ANTI-BARFING SPIKES.
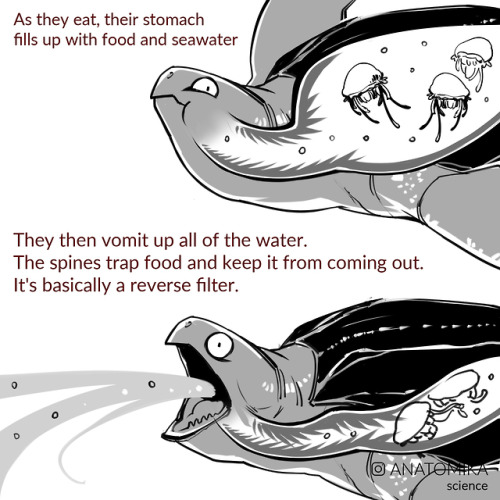





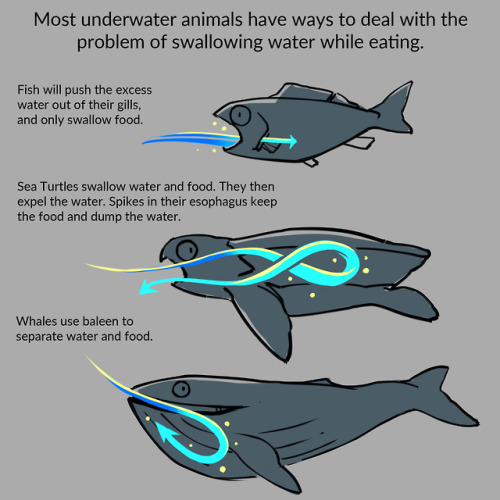

ANTI-BARFING SPIKES.
This is why they have such a problem with plastic bags. It’s because the unique structure of their esophagus makes it so that they can’t get rid of them.
Other places to see my posts: INSTAGRAM / FACEBOOK / ETSY / KICKSTARTER
More Posts from Thejoyofscience and Others
chappelle-“remember bitch you clicked on my face”
of course i did...that’s cuz you used to be funny

For decades, scientists have been capitalizing off discoveries made from Henrietta Lacks’ family’s cells. That may change.







Amazing Annual Monarch Butterfly Migrations
Monarch butterflies in other countries also migrate with the season, but it’s those in North America that travel the greatest distance. Each year, there are two major Monarch Butterfly migrations in North America. Those monarchs that live east of the Rocky Mountains fly down to Mexico, while the more western population stops in California. Monarchs do not like the cold, and as soon as things start to get a little chilly up north, they take off south (and west) for warmer climates.
The largest group travels over 1,250 miles from the Rocky Mountains to spend the winter in Michoacán, Mexico. The government of Mexico has managed to almost stamp out logging in the monarch’s wintering areas, a practice which once threatened the migrating insects. Working with environmental organizations and individuals, they have been encouraging communities to start eco-tourism enterprises by planting trees for the butterflies to nest. The monarch is a butterfly ruled by the sun. When the autumn sun reaches fifty two degrees above the horizon, the monarch reproduction cycle shuts down, and their great migration begins. When they begin their flight down to Mexico, they have never been there, yet every generation is able to find the exact same spot year after year where their previous ancestors spent the winter.
The second group travels from Ontario, Canado to spend their winters in Santa Cruz, California. You may wonder why the monarchs don’t simply stay and enjoy the warmer weather there year round. That’s because they need the milkweed plants on which their larvae feed, and those are more plentiful up north. So as soon as the weather starts to warm up, that’s where they return every year. Interestingly, not every generation of monarchs migrate. Some simply remain in their breeding ground. Those that do migrate are born at the end of summer or early autumn. Because of their trip to warmer climes, this special generation will outlive several younger generations that stay put. It will then be the migratory monarchs’ great grandchildren that follow the beat of their forebears’ wings.
in Ontario, Canada, in their summer home. It’s thought that the distinctive bright coloring of the monarchs acts as a warning to predators to stay away. Monarch butterflies are also poisonous and will make any animal that tries to eat them sick – hopefully sick enough not to try snacking on them a second time! The poison comes from the milkweed that they eat while they are caterpillars. This doesn’t always work, however. Certain bird species, for example, have learned that some parts of the butterflies are not as toxic, while other predators are resistant or immune to the poison altogether.
source

This bad little boy is super rare to find!!! This is a mitotically active cell present in peripheral blood circulation from a dog - only the second one I have ever seen!!
As a game, in the diagnostic lab we yell KABLAM! anytime we see a mitotic figure. The first one to say kablam wins :-P We should so turn it into a drinking game…
science side of tumblr tell me why
ain’t nothin but a heartache
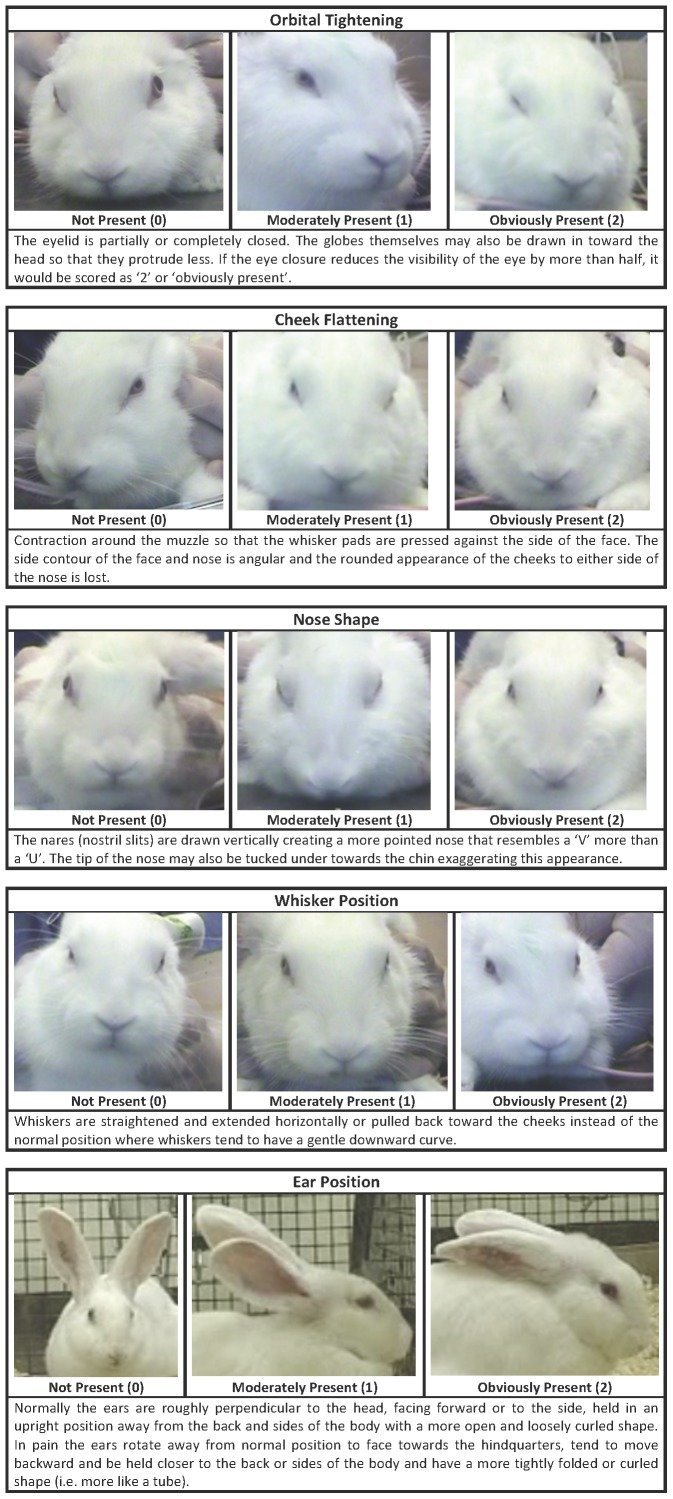



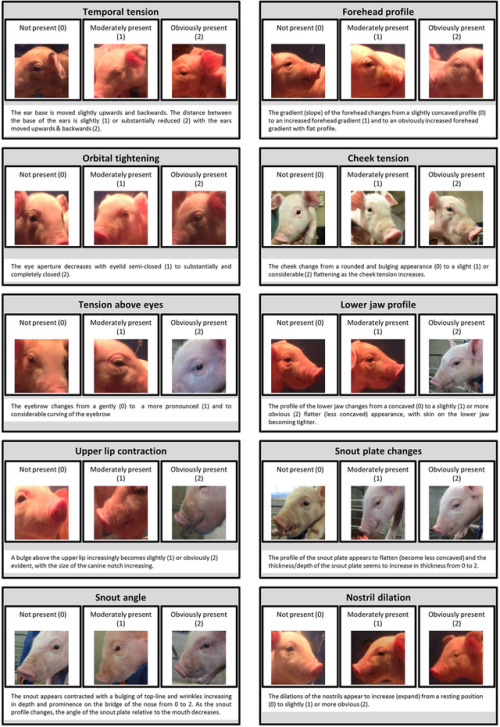





Recognising silent acute pain in animals - assorted species grimace scales:
Development of the Horse Grimace Scale (HGS) as a Pain Assessment Tool in Horses Undergoing Routine Castration
The composition and initial evaluation of a grimace scale in ferrets after surgical implantation of a telemetry probe
The Assessment of Facial Expressions in Piglets Undergoing Tail Docking and Castration: Toward the Development of the Piglet Grimace Scale
The Sheep Grimace Scale as an indicator of post-operative distress and pain in laboratory sheep and the Coding and quantification of a facial expression for pain in lambs
Mouse - How to be a pain management advocate for exotic and zoo animals (full text available - includes additional species)
The Rat Grimace Scale: A partially automated method for quantifying pain in the laboratory rat via facial expressions
Evaluation of EMLA Cream for Preventing Pain during Tattooing of Rabbits: Changes in Physiological, Behavioural and Facial Expression Responses
Pain evaluation in dairy cattle
Pain is subtle - we cannot depend on vocalisations or extreme abnormal behaviour to determine if an animal is on pain - animals can cover up pain while going about their daily life. Grimace scales have been found to be reliable indicators of pain (full text available)
Unfortunately, I could not find a clear visual grimace scale for dogs, cats or birds :(
Which is a shame, because perhaps I could have recognised my own dog’s discomfort for the acute pain it was sooner:

(left: dog in pain. See eyes, tension, cheeks, whiskers, ears compared to the multiple species grimace charts above. right: tired but not in pain dog)
Perhaps my new books that arrived today might have some on dogs at least. There’s this visual blog post of a stressed dog at the vet - stress in the absence of a trigger looks very much like pain.
Here is a small comparative cats, with the link going into more detail. Not a scale but better than nothing:


Bonus round - you can get free A3 posters on recognising pain for Rabbits, Mice and Rats from the National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research. My rabbit specialist vet has the rabbit one!








Journey to the Microcosmos- The Complicated Legacy of Lynn Margulis
Images originally captured by Jam’s Germs
I just read that bees don't have lungs how do their respiratory system works??
Correct. Insects do not have lungs they breathe through spiracles (tiny openings) that can open and close, as well as having filters to keep dust and other external contaminants out.

The spiracles run across their abdomen connecting to tracheae which is where oxygen exchange takes place (In mammals this happens in the blood), that then connect to tracheole. The air sacs expand and collapse so force the air in the spiracles and into the trachea and almost function in that they can reserve air in them so insects can conserve water.

Honey bees have 10 pairs of spiracles, 3 pairs on the thorax and 7 pairs on the abdomen. Bees can use and accelerate the passage of air in their bodies via their air sacs, contacting them and increasing their respiration rate.
This adaptive function of their respiratory system actually helps them to fly and the first few spiracles are used for air to exit while the others for air entering, they also have valves to prevent backflow. This also allows the bee to cool down or heat up if it needs to, which is why you’ll see bees abdomens wiggling while they’re resting. They’re forcing air in and out of their bodies in order to rapidly cool down or heat up, which is important for flight.

-
 colorfulpuppychaos liked this · 1 week ago
colorfulpuppychaos liked this · 1 week ago -
 favoredbyurmom liked this · 1 week ago
favoredbyurmom liked this · 1 week ago -
 theperpetualartist reblogged this · 1 week ago
theperpetualartist reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 thedutchdemon reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
thedutchdemon reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 thedutchdemon liked this · 2 weeks ago
thedutchdemon liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 fandomvoiager reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
fandomvoiager reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 fandomvoiager liked this · 2 weeks ago
fandomvoiager liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 miscellaneousjo liked this · 3 weeks ago
miscellaneousjo liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 idontliketomatoesleavemealone liked this · 3 weeks ago
idontliketomatoesleavemealone liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 warm-throated liked this · 3 weeks ago
warm-throated liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 spiderfilleddonut liked this · 3 weeks ago
spiderfilleddonut liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 seveneyesoup reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
seveneyesoup reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 homestuckian reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
homestuckian reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 homestuckian liked this · 3 weeks ago
homestuckian liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 vampirecatprince liked this · 3 weeks ago
vampirecatprince liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 willgrahampussypower reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
willgrahampussypower reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 willgrahampussypower liked this · 3 weeks ago
willgrahampussypower liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 meems-beems liked this · 4 weeks ago
meems-beems liked this · 4 weeks ago -
 hip-eponymous-poor-boy liked this · 4 weeks ago
hip-eponymous-poor-boy liked this · 4 weeks ago -
 sunstonedragons reblogged this · 1 month ago
sunstonedragons reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 spaceofmischief liked this · 1 month ago
spaceofmischief liked this · 1 month ago -
 mazyisgay reblogged this · 1 month ago
mazyisgay reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 mazyisgay liked this · 1 month ago
mazyisgay liked this · 1 month ago -
 theoryfan205 reblogged this · 1 month ago
theoryfan205 reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 theoryfan205 liked this · 1 month ago
theoryfan205 liked this · 1 month ago -
 innovative-detritus reblogged this · 1 month ago
innovative-detritus reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 slave-boy-ceq-88 liked this · 1 month ago
slave-boy-ceq-88 liked this · 1 month ago -
 chopstick-enby liked this · 1 month ago
chopstick-enby liked this · 1 month ago -
 celeglossata liked this · 1 month ago
celeglossata liked this · 1 month ago -
 emilygloom liked this · 1 month ago
emilygloom liked this · 1 month ago -
 demitree liked this · 1 month ago
demitree liked this · 1 month ago -
 ihavemace reblogged this · 1 month ago
ihavemace reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 pickupstyx reblogged this · 1 month ago
pickupstyx reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 pickupstyx liked this · 1 month ago
pickupstyx liked this · 1 month ago -
 littlemxunearthly liked this · 1 month ago
littlemxunearthly liked this · 1 month ago -
 some-weirdo-person reblogged this · 1 month ago
some-weirdo-person reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 z-zipster liked this · 1 month ago
z-zipster liked this · 1 month ago -
 boopjuice reblogged this · 1 month ago
boopjuice reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 fuzzytheduck liked this · 1 month ago
fuzzytheduck liked this · 1 month ago -
 itsanotherboxofdogs reblogged this · 1 month ago
itsanotherboxofdogs reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 raska-tmg reblogged this · 1 month ago
raska-tmg reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 raska-tmg liked this · 1 month ago
raska-tmg liked this · 1 month ago -
 daydreamsandcrashingwaves reblogged this · 1 month ago
daydreamsandcrashingwaves reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 daydreamsandcrashingwaves liked this · 1 month ago
daydreamsandcrashingwaves liked this · 1 month ago -
 unabashedvoidtraveler liked this · 1 month ago
unabashedvoidtraveler liked this · 1 month ago -
 unova-state-of-mind liked this · 1 month ago
unova-state-of-mind liked this · 1 month ago -
 lesser-flamingo reblogged this · 1 month ago
lesser-flamingo reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 lesser-flamingo liked this · 1 month ago
lesser-flamingo liked this · 1 month ago -
 matsunehiku144 liked this · 1 month ago
matsunehiku144 liked this · 1 month ago
An assortment of scientific things from the wonderful world of biology
77 posts


