the technology we’ve developed by living in space and exploring our solar system and universe – is returning benefits every day to people around the world, particularly those who are working on environmental issues. From documenting Earth’s changing climate to creating green technologies to save energy and natural resources, we’re working to help us all live more sustainably on our home planet and adapt to natural and human-caused changes.

NASA Earth Science Fun Facts!
From space we study: dust storms, volcanoes, flooding, coral reefs, night lights, wildfires, urban growth, food production, mosquito tracking and other human health issues, precipitation across the world, hurricanes and typhoons, soil moisture, land and sea ice, and changes to the land and sea surfaces.
From airborne research planes we track: changes in polar ice, glaciers, sea level rise, cloud formation, storms, sea level rise and Earth’s changing landscape.
Our Earth science focus areas include: Atmospheric Composition, Weather and Atmospheric Dynamics, Climate Variability and Change, Water and Energy Cycle, Carbon Cycle and Ecosystems, Earth Surface and Interior
Keep up to date with all our Earth Science missions and research by following NASA Earth on Twitter, Facebook and Instagram.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Up for some virtual cloud watching? ☁️
What do you see in Jupiter's hazy atmosphere?
Our NASA JunoCam mission captured this look at the planet’s thunderous northern region during the spacecraft’s close approach to the planet on Feb. 17, 2020.
Some notable features in this view are the long, thin bands that run through the center of the image from top to bottom. Juno has observed these long streaks since its first close pass by Jupiter in 2016.
Image Credits: Image data: NASA / JPL / SwRI / MSSS Image Processing: Citizen Scientist Eichstädt
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Cosmic Piece of Pi!
Did you know that pi is involved nearly anywhere you look? We’re not talking about your favorite pastry! Pi (also written as the Greek letter 𝞹, or the number 3.14159...) is an irrational number, which means it can’t be written as a simple fraction like ½. It is the ratio of a circle’s circumference (the distance around its edge) to its diameter (the distance across it) and will always be the same number, regardless of the circle’s size. Here are some places you can find pi in the universe around us!

Our Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite, TESS, watches slices of the sky in its hunt for worlds outside our solar system — how many exoplanets are in its night-sky pie? Last July, TESS scientists created a mosaic of 208 images of the southern sky. At that time, it contained 29 confirmed and 1,000 possible exoplanets, and we’re still studying the data to find more. Since this awe-inspiring image is of the southern hemisphere (or half of a 3D circle), there will always be pi! Every slice contains something delicious for scientists to study.

Pi recently played a crucial role in new discoveries about Alpha Draconis, a well-studied pair of stars. After discovering these stars regularly eclipse each other, pi helped scientists learn more about them. Scientists detected the eclipses while monitoring the brightness of Alpha Draconis for periodic dips that could’ve been caused by planets passing between the star and us. Instead of a planet, though, researchers found that its smaller partner in crime was passing in between us and the larger star for about six hours at a time! 💫

Pi comes in handy as we learn more about these two stars. Knowing the percentage of the decrease in Alpha Draconis’ light and the formula for the area of a circle (A=𝞹r2 — or area equals pi times the square of the circle's radius), scientists can predict the sizes of both stars. Because stars typically orbit in an elliptical (or oval) shape, pi also helps scientists use the detection of these eclipses to figure out the orbits of the two stars!
So far we’ve seen pi in many places! But it's also interesting to look at where pi can't be found! We mentioned earlier that many orbit calculations involve pi … but not every one does! Pi does not factor into calculations of hyperbolic orbits — orbits that aren't complete, or don't return to where they started — the same way that it does with elliptical orbits! This is most commonly seen with comets. While many comets orbit normally in our solar system, some oddballs just pass through, like the interstellar ‘Oumuamua that zipped passed us in 2017. ☄️

Perhaps the most popular place you may find pi is in the shape of a typical pie! While NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope studies gamma-rays, and not blueberries, we think this cool Fermi pie is worth sharing for Pi Day!
Find more ways scientists look up at the night sky and use pi here. And now, don’t be irrational, and go have some pi(e)! 🥧
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Weird Magnetic Behavior in Space
In between the planets, stars and other bits of rock and dust, space seems pretty much empty. But the super-spread out matter that is there follows a different set of rules than what we know here on Earth.
For the most part, what we think of as empty space is filled with plasma. Plasma is ionized gas, where electrons have split off from positive ions, creating a sea of charged particles. In most of space, this plasma is so thin and spread out that space is still about a thousand times emptier than the vacuums we can create on Earth. Even still, plasma is often the only thing out there in vast swaths of space — and its unique characteristics mean that it interacts with electric and magnetic fields in complicated ways that we are just beginning to understand.

Five years ago, we launched a quartet of satellites to study one of the most important yet most elusive behaviors of that material in space — a kind of magnetic explosion that had never before been adequately studied up close, called magnetic reconnection. Here are five of the ways the Magnetospheric Multiscale mission (MMS) has helped us study this intriguing magnetic phenomenon.
1. Seeing magnetic explosions up close
Magnetic reconnection is the explosive snapping and forging of magnetic fields, a process that can only happen in plasmas — and it's at the heart of space weather storms that manifest around Earth.
When the Sun launches clouds of solar material — which is also made of plasma — toward Earth, the magnetic field embedded within the material collides with Earth's huge global magnetic field. This sets off magnetic reconnection that injects energy into near-Earth space, triggering a host of effects — induced electric currents that can harm power grids, to changes in the upper atmosphere that can affect satellites, to rains of particles into the atmosphere that can cause the glow of the aurora.

Though scientists had theorized about magnetic reconnection for decades, we'd never had a chance to study it on the small scales at which it occurs. Determining how magnetic reconnection works was one of the key jobs MMS was tasked with — and the mission quickly delivered. Using instruments that measured 100 times faster than previous missions, the MMS observations quickly determined which of several 50-year-old theories about magnetic reconnection were correct. It also showed how the physics of electrons dominates the process — a subject of debate before the launch.
2. Finding explosions in surprising new places
In the five years after launch, MMS made over a thousand trips around Earth, passing through countless magnetic reconnection events. It saw magnetic reconnection where scientists first expected it: at the nose of Earth's magnetic field, and far behind Earth, away from the Sun. But it also found this process in some unexpected places — including a region thought to be too tumultuous for magnetic reconnection to happen.
As solar material speeds away from the Sun in a flow called the solar wind, it piles up as it encounters Earth's magnetic field, creating a turbulent region called the magnetosheath. Scientists had only seen magnetic reconnection happening in relatively calm regions of space, and they weren't sure if this process could even happen in such a chaotic place. But MMS' precise measurements revealed that magnetic reconnection happens even in the magnetosheath.

MMS also spotted magnetic reconnection happening in giant magnetic tubes, leftover from earlier magnetic explosions, and in plasma vortices shaped like ocean waves — based on the mission's observations, it seems magnetic reconnection is virtually ubiquitous in any place where opposing magnetic fields in a plasma meet.
3. How energy is transferred
Magnetic reconnection is one of the major ways that energy is transferred in plasma throughout the universe — and the MMS mission discovered that tiny electrons hold the key to this process.
Electrons in a strong magnetic field usually exhibit a simple behavior: They spin tight spirals along the magnetic field. In a weaker field region, where the direction of the magnetic field reverses, the electrons go freestyle — bouncing and wagging back and forth in a type of movement called Speiser motion.

Flying just 4.5 miles apart, the MMS spacecraft measured what happens in a magnetic field with intermediate strength: These electrons dance a hybrid, meandering motion — spiraling and bouncing about before being ejected from the region. This takes away some of the magnetic field’s energy.
4. Surpassing computer simulations
Before we had direct measurements from the MMS mission, computer simulations were the best tool scientists had to study plasma's unusual magnetic behavior in space. But MMS' data has revealed that these processes are even more surprising than we thought — showing us new electron-scale physics that computer simulations are still trying to catch up with. Having such detailed data has spurred theoretical physicists to rethink their models and understand the specific mechanisms behind magnetic reconnection in unexpected ways.

5. In deep space & nuclear reactions
Although MMS studies plasma near Earth, what we learn helps us understand plasma everywhere. In space, magnetic reconnection happens in explosions on the Sun, in supernovas, and near black holes.
These magnetic explosions also happen on Earth, but only under the most extreme circumstances: for example, in nuclear fusion experiments. MMS' measurements of plasma's behavior are helping scientists better understand and potentially control magnetic reconnection, which may lead to improved nuclear fusion techniques to generate energy more efficiently.

This quartet of spacecraft was originally designed for a two-year mission, and they still have plenty of fuel left — meaning we have the chance to keep uncovering new facets of plasma's intriguing behavior for years to come. Keep up with the latest on the mission at nasa.gov/mms.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
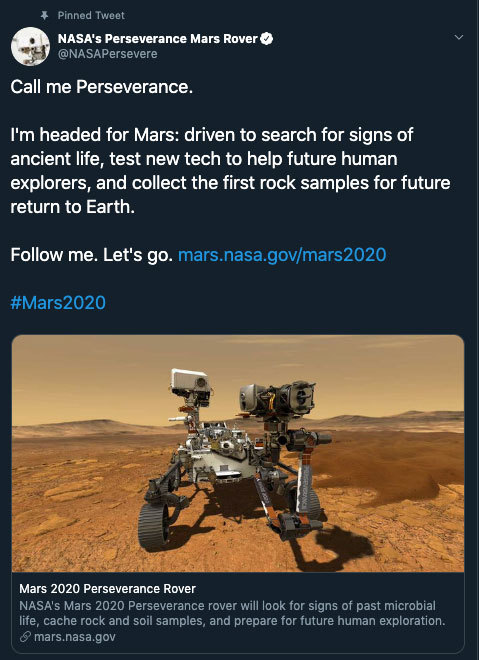
Allow us to reintroduce someone ... the name’s Perseverance.
With this new name, our Mars 2020 rover has now come to life! Chosen by middle school student Alex Mather, Perseverance helps to remind ourselves that no matter what obstacles we face, whether it's on the way to reaching our goals or on the way to Mars, we will push through. In Alex’s own words,
“We are a species of explorers, and we will meet many setbacks on the way to Mars. However, we can persevere. We, not as a nation but as humans, will not give up. The human race will always persevere into the future.”
Welcome to the family. ❤️
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.