Cervical Cancer
Cervical Cancer

Introduction
Cervical cancer is a significant health concern affecting women worldwide. It arises from abnormal cell growth in the cervix, often linked to the human papillomavirus (HPV). Despite advancements in prevention and treatment, cervical cancer remains a leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women. Understanding its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and prevention strategies is crucial for early detection and effective management.
1. Understanding Cervical Cancer

Cervical cancer originates in the cervix, the lower part of the uterus connecting to the vagina.
HPV, a common sexually transmitted infection, is a primary cause of cervical cancer, with certain strains posing higher risks.
The body’s immune response typically clears HPV infections, but persistent infections can lead to cervical cell abnormalities and eventually cancer.
2. Symptoms and Diagnosis

Cervical cancer may not present noticeable symptoms initially, making regular screenings essential for early detection.
Symptoms can include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, and unusual discharge.
Diagnostic methods include Pap tests, HPV DNA testing, colposcopy, and biopsy to confirm cervical cancer and determine its stage.
3. Treatment Options

Treatment depends on the cancer’s stage, size, and type, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences.
Surgical interventions, such as hysterectomy or removal of cancerous tissue, are common for early-stage cervical cancer.
Advanced stages may require a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapy to eliminate cancer cells and prevent recurrence.
4. Risk Factors and Prevention
Several factors increase the risk of developing cervical cancer, including HPV infection, smoking, early sexual activity, and weakened immune system.
Prevention strategies include HPV vaccination, routine Pap tests for early detection of precancerous lesions, practicing safe sex, and smoking cessation.
5. Impact on Women’s Health

Cervical cancer not only affects physical health but also has emotional, social, and financial repercussions on women and their families.
Access to screening, vaccination, and treatment services significantly impacts the prognosis and survival rates of women diagnosed with cervical cancer.
Addressing disparities in healthcare access and promoting awareness about cervical cancer prevention are crucial for improving women’s health outcomes globally.
Conclusion
Cervical cancer remains a significant public health challenge despite advancements in prevention and treatment. Early detection through regular screenings and vaccination against HPV can significantly reduce the burden of this disease. Moreover, addressing risk factors such as smoking and promoting safe sexual practices are vital for cervical cancer prevention. By raising awareness, improving access to healthcare services, and advocating for comprehensive cervical cancer prevention programs, we can strive towards reducing the incidence and mortality associated with this preventable disease, ultimately enhancing women’s health and well-being worldwide.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance.
More Posts from Expertacademicassignmenthelp and Others
Leukemia in Children

Introduction
Leukemia in children presents a formidable challenge, demanding meticulous management and treatment. This detailed discussion aims to devolve into various facets of childhood leukemia, encompassing its definition, types, causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment modalities, potential complications, preventive measures, and strategies for supporting a child living with leukemia.
Understanding Leukemia in Children

1. Definition
Leukemia is a hematological malignancy affecting the blood and bone marrow. Its prominence in childhood stems from the rapid proliferation of abnormal blood cells, disrupting the delicate balance within the body.
2. Types of Blood Cells
Understanding the roles of
Red blood cells (erythrocytes),
2.platelets (thrombocytes), and
3.white blood cells (leukocytes)
Is fundamental. An imbalance in these cells results in a spectrum of symptoms, from anemia to increased infection susceptibility.
3. Types of Leukemia

. Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL): Predominant in children.
Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML): The second most common type.
Hybrid or Mixed Lineage Leukemia: A rare amalgamation of ALL and AML.
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML): Uncommon in children.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Extremely rare in pediatric cases.
Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia (JMML): A rare type with unique growth characteristics.
Causes and Risk Factors
1. Causes
The exact etiology of childhood leukemia remains elusive. Genetic mutations in bone marrow cell genes may occur sporadically or, in some instances, be inherited.
2. Risk Factors
Exposure to Radiation.
Particularly high levels.
Inherited Syndromes.
Down syndrome.
Li-Fraumeni syndrome.
Immune System Conditions.
Inherited disorders affecting immune function.
Family History.
Having a sibling with leukemia elevates the risk.
Symptoms of Leukemia in Children
A diverse array of symptoms underscores leukemia’s impact on children, including;
.Pale skin
. Fatigue
.Dizziness
.Headaches
.Shortness of breath
.Frequent infections
.Fever
. Easy bruising
.Bleeding
.Bone or Joint pain, and
.Abdominal swelling.
Diagnosis:
1. Procedures:
.Blood Tests (Complete Blood Count — CBC): Essential for initial assessment.
Bone Marrow Aspiration or Biopsy: Crucial in detecting leukemia cells.
Lab Tests: Precisely determine leukemia type.
Diagnostic Imaging: X-rays, ultrasound,
lymph node biopsy, and
Lumbar puncture offer a comprehensive diagnostic perspective.
2. Classification
Unlike other cancers, leukemia is not staged but rather classified into groups, subtypes, or both based on type and specific characteristics, aiding in targeted treatment approaches.
Treatment Options:
1. Primary Treatments:
Blood Transfusions: Address low blood counts, bleeding, or infections.
Chemotherapy: The mainstay, killing or inhibiting cancer cells.
Radiation Therapy: High-energy X-rays to target and eradicate cancer cells.
Stem Cell Transplant: Involves high-dose chemotherapy followed by stem cell replacement.
Targeted Therapy: Specific medications tailored to combat certain types of leukemia.
Immunotherapy: Enhances the body’s immune system to combat cancer cells.
Complications:
1. Short-term:
Serious Infections: Resulting from compromised immune function.
Severe Bleeding: A consequence of low platelet levels.
Thickened Blood: Accumulation of leukemia cells in the bloodstream.
2. Long-term:
Leukemia Recurrence: A persistent concern.
Development of Other Cancers: A potential consequence of treatment.
Heart and Lung Problems: Arising from the impact of leukemia or its treatment.
Learning Issues and Growth Delays: Impacts on cognitive development and physical growth.
Fertility Problems and Bone Issues: Osteoporosis as a potential long-term complication.
Prevention:
Preventing childhood leukemia remains challenging, with a focus on caution regarding unnecessary exposure to radiation, especially in diagnostic procedures involving pregnant women and children.
Supporting a Child with Leukemia:
1. Ongoing Care:
Regular visits to oncologists and healthcare providers are crucial for monitoring and addressing emerging issues.
2. Balanced Lifestyle:
Managing eating difficulties and encouraging appropriate exercise play a vital role in supporting overall health.
3. Emotional Support:
Seeking counseling or participating in support groups helps both the child and their family navigate the emotional challenges associated with leukemia.
4. Follow-up Appointments:
Attending all scheduled appointments ensures continuous monitoring and timely intervention if complications arise.
When to Contact Healthcare Provider:
Prompt communication with healthcare providers is essential if the child experiences fever, worsening symptoms, new symptoms, or side effects from treatment.
Key Points Summary:
Leukemia necessitates a comprehensive approach, involving diagnosis, tailored treatment, and ongoing monitoring.
Varied symptoms demand timely medical attention for an optimal prognosis.
Treatment modalities, including chemotherapy and stem cell transplant, are tailored to the specific leukemia type.
Complications, both short-term and long-term, underscore the importance of ongoing follow-up care.
Prevention is limited, with a focus on minimizing unnecessary radiation exposure.
Comprehensive support, encompassing medical, emotional, and lifestyle aspects, is essential for the child’s well-being.
Next Steps:
1. Follow-up Care:
Continued regular check-ups and imaging tests remain integral to post-treatment monitoring.
2. Communication:
Maintaining open and transparent communication with healthcare providers ensures timely intervention if issues arise.
3. Research:
Inquiring about ongoing clinical trials or new treatments enables families to stay informed about emerging possibilities.
Conclusion:
Childhood leukemia mandates a collaborative effort from medical professionals, caregivers, and support networks to optimize outcomes and enhance the quality of life for affected children. As the landscape of pediatric oncology evolves, the commitment to advancing treatment options and minimizing the impact of complications remains paramount, offering hope for a brighter future for children navigating the complexities of leukemia.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact us at expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance
Interesting Nursing Topics To Choose For A Case Study

Childhood Nursing
Antibiotics Impact on Childhood Immunities
Antibiotics have revolutionized modern medicine, significantly improving the prognosis for many infectious diseases. However, the impact of antibiotics on childhood immunities is a multifaceted topic that warrants careful examination. While antibiotics target harmful bacteria, they may also affect the delicate balance of the immune system in developing children.
Research could delve into the long-term consequences of antibiotic use during childhood, exploring how it may influence the development of the immune system. Are there specific types of antibiotics that pose greater risks? What role do probiotics play in mitigating the potential negative effects of antibiotics on the immune system? Understanding these dynamics is crucial for optimizing pediatric care and ensuring the long-term health of children.
Effects of Childhood Exposure to Environmental Pollutants

Children are particularly vulnerable to environmental pollutants, and exposure during early life stages can have lasting health implications. Research in this area could focus on specific pollutants, such as air pollutants, heavy metals, or endocrine disruptors, and their impact on children’s health.
Exploring the effects of second-hand smoke inhalation during early life stages is particularly relevant. What are the respiratory and cardiovascular consequences of childhood exposure to second-hand smoke? How does environmental pollution contribute to respiratory conditions in children, and what preventive measures can be implemented?
Ethics of Pediatric Care
The ethical dimensions of pediatric care are intricate, involving considerations of autonomy, beneficence, and justice. Topics within this realm could include ethical dilemmas faced by pediatric nurses, such as decision-making in cases where parental and child interests may conflict.
Research may also explore the ethical implications of emerging technologies in pediatric care. For instance, what are the ethical considerations surrounding genetic testing in children? How can nurses navigate the ethical challenges posed by advances in pediatric treatments and interventions?
Genetic Factors of Diabetes in Children

The increasing prevalence of diabetes in children raises questions about the genetic factors contributing to this trend. Research in this area could delve into the genetic markers associated with pediatric diabetes, exploring the hereditary aspects of the disease.
Understanding the interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental factors is crucial. What role do lifestyle factors play in the manifestation of diabetes in genetically predisposed children? How can nurses incorporate genetic counseling into pediatric diabetes management to empower families with the knowledge needed for preventive strategies?
How Health in Children Can Affect Their Health Later in Life
The concept that early life experiences can shape health outcomes in adulthood is a key area of interest. Research could investigate the link between childhood health and long-term health trajectories. Are there specific childhood health indicators that serve as predictors of adult health issues?
Exploring the mechanisms through which childhood health influences adulthood health can guide nursing interventions. How can nurses promote healthy behaviors in children that have lasting effects on their well-being? What preventive measures can be implemented during childhood to mitigate the risk of chronic diseases in adulthood?
Adult Nursing
Analyzing the Benefits of Collaborative Nursing
Collaborative nursing involves interdisciplinary teamwork to enhance patient care outcomes. Research in this area could explore the benefits of collaborative nursing practices in diverse healthcare settings. What are the positive outcomes associated with collaborative care, such as improved patient satisfaction, reduced hospital readmissions, or enhanced treatment adherence?
Understanding the factors that contribute to successful collaboration is essential. How do effective communication and shared decision-making impact collaborative nursing efforts? What challenges do nurses face in interprofessional collaboration, and how can these challenges be addressed to optimize patient care?
Analyzing the Causes of Depression

Depression is a prevalent mental health concern affecting a significant portion of the adult population. Research into the causes of depression can provide valuable insights into preventive measures and targeted interventions. This could involve exploring the interplay between genetic, environmental, and psychological factors in the development of depression.
Investigating the role of adverse childhood experiences in predisposing individuals to depression in adulthood is a pertinent avenue. How can nurses identify individuals at risk based on early life experiences? What interventions can be implemented to break the cycle of depression rooted in childhood trauma?
Ethics of Data Collection in Adult Health Care
The ethical considerations surrounding data collection in adult health care are paramount, especially in the era of electronic health records and data-driven healthcare. Research could delve into the ethical challenges nurses face in collecting, storing, and utilizing patient data.
Exploring the perspectives of patients regarding data privacy and consent is crucial. How do patients perceive the use of their health data for research purposes? What safeguards can be implemented to ensure ethical data practices in adult health care settings?
Evolution of Nursing in a Specific Time Period
The evolution of nursing over time reflects changes in healthcare practices, societal attitudes, and technological advancements. Research in this area could focus on a specific time period, examining how nursing roles, responsibilities, and education have transformed.
For example, a study could explore the evolution of nursing during a period of significant healthcare reform. What were the key drivers of change, and how did nurses adapt to new models of care? Understanding historical contexts can inform current nursing practices and guide future developments in the profession.
Nonchemical Treatments for Bipolar Disorders

Bipolar disorders present unique challenges in terms of management and treatment. Research into nonchemical treatments for bipolar disorders can provide valuable alternatives or complementary approaches to medication-based interventions.
Exploring the efficacy of psychotherapy, cognitive-behavioral interventions, and lifestyle modifications in managing bipolar disorders is essential. How can nurses incorporate nonchemical treatments into holistic care plans for individuals with bipolar disorders? What role does patient education play in promoting self-management strategies for bipolar conditions?
Midwifery Nursing
Analysis of Caseload and Quality of Care for Underrepresented Groups
Midwives play a crucial role in maternal and infant care, yet disparities in care outcomes persist among underrepresented groups. Research in this area could investigate the caseloads and quality of care provided to women from marginalized communities.
Examining the experiences of midwives in catering to diverse caseloads can provide insights into challenges and opportunities. How do midwives adapt their care approaches to address the unique needs of underrepresented populations? What strategies can be implemented to ensure equitable access to high-quality midwifery care?
Analysis of Childbirth Experiences of Women with Autism

Pregnancy and childbirth can pose unique challenges for women with autism spectrum disorders. Research could explore the childbirth experiences of women with autism, considering factors such as sensory sensitivities, communication preferences, and support needs.
Understanding the specific needs of this population can inform midwifery practices and improve the overall childbirth experience. What adjustments can be made in maternity care settings to accommodate the needs of women with autism? How can midwives collaborate with other healthcare professionals to provide holistic care for pregnant individuals with autism?
Nonchemical Pain Management in Labor
Labor pain is a central aspect of childbirth, and nonchemical pain management approaches are gaining attention. Research in this area could focus on the effectiveness of non-pharmacological pain management methods during labor.
Exploring techniques such as hydrotherapy, massage, acupuncture, and mindfulness can provide valuable insights. How do these nonchemical methods influence pain perception and labor outcomes? What role can midwives play in promoting and facilitating the use of non-pharmacological pain management strategies during childbirth?
Role of Midwifery in Emergency Care
While childbirth is often a natural process, emergencies can arise, requiring swift and effective interventions. Research could investigate the role of midwives in emergency care.
Conclusion
In this expansive discussion, we have explored a variety of nursing research topics across different specializations. Each topic presents unique challenges, opportunities, and areas for further exploration within the field of nursing. Whether focusing on pediatric care, mental health, women’s health, or health care management, the diverse range of topics reflects the major areas to consider.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Email us: expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional guidance.
How Does The Drug Got Excreted / Eliminated From The Body?

Drug excretion is an important process in pharmacology, encompassing the elimination of pharmaceutical substances from the body. While the ultimate elimination of all drugs is inevitable, the specific pathways involved can vary significantly. Some drugs undergo extensive metabolic transformations before being excreted, while others are expelled from the body in their original form.
The kidneys play a central role in excreting water-soluble substances, effectively filtering them from the bloodstream. Meanwhile, the biliary system handles drugs that remain unabsorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, providing an alternative route for elimination. Although excretion through auxiliary channels such as the intestines, saliva, sweat, breast milk, and lungs is typically minimal, certain volatile anesthetics and residual drug traces in breast milk can have notable impacts, particularly on vulnerable populations such as infants.
Renal excretion constitutes a significant portion of drug elimination, accounting for approximately 20% of the plasma that is filtered through the glomeruli. While most water and electrolytes are reabsorbed back into circulation, polar compounds like drug metabolites are excreted predominantly in urine. However, it’s important to note that renal excretion tends to decrease with age, necessitating careful dosage adjustments for elderly patients to mitigate potential adverse effects.
Numerous factors influence the process of renal excretion, including the extent of protein binding, the degree of drug ionization affecting reabsorption rates, fluctuations in urine pH that can alter excretion dynamics, and the impact of metabolic inhibitors on tubular secretion mechanisms.
Biliary elimination, on the other hand, occurs when drugs traverse the biliary epithelium via active transport mechanisms. However, this process is not without limitations, as transporter saturation can impose constraints on drug excretion rates. Typically, larger molecules containing polar and lipophilic groups are excreted through bile, while smaller molecules tend to favor renal elimination pathways.
In addition to renal and biliary routes, drugs may also be eliminated to varying extents through auxiliary pathways such as saliva, tears, feces, sweat, and exhalation. While the quantities eliminated through these routes are generally minimal, drug excretion in breast milk can pose significant concerns for lactating mothers, potentially exposing nursing infants to pharmacological agents.
Understanding the pharmacokinetic parameters governing drug excretion is paramount for optimizing therapeutic regimens and minimizing the risk of adverse effects. Key parameters include the rate of elimination, clearance, elimination rate constant, and biologic half-life for drugs undergoing first-order elimination kinetics.
In conclusion, drug excretion represents a broad process influenced by a myriad of factors, necessitating comprehensive consideration to ensure the safe and efficacious use of pharmacotherapy.
For medical students navigating the complexities of their studies, Expert Academic Assignment Help serves as a beacon of professionalism and expertise. With a steadfast dedication to excellence and competency, our team provides invaluable support and guidance tailored to your academic needs. Do not hesitate to reach out to us for assistance on your academic journey, email: expertassignment46@gmail.com
Your excellence our pride.
Anatomy of the Heart

Introduction
The heart, an extraordinary organ vital to human life, serves as the epicenter of the circulatory system, tirelessly pumping blood throughout the body. Its intricate anatomy and physiological functions are the focus of extensive study and admiration in medical science. This comprehensive overview aims to delve into the intricate details of the heart’s anatomy, its valves, the circulation of blood within its chambers, and the critical role it plays in sustaining life.
Anatomy of the Heart
The heart, nestled within the middle mediastinum, is encased by a protective serous sac known as the pericardium. Structurally resembling a quadrangular pyramid, its base aligns posteriorly while its apex points anteriorly towards the thoracic wall. The heart’s significance is unparalleled; while one can survive without certain organs, the absence of a heart is incompatible with life.
The heart’s architecture is meticulously organized, with distinct surfaces and margins showing its boundaries. Its internal structure comprises four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The right atrium and ventricle receive deoxygenated blood from systemic veins and propel it towards the lungs for oxygenation. Conversely, the left atrium and ventricle receive oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and distribute it throughout the body’s systemic vessels.
Heart Valves

Critical to maintaining unidirectional blood flow, the heart is equipped with valves that separate its chambers and prevent backflow. The atrioventricular valves, including the tricuspid and mitral valves, regulate blood flow between atria and ventricles. Semilunar valves, namely the pulmonary and aortic valves, guard the exits of the ventricles, ensuring blood flows into the appropriate vessels without regurgitation.
Blood Flow Through the Heart
The heart’s rhythmic contractions, orchestrated by the cardiac cycle, facilitate the circulation of blood through its chambers. Systole, characterized by ventricular contraction, propels blood into pulmonary and systemic circuits. Diastole, the phase of relaxation, allows chambers to refill with blood. This cyclical process ensures continuous nutrient and oxygen delivery to tissues and organs.
Coronary Circulation

To sustain its relentless activity, the heart receives its own blood supply through the coronary circulation. Coronary arteries originate from the aorta, branching to supply myocardial tissue. Cardiac veins collect deoxygenated blood and converge at the coronary sinus, which empties into the right atrium. This intricate network ensures the heart’s metabolic demands are met, essential for its function.
Great Vessels of the Heart
The great vessels, including the aorta, pulmonary artery, and pulmonary veins, facilitate blood transport to and from the heart. Major branches of the aorta distribute oxygenated blood throughout the body, while the superior and inferior vena cavae return deoxygenated blood from systemic circulation. These vessels play a pivotal role in maintaining systemic homeostasis.
Clinical Insights
Understanding the heart’s anatomy is crucial in diagnosing and managing various cardiac pathologies. Conditions such as angina pectoris, infective endocarditis, and congenital heart diseases underscore the importance of cardiac health. Medical professionals employ diverse interventions, ranging from pharmaceuticals to surgical procedures, to address these conditions and optimize patient outcomes.
In conclusion, the heart’s intricate structure and physiological functions underscore its indispensable role in sustaining life. A deeper comprehension of its anatomy and circulation elucidates the complexities of cardiovascular health and underscores the importance of preventive care and medical intervention in maintaining cardiac well-being.
This overview provides a comprehensive exploration of the heart’s anatomy and functions, offering insights into its pivotal role in human physiology and healthcare.
Best of luck in the strategic study of the heart,
In case you’re experiencing any challenges in the study journey,
Email us at;williamsassignmenthelpfredrick@gmail.com
First Aid Instructions for 10 Medical Emergencies

Introduction
First aid is the immediate care provided to a sick or injured person, often serving as a crucial bridge until professional medical help arrives. While formal first aid training is ideal, there are basic life-saving steps that everyone should be aware of. This article outlines first aid instructions for 10 common medical emergencies, along with practical tips and a comprehensive first aid kit list.
1.Stopped Heart (Cardiac Arrest)

In the event of a stopped heart, immediate action is crucial:
Initiate CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) to maintain blood circulation.
Use an AED (automated external defibrillator) if available to shock the heart.
Call 911 and continue care until professional help arrives.
2. Bleeding

Effective bleeding control is essential
Apply direct pressure with a clean cloth or bandage to control bleeding.
Elevate the bleeding body part if possible to reduce blood flow.
Seek immediate medical help for severe bleeding.
3. Choking
https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/0*acrWmV_gxPmZh9JX
Swift response is vital when someone is choking:
Perform the Heimlich maneuver for a conscious choking victim.
If unconscious, initiate CPR and call for help.
Monitor airway and breathing.
4. Burns
Proper handling of burns is crucial for minimizing damage:
Stop the burning process by cooling the burn with running water.
For minor burns, use a light gauze bandage and avoid breaking blisters.
Seek medical attention for severe burns.
5. Blisters
Appropriate care can aid in the healing of blisters:
Leave small, unopened blisters alone to promote healing.
For larger, painful blisters, clean, drain, and apply antibiotic ointment.
Monitor for signs of infection.
6. Broken Bone/Fracturey
https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/0*4NouIgQSR_QHj-t6.jpeg
Careful management of fractures is essential:
Call 911 for severe fractures and avoid moving the person if a spinal injury is suspected.
Immobilize the injured area with a splint, elevate, and apply a cold pack for pain.
Seek prompt medical attention.
7. Sprains
Proper first aid can alleviate symptoms of sprains:
Rest the injured limb, apply a cold pack, and elevate if possible.
Seek medical attention for severe pain, inability to bear weight, or signs of infection.
Follow R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) principles.
8. Nosebleeds
https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/0*jJd3qZg5Q8xI_IHf
Effective nosebleed management is essential:
Lean forward and pinch the nose just below the bridge to control bleeding.
Apply a cold pack and seek medical attention for persistent or frequent nosebleeds.
Address underlying causes such as dry air or trauma.
9. Frostbite
Timely response is critical to treating frostbite:
Get out of the cold and gradually warm the affected area with warm water.
Avoid rubbing the affected area, and do not use dry heat sources.
Seek medical attention for severe cases.
10. Bee Sting
Proper care for bee stings is vital, especially for allergic reactions:
Remove the stinger immediately using a straight-edged object.
Monitor for signs of an allergic reaction and call 911 if necessary.
Clean the area, apply a cold pack, and use antihistamines for swelling.
First Aid Kit List
https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/800/0*WM_HfAvd_-O5fZMC
A well-prepared first aid kit is an essential tool for handling emergencies. The kit should include:
Adhesive bandages in various sizes and shapes
Gauze pads and compress dressings
Adhesive cloth tape, latex gloves, and antiseptic wipes
Antibiotic ointment and hydrocortisone ointment
A breathing barrier for performing CPR
Instant cold compress, tweezers, and an oral thermometer
Emergency blanket for warmth and comfort
Conclusion
While formal first aid training is highly recommended, understanding the basics of immediate care can make a significant difference in emergencies. The outlined first aid instructions cover a range of medical situations, and having a well-stocked first aid kit further enhances preparedness. Quick and appropriate action can be a crucial factor in saving lives during medical emergencies. Remember, being informed and ready can make you a valuable first responder in times of need.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact us expertassignment46@gmail.com for professional assistance and guidance
Study Tips For University Students

Introduction
Achieving success as a university student involves mastering effective study methods, time management, and maintaining overall well-being. In this comprehensive discussion, we will major into the top 10 university study tips that can prepare students for the challenges and opportunities that university life presents.
Preview and Review Study Resources
Understanding the importance of previewing study materials before lectures.
Incorporating regular reviews to consolidate knowledge and prepare for new concepts.
Exploring advanced reading techniques for improved comprehension.
2. Customizing Your Note-Taking System
Recognizing the power of note-taking in mastering any subject.
Exploring digital and handwritten note-taking approaches.
Utilizing advanced note-taking apps for organization and efficiency.
Discussing the Cornell Method, mind mapping, and other note-taking strategies.

. Establishing a daily study routine for consistency.
Adapting study habits during holidays to balance academics and festivities.
Creating to-do lists and prioritizing tasks for optimal time management.
Examining time-blocking techniques for enhanced productivity.
4. Setting Goals and Focusing
Setting specific, realistic goals to enhance study sessions.
Avoiding multitasking and using goal-oriented apps for focus.
Exploring the concept of SMART goals in academic settings.

Recognizing the importance of breaks for maintaining attention levels.
Introducing the Pomodoro Technique for efficient study sessions.
Discussing mindfulness and relaxation techniques during breaks.
6. Creating a Suitable Studying Environment
Maximizing productivity by minimizing distractions.
Establishing environmental cues to signal study mode.
Exploring the impact of ergonomics on study efficiency.

Motivating regular study habits by incorporating rewards.
Breaking down tasks into smaller goals for increased control.
Exploring the psychology of rewards and their impact on motivation.
8. Utilizing Study Groups
. Exploring the benefits of studying in groups.
Ensuring structured and accountable study group dynamics.
Discussing effective group communication and collaboration.
9 .Seeking Help When Needed
Overcoming the reluctance to ask for help.
Recognizing the importance of seeking assistance for academic success.
Discussing the role of tutors, mentors, and academic resources.

Understanding the impact of sleep and exercise on academic performance.
Incorporating a consistent sleep schedule and daily exercise routine.
Discussing the link between physical well-being and cognitive function.
Conclusion
In conclusion, success in university requires a holistic approach that encompasses effective study techniques, time management, and self-care. By implementing these ten study tips and delving into related topics, students can not only excel academically but also enhance their overall university experience. Balancing academic commitments with a healthy lifestyle is crucial for long-term success, and these strategies provide a foundation for thriving in the challenging yet rewarding university environment.
We wish you all the best in your University study program.
Incase of any challenges or need assistance and guidance during the process, do not hesitate ,just;
Email us at; williamsassignmenthelpfredrick@gmail.com
Interesting Nursing Research Topics To Choose

Childhood Nursing
Antibiotics Impact on Childhood Immunities
Antibiotics have revolutionized modern medicine, significantly improving the prognosis for many infectious diseases. However, the impact of antibiotics on childhood immunities is a multifaceted topic that warrants careful examination. While antibiotics target harmful bacteria, they may also affect the delicate balance of the immune system in developing children.
Research could delve into the long-term consequences of antibiotic use during childhood, exploring how it may influence the development of the immune system. Are there specific types of antibiotics that pose greater risks? What role do probiotics play in mitigating the potential negative effects of antibiotics on the immune system? Understanding these dynamics is crucial for optimizing pediatric care and ensuring the long-term health of children.
Effects of Childhood Exposure to Environmental Pollutants
Children are particularly vulnerable to environmental pollutants, and exposure during early life stages can have lasting health implications. Research in this area could focus on specific pollutants, such as air pollutants, heavy metals, or endocrine disruptors, and their impact on children’s health.
Exploring the effects of second-hand smoke inhalation during early life stages is particularly relevant. What are the respiratory and cardiovascular consequences of childhood exposure to second-hand smoke? How does environmental pollution contribute to respiratory conditions in children, and what preventive measures can be implemented?
Ethics of Pediatric Care
The ethical dimensions of pediatric care are intricate, involving considerations of autonomy, beneficence, and justice. Topics within this realm could include ethical dilemmas faced by pediatric nurses, such as decision-making in cases where parental and child interests may conflict.
Research may also explore the ethical implications of emerging technologies in pediatric care. For instance, what are the ethical considerations surrounding genetic testing in children? How can nurses navigate the ethical challenges posed by advances in pediatric treatments and interventions?
Genetic Factors of Diabetes in Children
The increasing prevalence of diabetes in children raises questions about the genetic factors contributing to this trend. Research in this area could delve into the genetic markers associated with pediatric diabetes, exploring the hereditary aspects of the disease.
Understanding the interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental factors is crucial. What role do lifestyle factors play in the manifestation of diabetes in genetically predisposed children? How can nurses incorporate genetic counseling into pediatric diabetes management to empower families with the knowledge needed for preventive strategies?
How Health in Children Can Affect Their Health Later in Life
The concept that early life experiences can shape health outcomes in adulthood is a key area of interest. Research could investigate the link between childhood health and long-term health trajectories. Are there specific childhood health indicators that serve as predictors of adult health issues?
Exploring the mechanisms through which childhood health influences adulthood health can guide nursing interventions. How can nurses promote healthy behaviors in children that have lasting effects on their well-being? What preventive measures can be implemented during childhood to mitigate the risk of chronic diseases in adulthood?
Adult Nursing
Analyzing the Benefits of Collaborative Nursing
Collaborative nursing involves interdisciplinary teamwork to enhance patient care outcomes. Research in this area could explore the benefits of collaborative nursing practices in diverse healthcare settings. What are the positive outcomes associated with collaborative care, such as improved patient satisfaction, reduced hospital readmissions, or enhanced treatment adherence?
Understanding the factors that contribute to successful collaboration is essential. How do effective communication and shared decision-making impact collaborative nursing efforts? What challenges do nurses face in interprofessional collaboration, and how can these challenges be addressed to optimize patient care?
Analyzing the Causes of Depression
Depression is a prevalent mental health concern affecting a significant portion of the adult population. Research into the causes of depression can provide valuable insights into preventive measures and targeted interventions. This could involve exploring the interplay between genetic, environmental, and psychological factors in the development of depression.
Investigating the role of adverse childhood experiences in predisposing individuals to depression in adulthood is a pertinent avenue. How can nurses identify individuals at risk based on early life experiences? What interventions can be implemented to break the cycle of depression rooted in childhood trauma?
Ethics of Data Collection in Adult Health Care
The ethical considerations surrounding data collection in adult health care are paramount, especially in the era of electronic health records and data-driven healthcare. Research could delve into the ethical challenges nurses face in collecting, storing, and utilizing patient data.
Exploring the perspectives of patients regarding data privacy and consent is crucial. How do patients perceive the use of their health data for research purposes? What safeguards can be implemented to ensure ethical data practices in adult health care settings?
Evolution of Nursing in a Specific Time Period
The evolution of nursing over time reflects changes in healthcare practices, societal attitudes, and technological advancements. Research in this area could focus on a specific time period, examining how nursing roles, responsibilities, and education have transformed.
For example, a study could explore the evolution of nursing during a period of significant healthcare reform. What were the key drivers of change, and how did nurses adapt to new models of care? Understanding historical contexts can inform current nursing practices and guide future developments in the profession.
Nonchemical Treatments for Bipolar Disorders
Bipolar disorders present unique challenges in terms of management and treatment. Research into nonchemical treatments for bipolar disorders can provide valuable alternatives or complementary approaches to medication-based interventions.
Exploring the efficacy of psychotherapy, cognitive-behavioral interventions, and lifestyle modifications in managing bipolar disorders is essential. How can nurses incorporate nonchemical treatments into holistic care plans for individuals with bipolar disorders? What role does patient education play in promoting self-management strategies for bipolar conditions?
Midwifery Nursing
Analysis of Caseload and Quality of Care for Underrepresented Groups
Midwives play a crucial role in maternal and infant care, yet disparities in care outcomes persist among underrepresented groups. Research in this area could investigate the caseloads and quality of care provided to women from marginalized communities.
Examining the experiences of midwives in catering to diverse caseloads can provide insights into challenges and opportunities. How do midwives adapt their care approaches to address the unique needs of underrepresented populations? What strategies can be implemented to ensure equitable access to high-quality midwifery care?
Analysis of Childbirth Experiences of Women with Autism
Pregnancy and childbirth can pose unique challenges for women with autism spectrum disorders. Research could explore the childbirth experiences of women with autism, considering factors such as sensory sensitivities, communication preferences, and support needs.
Understanding the specific needs of this population can inform midwifery practices and improve the overall childbirth experience. What adjustments can be made in maternity care settings to accommodate the needs of women with autism? How can midwives collaborate with other healthcare professionals to provide holistic care for pregnant individuals with autism?
Nonchemical Pain Management in Labor
Labor pain is a central aspect of childbirth, and nonchemical pain management approaches are gaining attention. Research in this area could focus on the effectiveness of non-pharmacological pain management methods during labor.
Exploring techniques such as hydrotherapy, massage, acupuncture, and mindfulness can provide valuable insights. How do these nonchemical methods influence pain perception and labor outcomes? What role can midwives play in promoting and facilitating the use of non-pharmacological pain management strategies during childbirth?
Role of Midwifery in Emergency Care
While childbirth is often a natural process, emergencies can arise, requiring swift and effective interventions. Research could investigate the role of midwives in emergency care.
Conclusion
In this expansive discussion, we have explored a variety of nursing research topics across different specializations. Each topic presents unique challenges, opportunities, and areas for further exploration within the field of nursing. Whether focusing on pediatric care, mental health, women’s health, or health care management, the diverse range of topics reflects the major areas to consider.
For further assistance and guidance, link to us on williamsliason@outlook.com
How Does The Brain Work?

The brain stands as a marvel of biological engineering, Composing of a multitude of bodily functions ranging from cognition and memory to emotions and sensory perception. Together with the spinal cord, it constitutes the central nervous system (CNS), the command center of the human body.
Composition of the Brain

Weighing approximately 3 pounds in adults, the brain’s main structure comprises about 60% fat, interspersed with water, protein, carbohydrates, and salts. Unlike muscles, it houses a complex network of blood vessels and nerves, including neurons and glial cells.
a) Gray and White Matter
Within the central nervous system, gray matter and white matter occupies distinct regions. In the brain, gray matter forms the outer layer, rich in neuron somas, while white matter constitutes the inner section, primarily composed of axons unsheathed in myelin. Conversely, in the spinal cord, this arrangement is reversed.
b) Brain Functionality
The brain operates by transmitting and receiving chemical and electrical signals throughout the body. These signals regulate a myriad of processes, with the brain disseminating each input. Some signals remain confined within the brain, while others traverse the spinal cord and nerves, disseminating information across the body’s expanse. This composes neural network relies on billions of interconnected neurons.
Major Brain Regions and Their Functions

1.Cerebrum
Dominating the brain’s landscape, the cerebrum encompasses the cerebral cortex and underlying white matter. It governs a spectrum of functions, including motor coordination, temperature regulation, language processing, emotional regulation, and sensory perception.
2. Brainstem
Serving as the bridge between the cerebrum and spinal cord, the brainstem comprises the midbrain, pons, and medulla. It regulates vital autonomic functions such as heart rate, breathing, and reflexive responses.
3. Cerebellum
Nestled at the posterior aspect of the brain, the cerebellum coordinates voluntary muscle movements, posture, balance, and motor learning.
Brain Coverings

a) Meninges
Three layers of protective membranes, collectively known as meninges, enshroud the brain and spinal cord. These layers — dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater — shield the delicate neural tissue from physical trauma and infection.
b) Lobes of the Brain
Each hemisphere of the brain comprises four lobes, each harboring distinct functional domains:
Frontal Lobe: Governing executive functions, motor control, and higher cognitive processes.
Parietal Lobe: Integrating sensory information, spatial awareness, and perception of pain and touch.
Occipital Lobe: Specialized for visual processing and perception.
Temporal Lobe: Involved in auditory processing, language comprehension, and memory consolidation.
Deeper Brain Structures
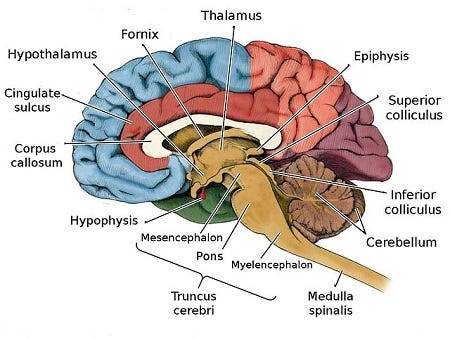
These encompass important structures such as the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, amygdala, hippocampus, and pineal gland, orchestrating hormone secretion, emotional regulation, memory consolidation, and circadian rhythms.
Blood Supply
The brain receives its oxygenated blood supply through the vertebral and carotid arteries, ensuring adequate perfusion of neural tissue. The main network of blood vessels, including the Circle of Willis, safeguards against ischemic insults and facilitates intraarterial communication.
Cranial Nerves

The twelve pairs of cranial nerves, originating from the brainstem, mediate a diverse array of sensory and motor functions, encompassing olfaction, vision, facial expression, and auditory perception.
Comprehending the anatomy and functionality of the brain fosters a deeper appreciation of its complexity and facilitates advances in neuroscientific research and therapeutic interventions aimed at diminishing neurological disorders.
Understanding the detailed anatomy and functionality of the brain is crucial for medical students embarking on their journey of study. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers invaluable assistance in navigating the complexities of neuroscience and related subjects. By leveraging expert guidance and support, students can excel in their medical education and contribute to advancements in the field of Medicine. Email us at expertassignment46@gmail.com to embark on your path to scholarly excellence and professional competency.
First Aid Instructions for 10 Medical Emergencies

Introduction:
First aid is the immediate care provided to a sick or injured person, often serving as a crucial bridge until professional medical help arrives. While formal first aid training is ideal, there are basic life-saving steps that everyone should be aware of. This article outlines first aid instructions for 10 common medical emergencies, along with practical tips and a comprehensive first aid kit list.
1.Stopped Heart (Cardiac Arrest):
In the event of a stopped heart, immediate action is crucial:
Initiate CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) to maintain blood circulation.
Use an AED (automated external defibrillator) if available to shock the heart.
Call 911 and continue care until professional help arrives.
2. Bleeding:
Effective bleeding control is essential:
Apply direct pressure with a clean cloth or bandage to control bleeding.
Elevate the bleeding body part if possible to reduce blood flow.
Seek immediate medical help for severe bleeding.
3. Choking:
Swift response is vital when someone is choking:
Perform the Heimlich maneuver for a conscious choking victim.
If unconscious, initiate CPR and call for help.
Monitor airway and breathing.
4. Burns:
Proper handling of burns is crucial for minimizing damage:
Stop the burning process by cooling the burn with running water.
For minor burns, use a light gauze bandage and avoid breaking blisters.
Seek medical attention for severe burns.
5. Blisters:
Appropriate care can aid in the healing of blisters:
Leave small, unopened blisters alone to promote healing.
For larger, painful blisters, clean, drain, and apply antibiotic ointment.
Monitor for signs of infection.
6. Broken Bone/Fracture:
Careful management of fractures is essential:
Call 911 for severe fractures and avoid moving the person if a spinal injury is suspected.
Immobilize the injured area with a splint, elevate, and apply a cold pack for pain.
Seek prompt medical attention.
7. Sprains:
Proper first aid can alleviate symptoms of sprains:
Rest the injured limb, apply a cold pack, and elevate if possible.
Seek medical attention for severe pain, inability to bear weight, or signs of infection.
Follow R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) principles.
8. Nosebleeds:
Effective nosebleed management is essential:
Lean forward and pinch the nose just below the bridge to control bleeding.
Apply a cold pack and seek medical attention for persistent or frequent nosebleeds.
Address underlying causes such as dry air or trauma.
9. Frostbite:
Timely response is critical to treating frostbite:
Get out of the cold and gradually warm the affected area with warm water.
Avoid rubbing the affected area, and do not use dry heat sources.
Seek medical attention for severe cases.
10. Bee Sting:
Proper care for bee stings is vital, especially for allergic reactions:
Remove the stinger immediately using a straight-edged object.
Monitor for signs of an allergic reaction and call 911 if necessary.
Clean the area, apply a cold pack, and use antihistamines for swelling.
First Aid Kit List:
A well-prepared first aid kit is an essential tool for handling emergencies. The kit should include:
Adhesive bandages in various sizes and shapes
Gauze pads and compress dressings
Adhesive cloth tape, latex gloves, and antiseptic wipes
Antibiotic ointment and hydrocortisone ointment
A breathing barrier for performing CPR
Instant cold compress, tweezers, and an oral thermometer
Emergency blanket for warmth and comfort
Conclusion:
While formal first aid training is highly recommended, understanding the basics of immediate care can make a significant difference in emergencies. The outlined first aid instructions cover a range of medical situations, and having a well-stocked first aid kit further enhances preparedness. Quick and appropriate action can be a crucial factor in saving lives during medical emergencies. Remember, being informed and ready can make you a valuable first responder in times of need.
For Health Sciences Assignment Help;
Email Us At;
